Abstract
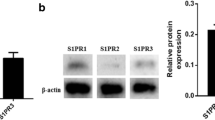
Endothelial dysfunction plays a vital role during the initial stage of atherosclerosis. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) induces vascular endothelial injury and vessel wall inflammation. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) exerts numerous vasoprotective effects by binding to diverse S1P receptors (S1PRs; S1PR1-5). A number of studies have shown that in endothelial cells (ECs), S1PR2 acts as a pro-atherosclerotic mediator by stimulating vessel wall inflammation through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. Scavenger receptor class B member I (SR-BI), a high-affinity receptor for apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I)/high-density lipoprotein (HDL), inhibits nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) translocation and decreases the plasma levels of inflammatory mediators via the PI3K/Akt pathway. We hypothesized that the inflammatory effects of S1P/S1PR2 on ECs may be regulated by apoA-I/SR-BI. The results showed that ox-LDL, a pro-inflammatory factor, augmented the S1PR2 level in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a dose- and time-dependent manner. In addition, S1P/S1PR2 signaling influenced the levels of inflammatory factors, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and IL-10, aggravating inflammation in HUVECs. Moreover, the pro-inflammatory effects induced by S1P/S1PR2 were attenuated by SR-BI overexpression and enhanced by an SR-BI inhibitor, BLT-1. Further experiments showed that the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway was involved in this process. Taken together, these results demonstrate that apoA-I/SR-BI negatively regulates S1P/S1PR2-mediated inflammation in HUVECs by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ox-LDL:
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein
- S1P:
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- S1PR:
-
S1P receptor
- ECs:
-
Endothelial cells
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- SR-BI:
-
Scavenger receptor class B member 1
- Apo:
-
Apolipoprotein
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- RCT:
-
Reverse cholesterol transport
- GPCR:
-
G-protein coupled receptor
- VSMC:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cell
- apoE−/−:
-
apoE deficient
- S1PR2−/−:
-
S1PR2 deficient
- S1PR2+/+:
-
S1PR2 non-deficient
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein-1
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1
- HDL-C:
-
HDL-cholesterol
- HCAECs:
-
Human coronary artery endothelial cells
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- PMN:
-
Polymorphonuclear neutrophil
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- p-PI3K:
-
Phosphorylated PI3K
- p-Akt:
-
Phosphorylated Akt
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- alb-S1P:
-
Albumin-bound S1P
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- RT-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
References
Anderson RG (1998) The caveolae membrane system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:199–225
Bielawski J, Szulc ZM, Hannun YA, Bielawska A (2006) Simultaneous quantitative analysis of bioactive sphingolipids by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Methods 39:82–91
Christoffersen C, Obinata H, Kumaraswamy SB, Galvani S, Ahnstrom J, Sevvana M, Egerer-Sieber C, Muller YA, Hla T, Nielsen LB, Dahlback B (2011) Endothelium-protective sphingosine-1-phosphate provided by HDL-associated apolipoprotein M. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:9613–9618
DiVito C, Abdel Hadi L, Navone SE, Marfia G, Campanella R, Mancuso ME & Riboni L. (2016). Platelet-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate and inflammation: from basic mechanisms to clinical implications. Platelets, 1–9
English D, Welch Z, Kovala AT, Harvey K, Volpert OV, Brindley DN, Garcia JG (2000) Sphingosine 1-phosphate released from platelets during clotting accounts for the potent endothelial cell chemotactic activity of blood serum and provides a novel link between hemostasis and angiogenesis. FASEB J 14:2255–2265
Galvani S, Sanson M, Blaho VA, Swendeman SL, Obinata H, Conger H, Dahlback B, Kono M, Proia RL, Smith JD, Hla T (2015) HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P1 to limit vascular inflammation. Sci Signal 8:ra79
Ishii I, Fukushima N, Ye X, Chun J (2004) Lysophospholipid receptors: signaling and biology. Annu Rev Biochem 73:321–354
Karuna R, Park R, Othman A, Holleboom AG, Motazacker MM, Sutter I, Kuivenhoven JA, Rohrer L, Matile H, Hornemann T, Stoffel M, Rentsch KM, von Eckardstein A (2011) Plasma levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate and apolipoprotein M in patients with monogenic disorders of HDL metabolism. Atherosclerosis 219:855–863
Levkau B (2015) HDL-S1P: cardiovascular functions, disease-associated alterations, and therapeutic applications. Front Pharmacol 6:243
Liu W, Liu B, Liu S, Zhang J, Lin S (2016) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 mediates endothelial cells dysfunction by PI3K-Akt pathway under high glucose condition. Eur J Pharmacol 776:19–25
Liu X, Xiong SL, Yi GH (2012) ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR-BI: transit of HDL-associated sphingosine-1-phosphate. Clin Chim Acta 413:384–390
