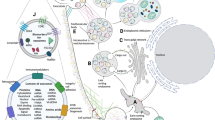
Abstract
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles secreted by almost all cell types, and carry diverse cargo including RNA, and other substances. Recent studies have focused exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) on various human diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and metabolic syndrome (METS) which accompany the occurrence of insulin resistance. The regulation of insulin signaling has connected with some miRNA expression which play a significant regulatory character in insulin targeted cells or organs, such as fat, muscle, and liver. The miRNAs carried by exosomes, through the circulation in the body fluids, mediate all kinds of physiological and pathological process involved in the human body. Studies have found that exosome derived miRNAs are abnormally expressed and cross-talked with insulin targeted cells or organs to affect insulin pathways. Further investigations of the mechanisms of exosomal miRNAs in T2DM will be valuable for the diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets of T2DM. This review will summarize the molecular mechanism of action of the miRNAs carried by exosomes which are secreted from insulin signaling related cells, and elucidate the pathogenesis of insulin resistance to provide a new strategy for the potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for the type 2 diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
An P, Peng Q, Guo T, Xing PC, Zhao LD, Zhou MJ (2020) Potential influence of miR-192 on the efficacy of saxagliptin treatment in T2DM complicated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 34(4):1411–1415. https://doi.org/10.23812/20-147-L
Aswad H, Forterre A, Wiklander OP et al (2014) Exosomes participate in the alteration of muscle homeostasis during lipid-induced insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia 57(10):2155–2164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-014-3337-2
Barile L, Lionetti V, Cervio E et al (2014) Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 103(4):530–541. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvu167
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Beltrami C, Besnier M, Shantikumar S et al (2017) Human pericardial fluid contains exosomes enriched with cardiovascular-expressed micrornas and promotes therapeutic angiogenesis. Mol Ther 25(3):679–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.12.022
Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL (2006) RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13(12):1097–1101. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1167
Bosque A, Dietz L, Gallego-Lleyda A et al (2016) Comparative proteomics of exosomes secreted by tumoral Jurkat T cells and normal human T cell blasts unravels a potential tumorigenic role for valosin-containing protein. Oncotarget. 7(20):29287–29305. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8678
Broussard JL, Castro AV, Iyer M et al (2016) Insulin access to skeletal muscle is impaired during the early stages of diet-induced obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 24:1922–1928. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21562
Castaño C, Kalko S, Novials A, Párrizas M (2018) Obesity-associated exosomal miRNAs modulate glucose and lipid metabolism in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(48):12158–12163. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1808855115
Castaño C, Mirasierra M, Vallejo M, Novials A, Párrizas M (2020) Delivery of muscle-derived exosomal miRNAs induced by HIIT improves insulin sensitivity through down-regulation of hepatic FoxO1 in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(48):30335–30343. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2016112117
Chairoungdua A, Smith DL, Pochard P, Hull M, Caplan MJ (2010) Exosome release of β-catenin: a novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol 190(6):1079–1091. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201002049
Chakraborty C, Doss CG, Bandyopadhyay S, Agoramoorthy G (2014) Influence of miRNA in insulin signaling pathway and insulin resistance: micro-molecules with a major role in type-2 diabetes. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 5(5):697–712. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1240
Chang W, Wang J (2019) Exosomes and their noncoding RNA cargo are emerging as new modulators for diabetes mellitus. Cells 8(8):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080853
Chen B, Sang Y, Song X et al (2021) Exosomal miR-500a-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through targeting USP28. Theranostics 11(8):3932–3947. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.53412
Colombo M, Moita C, van Niel G et al (2013) Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 24):5553–5565. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.128868
Dai J, Su Y, Zhong S et al (2020) Exosomes: key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00261-0
Dang SY, Leng Y, Wang ZX et al (2019) Exosomal transfer of obesity adipose tissue for decreased miR-141-3p mediate insulin resistance of hepatocytes. Int J Biol Sci 15(2):351–368. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.28522
de Jong OG, Verhaar MC, Chen Y et al (2012) Cellular stress conditions are reflected in the protein and RNA content of endothelial cell-derived exosomes. J Extracell Vesicles 16:1. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v1i0.18396
Diederichs S, Haber DA (2007) Dual role for argonautes in microRNA processing and posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA expression. Cell 131(6):1097–1108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.032
