Abstract
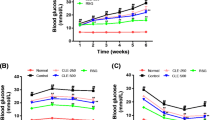
The aim of this present study was to investigate the effect of ursolic acid (UA) and rosiglitazone (RSG) on insulin sensitivity and proximal insulin signaling pathways in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed C57/BL/6J mice. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed either normal diet or HFD for 10 weeks, after which animals in each dietary group were divided into the following six groups (normal diet, normal diet plus UA and RSG, HFD alone, HFD plus UA, HFD plus RSG, and HFD plus UA and RSG) for the next 5 weeks. UA (5 mg/kg BW) and RSG (4 mg/kg BW) were administered as suspensions directly into the stomach using a gastric tube. The HFD diet elevated fasting plasma glucose, insulin, and homeostasis model assessment index. The expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-kinase), Akt, and glucose transporter (GLUT) 4 were determined by Western blot analyses. The results demonstrated that combination treatment (UA/RSG) ameliorated HFD-induced glucose intolerance and insulin resistance by improving the homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) index. Further, combination treatment (UA/RSG) stimulated the IRS-1, PI3-kinase, Akt, and GLUT 4 translocation. These results strongly suggest that combination treatment (UA/RSG) activates IRS-PI3-kinase-Akt-dependent signaling pathways to induce GLUT 4 translocation and increases the expression of insulin receptor to improve glucose intolerance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdin AA, Baalash AA, Hamooda HE (2010) Effects of rosiglitazone and aspirin on experimental model of induced type 2 diabetes in rats: focus on insulin resistance and inflammatory markers. J Diabetes Complicat 24(3):168–178
Bonora E, Formentini G, Calcaterra F, Lombardi S, Marini F, Zenari L, Saggiani F, Poli M, Perbellini S, Raffaelli A, Cacciatori V, Santi L, Targher, Bonadonna R, Muggeo M (2002) HOMA-estimated insulin resistance is an independent predictor of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 25(7):1135–1141
Burgi W, Briner M, Franken N, Kessler AC (1998) One step sandwich enzyme immunoassay for insulin using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Biochem 21(5):311–314
Carvalho E, Rondinone C, Smith U (2000) Insulin resistance in fat cells from obese Zucker rats—evidence for an impaired activation and translocation of protein kinase B and glucose transporter 4. Mol Cell Biochem 206(1-2):7–16
Chakraborty C (2006) Biochemical and molecular basis of insulin resistance. Curr Protein Pept Sci 7(2):113–121
Chang L, Chiang SH, Saltiel AR (2004) Insulin signaling and the regulation of glucose transport. Mol Med 10(7-12):65–71
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E (1991) Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 14(3):173–194
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Simonson DC (1989) Fasting hyperglycemia in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: contributions of excessive hepatic glucose production and impaired tissue glucose uptake. Metabolism 38(4):387–395
Fujitani Y, Ueno T, Watada H (2010) The role of pancreatic beta-cell autophagy in health and diabetes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299(1):C1–C6
Grundy SM (2006) Drug therapy of the metabolic syndrome: minimizing the emerging crisis in polypharmacy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(4):295–309
Grundy SM (2007) Metabolic syndrome: a multiplex cardiovascular risk factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(2):399–404
Huang S, Czech MP (2007) The GLUT4 glucose transporter. Cell Metab 5(4):237–252
Jayaprakasam B, Olson LK, Schutzki RE, Tai MH, Nair MG (2005) Amelioration of obesity and glucose intolerance in high-fat-fed C57BL/6 mice by anthocyanins and ursolic acid in cornelian cherry (cornus mas). J Agric Food Chem 54(1):243–248
Johnson AM, Olefsky JM (2013) The origins and drivers of insulin resistance. Cell 152(4):673–684
Kersten S, Desvergne B, Wahli W (2000) Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature 405(6785):421–424
Kim JK, Michael MD, Previs SF, Peroni OD, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Neschen S, Kahn BB, Kahn CR, Shulman GI (2000) Redistribution of substrates to adipose tissue promotes obesity in mice with selective insulin resistance in muscle. J Clin Invest 105(12):1791–1797
Kruszynska YT, Olefsky JM (1996) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Investig Med 44(8):413–428
Larsen MO, Juhl CB, Pørksen N, Gotfredsen CF, Carr RD, Ribel U, Wilken M, Rolin B (2005) Beta-cell function and islet morphology in normal, obese, and obese beta-cell mass-reduced Göttingen minipigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288(2):E412–E421
Lee YS, Cha BY, Saito K, Yamakawa H, Choi SS, Yamaguchi K, Yonezawa T, Teruya T, Nagai K, Woo JT (2010) Nobiletin improves hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Biochem Pharmacol 79(11):1674–1683
