Abstract
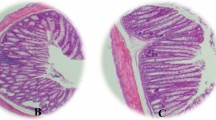
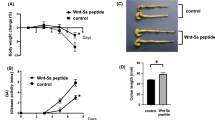
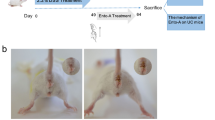
The ulcerative colitis (UC) is a typical inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) causing great damages, while strictosamide (STR) is a natural alkaloid that possesses strong anti-inflammatory property in infection and inflammation-related diseases. Our study is aimed at evaluating the anti-inflammatory activity of STR in the course of UC. Briefly, male Balb/c mice were treated with 3.5% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) for 6 consecutive days to establish an acute model of UC, and the administration of gradient concentrations of STR was subsequently performed. Accordingly, colonic pathological alterations including the reduced ratio of colon weight/length, decreased disease activity index (DAI), and attenuated H&E damage were found in UC mice after STR treatment. Based on the analyses of real-time PCR and western blot, downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) was also determined in the colonic tissue of UC mice after the treatment of STR. ELISA and immunohistochemical staining further suggest the relief of inflammation in UC mice with decreased expressions of MPO and iNOS after STR treatment. In addition, STR was also validated to significantly inhibit NF-κB signaling in UC mice by western blot and Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). Meanwhile, restricted inflammation was also determined in STR-treated IEC6 and HT-29 cells. The utilization of PDTC, an inhibitor of NF-κB, further demonstrated that STR ameliorated the inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling in vitro. In summary, our study suggests that STR could be a potential candidate for IBD therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonina IS, Zhong Z, Karin M, Beyaert R (2017) Limiting inflammation-the negative regulation of NF-kappaB and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol 18:861–869. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3772
Anavi S, Tirosh O (2020) iNOS as a metabolic enzyme under stress conditions. Free Radic Biol Med 146:16–35
Antonelli E, Villanacci V, Bassotti G (2018) Novel oral-targeted therapies for mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 24:5322–5330. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i47.5322
Barbalho SM, Goulart RA, Batista G (2019) Vitamin A and inflammatory bowel diseases: from cellular studies and animal models to human disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2019.1543588
Candeias MF, Abreu P, Pereira A, Cruz-Morais J (2009) Effects of strictosamide on mouse brain and kidney Na+,K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities. J Ethnopharmacol 121:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2008.08.032
Chen G, Ran X, Li B, Li Y, He D, Huang B, Fu S, Liu J, Wang W (2018) Sodium butyrate inhibits inflammation and maintains epithelium barrier integrity in a TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease mice model. EBioMedicine 30:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.03.030
Cheng D, Talib J, Stanley CP, Rashid I, Michaëlsson E, Lindstedt EL, Croft KD, Kettle AJ, Maghzal GJ, Stocker R (2019) Inhibition of MPO (myeloperoxidase) attenuates endothelial dysfunction in mouse models of vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 39:1448–1457
Chu H, Tao X, Sun Z, Hao W, Wei X (2020) Galactooligosaccharides protects against DSS-induced murine colitis through regulating intestinal flora and inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway. Life Sci 242:117220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117220
Dugani A, Dakhil B, Treesh S (2016) Protective effect of the methanolic extract of malva parviflora l. leaves on acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Saudi J Gastroenterol 22:226–233. https://doi.org/10.4103/1319-3767.182459
Dyson JK, Rutter MD (2012) Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: what is the real magnitude of the risk? World J Gastroenterol 18:3839–3848. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i29.3839
Ellis CT, Fichera A (2018) Management of acute ulcerative colitis. Dis Colon Rectum 61:1010–1013. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0000000000001173