Ding X, Jian T, Wu Y et al (2019) Ellagic acid ameliorates oxidative stress and insulin resistance in high glucose-treated HepG2 cells via miR-223/keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 110:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.018
Dos Santos B, Estadella D, Hachul AC et al (2013) Effects of a diet enriched with polyunsaturated, saturated, or trans fatty acids on cytokine content in the liver, white adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle of adult mice. Mediat Inflamm 2013:594958. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/594958
Duan YR, Chen BP, Chen F, Yang SX, Zhu CY, Ma YL, Li Y, Shi J (2021) Exosomal microRNA-16-5p from human urine-derived stem cells ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through protection of podocyte. J Cell Mol Med 25(23):10798–10813. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14558
Escola JM, Kleijmeer MJ, Stoorvogel W, Griffith JM, Yoshie O, Geuze HJ (1998) Selective enrichment of tetraspan proteins on the internal vesicles of multivesicular endosomes and on exosomes secreted by human B-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 273(32):20121–20127. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.32.20121
Fan C, Li Y, Lan T, Wang W, Long Y, Yu SY (2022) Microglia secrete miR-146a-5p-containing exosomes to regulate neurogenesis in depression. Mol Ther 30(3):1300–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.006
Feng T, Li K, Zheng P et al (2019) Weighted gene coexpression network analysis identified microrna coexpression modules and related pathways in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 13(2019):9567641. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9567641
Gallagher EJ, Leroith D, Karnieli E (2010) Insulin resistance in obesity as the underlying cause for the metabolic syndrome. Mt Sinai J Med 77:511–523. https://doi.org/10.1002/msj.20212
Gebert LFR, MacRae IJ (2019) Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20(1):21–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0045-7
Goedeke L, Perry RJ, Shulman GI (2019) Emerging pharmacological targets for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 59:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010716-104727
Gong H, Chen H, Xiao P et al (2022) miR-146a impedes the anti-aging effect of AMPK via NAMPT suppression and NAD+/SIRT inactivation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-00886-3
Greenberg AS, Reeves AR (2021) The good and bad of adipose tissue macrophage exosomes in obesity. Cell Metab 33(4):700–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.03.011
Guo X, Asthana P, Gurung S et al (2022) Regulation of age-associated insulin resistance by MT1-MMP-mediated cleavage of insulin receptor. Nat Commun 13(1):3749. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31563-2
Hall E, Volkov P, Dayeh T et al (2014) Sex differences in the genome-wide DNA methylation pattern and impact on gene expression, microRNA levels and insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets. Genome Biol 15:522. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0522-z
Henne WM, Stenmark H, Emr SD (2013) Molecular mechanisms of the membrane sculpting ESCRT pathway. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5(9):a016766. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016766
Ho PTB, Clark IM, Le LTT (2022) MicroRNA-based diagnosis and therapy. Int J Mol Sci 23(13):7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137167
Indrakusuma I, Sell H, Eckel J (2015) Novel mediators of adipose tissue and muscle crosstalk. Curr Obes Rep 4(4):411–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-015-0174-7
Ji J, Qin Y, Ren J et al (2015) Mitochondria-related miR-141-3p contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in HFD-induced obesity by inhibiting PTEN. Sci Rep 9(5):16262. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16262
Ji Y, Luo Z, Gao H et al (2021) Hepatocyte-derived exosomes from early onset obese mice promote insulin sensitivity through miR-3075. Nat Metab 3(9):1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-021-00444-1
Kim Y, Kim OK (2021) Potential roles of adipocyte extracellular vesicle-derived mirnas in obesity-mediated insulin resistance. Adv Nutr 12(2):566–574. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmaa105
Kukreti H, Amuthavalli K (2020) MicroRNA-34a causes ceramide accumulation and effects insulin signaling pathway by targeting ceramide kinase (CERK) in aging skeletal muscle. J Cell Biochem 121(5-6):3070–3089. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29312
Kurtz CL, Peck BC, Fannin EE et al (2014) MicroRNA-29 fine-tunes the expression of key FOXA2-activated lipid metabolism genes and is dysregulated in animal models of insulin resistance and diabetes. Diabetes:DB_131015. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1015
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J et al (2003) The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 425(6956):415–419. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01957
Lee Y, Jeon K, Lee JT, Kim S, Kim VN (2002) MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO J 21(17):4663–4670. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdf476
Li D, Song H, Shuo L et al (2020) Gonadal white adipose tissue-derived exosomal MiR-222 promotes obesity-associated insulin resistance. Aging (Albany NY) 12(22):22719–22743. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103891