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Lu J, Zheng YL, Wu DM, Luo L, Sun DX, Shan Q (2007) Ursolic acid ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative damage in the brain of senescent mice induced by D-galactose. Biochem Pharmacol 74(7):1078–1090
Maier VH, Gould GW (2000) Long term insulin treatment of 3T3-L1 adipocytes results in mis-targeting of GLUT4: implications for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Diabetologia 43(10):1273–1281
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and B-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7):412–419
Miyazaki Y, He H, Mandarino LJ, DeFronzo RA (2003) Rosiglitazone improves downstream insulin receptor signaling in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 52(8):1943–1950
Nesto RW, Bell D, Bonow RO, Fonseca V, Grundy SM, Horton ES, Le Winter M, Porte D, Semenkovich CF, Smith S, Young LH, Kahn R (2003) Thiazolidinedione use, fluid retention, and congestive heart failure: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. October 7, 2003. Circulation 108(23):2941–2948
Osborn O, Olefsky JM (2012) The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat Med 18(3):363–374
Otto C, Lehrke M, Goke B (2002) Novel insulin sensitizers: pharmacogenomic aspects. Pharmacogenomics 3(1):99–116
Pessin JE, Saltiel AR (2000) Signalling pathways in insulin action: molecular targets of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 106(2):165–169
Phillips LS, Grunberger G, Miller E, Patwardhan R, Rappaport EB, Salzman A (2001) Once- and twice-daily dosing with rosiglitazone improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 24(2):308–315
Pittas AG, Joseph NA, Greenberg AS (2004) Adipocytokines and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(2):447–452
Radhiga T, Rajamanickam C, Sundaresan A, Ezhumalai M, Pugalendi KV (2012) Effect of ursolic acid treatment on apoptosis and DNA damage in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction. Biochimie 94(5):1135–1142
Ruderman NB, Cacicedo JM, Itani S, Yagihashi N, Saha AK, Ye JM, Chen K, Zou M, Carling D, Boden G, Cohen RA, Keaney J, Kraegen EW, Ido Y (2003) Malonyl-CoA and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK): possible links between insulin resistance in muscle and early endothelial cell damage in diabetes. Biochem Soc Trans 31(1):202–206
Saltiel AR, Pessin JE (2002) Insulin signaling pathways in time and space. Trends Cell Biol 12(2):65–71
Schrauwen-Hinderling VB, Kooi ME, Hesselink MK, Moonen-Kornips E, Schaart G, Mustard KJ, Hardie DG, Saris WH, Nicolay K, Schrauwen P (2005) Intramyocellular lipid content and molecular adaptations in response to a 1-week high-fat diet. Obes Res 13(12):2088–2094
Shulman GI (2000) Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 106(2):171–176
Surwit RS, Kuhn CM, Cochrane C, McCubbin JA, Feinglos MN (1988) Diet-induced type II diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes 37(9):1163–1167
Vasudevan AR, Balasubramanyam A (2004) Thiazolidinediones: a review of their mechanisms of insulin sensitization, therapeutic potential, clinical efficacy, and tolerability. Diabetes Technol Ther 6(6):850–863
Virkamäki A, Ueki K, Kahn CR (1999) Protein-protein interaction in insulin signaling and the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 103(7):931–943
Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S (2007) A dominant role of glucose in β-cell compensation of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 117(1):81–83
Weir GC, Laybutt DR, Kaneto H, Bonner-Weir S, Sharma A (2001) β-cell adaptation and decomposition during the progression of diabetes. Diabetes 50(1):S154–S159
White MF (2003) Insulin signaling in health and disease. Science 302(5651):1710–1711
Zhang F, Ye C, Li G, Ding W, Zhou W, Zhu H, Chen G, Luo T, Guang M, Liu Y, Zhang D, Zheng S, Yang J, Gu Y, Xie X, Luo M (2003) The rat model of type 2 diabetic mellitus and its glycol metabolism characters. Exp Anim 52(5):401–407
Zhang W, Hong D, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Shen Q, Li JY, Hu LH, Li J (2006) Ursolic acid and its derivative inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, enhancing insulin receptor phosphorylation and stimulating glucose uptake. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760(10):1505–1512
Acknowledgments
The financial support to Arjunan Sundaresan as Senior Research Fellowship (No. 3/1/2/22/2010-RHNdated16.08.2010) from Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundaresan, A., Radhiga, T. & Pugalendi, K.V. Ursolic acid and rosiglitazone combination improves insulin sensitivity by increasing the skeletal muscle insulin-stimulated IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. J Physiol Biochem 72, 345–352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0484-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0484-6