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Yamamoto-Furusho JK (2015) Immunoregulatory pathways involved in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 21:2188–2193
Gajendran M, Loganathan P, Jimenez G, Catinella AP, Ng N, Umapathy C, Ziade N, Hashash JG (2019) A comprehensive review and update on ulcerative colitis. Dis Mon 65:100851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disamonth.2019.02.004
Hindryckx P, Jairath V, D'Haens G (2016) Acute severe ulcerative colitis: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:654–664. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.116
Hoffmann P, Wehling C, Krisam J, Pfeiffenberger J, Belling N, Gauss A (2019) Performance of tacrolimus in hospitalized patients with steroid-refractory acute severe ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 25:1603–1617. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1603
Hung SP, Sheu MJ, Ma MC, Hu JT, Sun YY, Lee CC, Chung YC, Tsai YJ, Wang JY, Chen CL (2014) Runx1-deficient afferents impair visceral nociception, exacerbating dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Brain Behav Immun 35:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2013.09.003
Kan S, Zhou H, Jin C, Yang H (2015) Effects of PDTC on NF-κB expression and apoptosis in rats with severe acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:3258–3270
Kawalec P (2016) Indirect costs of inflammatory bowel diseases: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. A systematic review. Arch Med Sci 12:295–302. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2016.59254
Li N, Cao L, Cheng Y, Meng ZQ, Tang ZH, Liu WJ, Wang ZZ, Ding G, Xiao W (2014) In vivo anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of strictosamide from Nauclea officinalis. Pharm Biol 52:1445–1450. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.895910
Li Z, Li Z, Lin Y, Meng Z, Ding G, Cao L, Li N, Liu W, Xiao W, Wu X, Xu J (2015) Synthesis and biological evaluation of strictosamide derivatives with improved antiviral and antiproliferative activities. Chem Biol Drug Des 86:523–530
Li PA, Hou X, Hao S (2017) Mitochondrial biogenesis in neurodegeneration. J Neurosci Res 95:2025–2029. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24042
Masoodi I, Kochhar R, Fau-Dutta U, Dutta U, Fau-Vaishnavi C, Vaishnavi C, Fau-Prasad KK, Prasad KK, Fau-Vaiphei K, Vaiphei K, Fau-Hussain S, Hussain S, Fau-Singh K, Singh K (2012) Evaluation of fecal myeloperoxidase as a biomarker of disease activity and severity in ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 57:1336–1340
Medzhitov R (2008) Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454:428–435
Melgar S, Karlsson A, Michaëlsson E (2005) Acute colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium progresses to chronicity in C57BL/6 but not in BALB/c mice: correlation between symptoms and inflammation. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G1328–G1338. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00467.2004
Moein S, Vaghari-Tabari M, Qujeq D, Majidinia M, Nabavi SM, Yousefi B (2019) MiRNAs and inflammatory bowel disease: an interesting new story. J Cell Physiol 234:3277–3293. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27173
Murano M, Maemura K, Hirata I, Toshina K, Nishikawa T, Hamamoto N, Sasaki S, Saitoh O, Katsu K (2000) Therapeutic effect of intracolonically administered nuclear factor kappa B (p65) antisense oligonucleotide on mouse dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Clin Exp Immunol 120:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01183.x
Nuij V, Fuhler GM, Edel AJ, Ouwendijk RJ, Rijk MC, Beukers R, Quispel R, van Tilburg AJ, Tang TJ, Smalbraak H, Bruin KF, Lindenburg F, Peyrin-Biroulet L, van der Woude CJ, Dutch Delta IBDG (2015) Benefit of earlier anti-TNF treatment on IBD disease complications? J Crohns Colitis 9:997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv130
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R (1990) A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(90)90290-h
Perner RM (1999) Review article: the potential role of nitric oxide in chronic inflammatory bowel disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 13:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00453.x