Li W, Jin LY, Cui YB, Xie N (2021) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-17-3p ameliorates inflammatory reaction and antioxidant injury of mice with diabetic retinopathy via targeting STAT1. Int Immunopharmacol 90:107010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107010
Li W, Li F, Zhang Y et al (2022) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (xiap)-loaded magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles incorporated with miR-233 to improve radio sensitization of cervical cancer cells and promote apoptosis. J Biomed Nanotechnol 18(3):747–753. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2022.3281
Liang ZH, Lin SS, Pan NF et al (2023) UCMSCs-derived exosomal circHIPK3 promotes ulcer wound angiogenesis of diabetes mellitus via miR-20b-5p/Nrf2/VEGFA axis. Diabet Med 40(2):e14968. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14968
Liu T, Sun YC, Cheng P, Shao HG (2019) Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miR-29a regulates obesity-associated insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 515(2):352–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.113
Maas SLN, Breakefield XO, Weaver AM (2017) Extracellular vesicles: unique intercellular delivery vehicles. Trends Cell Biol 27(3):172–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2016.11.003
Mastrototaro L, Roden M (2021) Insulin resistance and insulin sensitizing agents. Metabolism 125:154892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154892
Meijer RI, Bakker W, Alta CL et al (2013) Perivascular adipose tissue control of insulin-induced vasoreactivity in muscle is impaired in db/db mice. Diabetes 62(2):590–598. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1603
Mizushima N, Levine B (2010) Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 12(9):823–830. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0910-823
Mori MA, Ludwig RG, Garcia-Martin R, Brandão BB, Kahn CR (2019) Extracellular miRNAs: from biomarkers to mediators of physiology and disease. Cell Metab 30(4):656–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.07.011
Muthiah A, Angulo MS, Walker NN, Keller SR, Lee JK (2018) Biologically anchored knowledge expansion approach uncovers KLF4 as a novel insulin signaling regulator. PLoS One 13(9):e0204100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204100
Nishiwada S, Cui Y, Sho M et al (2022) Transcriptomic profiling identifies an exosomal microrna signature for predicting recurrence following surgery in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 276(6):e876–e885. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004993
Niu B, Xia X, Ma L, Yao L, Zhang Y, Su H (2023) LncRNA AC040162.3 promotes HCV-induced T2DM deterioration through the miRNA-223-3p/NLRP3 molecular axis. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 17:5350999. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/5350999
Pan Y, Hui X, Hoo RLC et al (2019) Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation. J Clin Invest 129(2):834–849. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI123069
Qin X, Guo H, Wang X et al (2019) Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol 20(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1604-0
Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W et al (1996) B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med 183(3):1161–1172. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.183.3.1161
Ruan Y, Lin N, Ma Q et al (2018) circulating lncrnas analysis in patients with type 2 diabetes reveals novel genes influencing glucose metabolism and islet β-cell function. Cell Physiol Biochem 46(1):335–350. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488434
Safwat A, Sabry D, Ragiae A, Amer E, Mahmoud RH, Shamardan RM (2018) Adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuate retina degeneration of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rabbits. J Circ Biomark 28(7):1849454418807827. https://doi.org/10.1177/1849454418807827
Saravanan PB, Vasu S, Yoshimatsu G et al (2019) Differential expression and release of exosomal miRNAs by human islets under inflammatory and hypoxic stress. Diabetologia 62(10):1901–1914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-4950-x
Shah MY, Calin GA (2014) MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in human cancers. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 5(4):537–548. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1229
Sharma A, Oonthonpan L, Sheldon RD et al (2019) Impaired skeletal muscle mitochondrial pyruvate uptake rewires glucose metabolism to drive whole-body leanness. Elife 18(8):e45873. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45873
Shen K, Duan A, Cheng J et al (2022) Exosomes derived from hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells laden in a silk hydrogel promote cartilage regeneration via the miR-205-5p/PTEN/AKT pathway. Acta Biomater 143:173–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2022.02.026
Shi H, Hao X, Sun Y et al (2023) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce insulin resistance and obesity in mice via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio 13(6):1015–1026. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.13615
Sira J, Zhang X, Gao L et al (2023) Effects of inorganic arsenic on type 2 diabetes mellitus in vivo: the roles and mechanisms of miRNAs. Biol Trace Elem Res 202(1):111–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03669-1
Stuffers S, Sem Wegner C, Stenmark H, Brech A (2009) Multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the absence of ESCRTs. Traffic 10(7):925–937. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00920.x