Liu Y, Wada R, Yamashita T, Mi Y, Deng CX, Hobson JP, Rosenfeldt HM, Nava VE, Chae SS, Lee MJ, Liu CH, Hla T, Spiegel S, Proia RL (2000) Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation. J Clin Invest 106:951–961
Michaud J, Im DS, Hla T (2010) Inhibitory role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 in macrophage recruitment during inflammation. J Immunol 184:1475–1483
Mo ZC, Ren K, Liu X, Tang ZL & Yi GH. (2016). A high-density lipoprotein-mediated drug delivery system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev
Panzenboeck U, Balazs Z, Sovic A, Hrzenjak A, Levak-Frank S, Wintersperger A, Malle E, Sattler W (2002) ABCA1 and scavenger receptor class B, type I, are modulators of reverse sterol transport at an in vitro blood-brain barrier constituted of porcine brain capillary endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 277:42781–42789
Pappu R, Schwab SR, Cornelissen I, Pereira JP, Regard JB, Xu Y, Camerer E, Zheng YW, Huang Y, Cyster JG, Coughlin SR (2007) Promotion of lymphocyte egress into blood and lymph by distinct sources of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 316:295–298
Podrez EA (2010) Anti-oxidant properties of high-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37:719–725
Rigotti A, Trigatti BL, Penman M, Rayburn H, Herz J, Krieger M (1997) A targeted mutation in the murine gene encoding the high density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor scavenger receptor class B type I reveals its key role in HDL metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:12610–12615
Ross R (1993) The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature 362:801–809
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease. Am Heart J 138:S419–S420
Sattler K, Levkau B (2009) Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a mediator of high-density lipoprotein effects in cardiovascular protection. Cardiovasc Res 82:201–211
Schwab SR, Pereira JP, Matloubian M, Xu Y, Huang Y, Cyster JG (2005) Lymphocyte sequestration through S1P lyase inhibition and disruption of S1P gradients. Science 309:1735–1739
Skoura A, Michaud J, Im DS, Thangada S, Xiong Y, Smith JD, Hla T (2011) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 function in myeloid cells regulates vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:81–85
Song GJ, Kim SM, Park KH, Kim J, Choi I, Cho KH (2015) SR-BI mediates high density lipoprotein (HDL)-induced anti-inflammatory effect in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457:112–118
Takashima S, Sugimoto N, Takuwa N, Okamoto Y, Yoshioka K, Takamura M, Takata S, Kaneko S, Takuwa Y (2008) G12/13 and Gq mediate S1P2-induced inhibition of Rac and migration in vascular smooth muscle in a manner dependent on Rho but not Rho kinase. Cardiovasc Res 79:689–697
Vaisman BL, Vishnyakova TG, Freeman LA, Amar MJ, Demosky SJ, Liu C, Stonik JA, Sampson ML, Pryor M, Bocharov AV, Eggerman TL, Patterson AP, Remaley AT (2015) Endothelial expression of scavenger receptor class B, type I protects against development of atherosclerosis in mice. Biomed Res Int 2015:607120
Venkataraman K, Lee YM, Michaud J, Thangada S, Ai Y, Bonkovsky HL, Parikh NS, Habrukowich C, Hla T (2008) Vascular endothelium as a contributor of plasma sphingosine 1-phosphate. Circ Res 102:669–676
Wang F, Okamoto Y, Inoki I, Yoshioka K, Du W, Qi X, Takuwa N, Gonda K, Yamamoto Y, Ohkawa R, Nishiuchi T, Sugimoto N, Yatomi Y, Mitsumori K, Asano M, Kinoshita M, Takuwa Y (2010) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 deficiency leads to inhibition of macrophage proinflammatory activities and atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 120:3979–3995
Xu J, Qian J, Xie X, Lin L, Ma J, Huang Z, Fu M, Zou Y, Ge J (2012) High density lipoprotein cholesterol promotes the proliferation of bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells via binding scavenger receptor-B type I and activation of PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 371:55–64
Zhang QH, Zu XY, Cao RX, Liu JH, Mo ZC, Zeng Y, Li YB, Xiong SL, Liu X, Liao DF, Yi GH (2012) An involvement of SR-B1 mediated PI3K-Akt-eNOS signaling in HDL-induced cyclooxygenase 2 expression and prostacyclin production in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 420:17–23
Zhang W, An J, Jawadi H, Siow DL, Lee JF, Zhao J, Gartung A, Maddipati KR, Honn KV, Wattenberg BW, Lee MJ (2013) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 mediated NFkappaB activation contributes to tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 106:62–71
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81270360 and 81670401), the Scientific Research Fund of the Hunan Provincial Education Department (13C838), the Science and Technology Planning Project of the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department (2014FJ2012), the Aid Program for Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Hunan Province (2008-244), and the construct program of the key discipline in Hunan Province (2011-76).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kun Ren and Yan-Ju Lu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, K., Lu, YJ., Mo, ZC. et al. ApoA-I/SR-BI modulates S1P/S1PR2-mediated inflammation through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in HUVECs. J Physiol Biochem 73, 287–296 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0553-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0553-5