Porcari S, Viola A, Orlando A, Privitera AC, Ferracane C, Cappello M, Vitello A, Siringo S, Inserra G, Magnano A, Mocciaro F, Di Mitri R, Belluardo N, Fidanza O, Garufi S, Magri G, Bertolami C, Carroccio A, Macaluso FS, Renna S, Ventimiglia M, Alibrandi A, Cottone M, Fries W, Sicilian Network for Inflammatory Bowel D (2020) Persistence on anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy in older patients with inflammatory bowel disease compared with younger patients: data from the Sicilian Network for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (SN-IBD). Drugs Aging 37:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-020-00744-3
Rungoe C, Langholz E, Andersson M, Basit S, Nielsen NM, Wohlfahrt J, Jess T (2014) Changes in medical treatment and surgery rates in inflammatory bowel disease: a nationwide cohort study 1979–2011. Gut 63:1607–1616. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305607
Seyedian SS, Nokhostin F, Malamir MD (2019) A review of the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment methods of inflammatory bowel disease. J Med Life 12:113–122. https://doi.org/10.25122/jml-2018-0075
Varshosaz J, Ahmadi F, Emami J, Tavakoli N, Minaiyan M, Mahzouni P, Dorkoosh F (2010) Colon delivery of budesonide using solid dispersion in dextran for the treatment and secondary prevention of ulcerative colitis in rat. Int J Prev Med 1:115–123
Wang J, Cao Y, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ji F, Li J, Zou Y (2019) PIM1 inhibitor SMI-4a attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through suppressing macrophage inflammatory responses via modulating p65 phosphorylation. Int Immunopharmacol 73:568–574
Wechsler JB, Szabo A, Hsu CL, Krier-Burris RA, Schroeder HA, Wang MY, Carter RG, Velez TE, Aguiniga LM, Brown JB, Miller ML, Wershil BK, Barrett TA, Bryce PJ (2018) Histamine drives severity of innate inflammation via histamine 4 receptor in murine experimental colitis. Mucosal Immunol 11:861–870. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2017.121
Xue Q, Yan Y, Zhang R, Xiong H (2018) Regulation of iNOS on immune cells and its role in diseases. Int J Mol Sci 19:3805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123805
Yang L, Chen H, Wang D, Nie S, Du J, Lu M (2019) PDTC alleviates depressive symptoms and colon tissue injury via inhibiting NO overproduction in CUMS rats. Front Neurosci 13:1327
Zhang JJ, Xu ZM, Fau-Chang H, Chang H, Fau-Zhang C-M, Zhang CM, Fau-Dai H-Y, Dai HY, Fau-Ji X-Q, Ji XQ, Fau-Li C, Li C, Fau-Wang X-F, Wang XF (2011) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates nuclear factor-ĸB activation, cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E2 production in human endometriotic epithelial cells. Gynecol Obstet Investig 72:163–168
Funding
This research was funded by the Top Talent Project for Youths of Hebei Province (No. 180443), the Doctoral Startup Foundation of Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology (No. 2018YB018 and No. 2019YB005), the Project of Department of Science and Technology, Hebei Province (No. C2019407111), the Talent Engineering Training Funds of Hebei Province (No. A201903012), and the High School Hundred Excellent Innovation Talent Program of Hebei Province (No. SLRC2019048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QHJ, HHZ, and MSF designed the study. HHZ, YMS, and XL performed the research. QHJ and JSB analyzed the data. WYL and QMS contributed to the details of methods and materials. QHJ and HHZ wrote the paper. MSF revised and modified the manuscript to the final version. QHJ and HHZ contributed equally to this research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology. All operations were conducted according to the Guide to the Care and Use of Experimental Animals.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Points
1. Strictosamide alleviated the pathological alterations in DSS-induced acute UC mice.
2. Strictosamide relieved the inflammation in DSS-induced acute UC mice.
3. Strictosamide inhibited the inflammatory response in LPS-induced IEC6/HT-29 cells by restricting the NF-κB pathway.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Q., Zhang, H., Su, Y. et al. Strictosamide alleviates the inflammation in an acute ulcerative colitis (UC) model. J Physiol Biochem 77, 283–294 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-021-00796-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-021-00796-y