Su T, Xiao Y, Xiao Y et al (2019) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal MiR-29b-3p regulates aging-associated insulin resistance. ACS Nano 13(2):2450e2462. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b09375
Sun Y, Zhou Y, Shi Y et al (2021) Expression of miRNA-29 in pancreatic β Cells promotes inflammation and diabetes via TRAF3. Cell Rep 34(1):108576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108576
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C (2008) MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.033
Thomou T, Mori MA, Dreyfuss JM et al (2017) Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature 542(7642):450–455. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21365
Tian F, Tang P, Sun Z et al (2020) miR-210 in exosomes derived from macrophages under high glucose promotes mouse diabetic obesity pathogenesis by suppressing NDUFA4 expression. J Diabetes Res 19(2020):6894684. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6894684
Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N Jr, Heine U (1981) Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 645(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(81)90512-5
Viscarra JA, Ortiz RM (2013) Cellular mechanisms regulating fuel metabolism in mammals: role of adipose tissue and lipids during prolonged food deprivation. Metabolism 62(7):889–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2012.12.014
Wu J, Dong T, Chen T et al (2020) Hepatic exosome-derived miR-130a-3p attenuates glucose intolerance via suppressing PHLPP2 gene in adipocyte. Metabolism 103:154006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154006
Xu G, Ji C, Song G et al (2015) MiR-26b modulates insulin sensitivity in adipocytes by interrupting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Int J Obes 39(10):1523–1530. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.95
Ye D, Zhang T, Lou G et al (2018) Plasma miR-17, miR-20a, miR-20b and miR-122 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of NAFLD in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Life Sci 1(208):201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.07.029
Yi R, Qin Y, Macara IG, Cullen BR (2003) Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev 17(24):3011–3016. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1158803
Ying W, Gao H, Dos Reis FCG et al (2021) MiR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Cell Metab 33(4):781–790.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.12.019
Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G et al (2017) Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal mirnas can modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell 171(2):372–384.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.035
Yu Y, Du H, Wei S et al (2018) Adipocyte-derived exosomal MIR-27a induces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle through REPRession of PPARγ. Theranostics 8(8):2171–2188. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.22565
Żbikowski A, Błachnio-Zabielska A, Galli M, Zabielski P (2021) Adipose-derived exosomes as possible players in the development of insulin resistance. Int J Mol Sci 22(14):7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147427
Zhang L, Zhang S, Yao J et al (2015) Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth. Nature 527(7576):100–104. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15376
Zhang Q, Qu Y, Zhang Q et al (2023) Exosomes derived from hepatitis B virus-infected hepatocytes promote liver fibrosis via miR-222/TFRC axis. Cell Biol Toxicol 39(2):467–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09684-z
Zhang Y, Liu D, Chen X et al (2010) Secreted monocytic miR-150 enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell 39(1):133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.06.010
Acknowledgments
We want to acknowledge the help of the Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapy Key Laboratory.
Funding
The work was supported by the grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81974528 to C.F. Yuan, No. 82174035 to C.F. Yuan, No. 82374107 to C.F. Yuan and No. 81773959 to C.F. Yuan), the innovational group project of Hubei Province Natural Science Foundation in China (Grant No. 2021CFA015 to C.F. Yuan), and the Central Funds Guiding the Local Science and Technology Development (Grant No. 2020ZYYD016 to C.F. Yuan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ting Lu was responsible for literature search and for the first draft. Ying Zheng, Xiaoling Chen and Zhiyong Lin were involved in manuscript reading and correction, while Chaoqi Liu and Chengfu Yuan were responsible for the last version of the manuscript and are the senior author. “The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used”.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Research involving human participants and/or animals
No.
Informed consent
Non-applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key points
1 Exosome-derived miRNAs are key to insulin resistance and T2DM through crosstalk between insulin target cells and target organs.
2 Exosomes-derived miRNAs exert biological effects by affecting insulin signal transduction of insulin target cells.
3 Exosomes-derived miRNAs may be researchable for diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets of diseases, including T2DM.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, T., Zheng, Y., Chen, X. et al. The role of exosome derived miRNAs in inter-cell crosstalk among insulin-related organs in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Physiol Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-024-01026-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-024-01026-x