Abstract
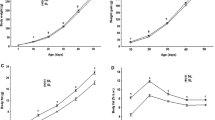
We have previously described the development of substantial, but reversible obesity in Wistar rats fed with palatable liquid nutrition (Fresubin). In this study, we investigated changes in serum hormone levels, glycemia, fat mass, adipocyte size, and gene expression of adipokines and inflammatory markers in adipose tissue of Wistar rats fed by Fresubin (i) for 5 months, (ii) up to 90 days of age, or (iii) after 90 days of age to characterize metabolic alterations and their reversibility in rats fed with Fresubin. An intra-peritoneal glucose tolerance test was also performed to determine levels of serum leptin, adiponectin, insulin, and C-peptide in 2- and 4-month-old animals. In addition, mesenteric and epididymal adipose tissue weight, adipocyte diameter, and gene expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory adipokines and other markers were determined at the end of the study. Chronic Fresubin intake significantly increased adipocyte diameter, reduced glucose tolerance, and increased serum leptin, adiponectin, insulin, and C-peptide levels. Moreover, gene expression of leptin, adiponectin, CD68, and nuclear factor kappa B was significantly increased in mesenteric adipose tissue of Fresubin fed rats. Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 messenger RNA (mRNA) levels increased in mesenteric adipose tissue only in the group fed Fresubin during the entire experiment. In epididymal adipose tissue, fatty acid binding protein 4 mRNA levels were significantly increased in rats fed by Fresubin during adulthood. In conclusion, chronic Fresubin intake induced complex metabolic alterations in Wistar rats characteristic of metabolic syndrome. However, transition of rats from Fresubin to standard diet reversed these alterations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ailhaud G, Massiera F, Weill P, Legrand P, Alessandri JM, Guesnet P (2006) Temporal changes in dietary fats: role of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in excessive adipose tissue development and relationship to obesity. Prog Lipid Res 45:203–236
Al-Hasani H, Joost HG (2005) Nutrition-/diet-induced changes in gene expression in white adipose tissue. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 19:589–603
Archer ZA, Corneloup J, Rayner DV, Barrett P, Moar KM, Mercer JG (2007) Solid and liquid obesogenic diets induce obesity and counter-regulatory changes in hypothalamic gene expression in juvenile Sprague–Dawley rats. J Nutr 137:1483–1490
Archer ZA, Mercer JG (2007) Brain responses to obesogenic diets and diet-induced obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 66:124–130
Bandyopadhyay GK, Yu JG, Ofrecio J, Olefsky JM (2006) Increased malonyl-CoA levels in muscle from obese and type 2 diabetic subjects lead to decreased fatty acid oxidation and increased lipogenesis; thiazolidinedione treatment reverses these defects. Diabetes 55:2277–2285
Barnea M, Shamay A, Stark AH, Madar Z (2006) A high-fat diet has a tissue-specific effect on adiponectin and related enzyme expression. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14:2145–2153
Berger J, Moller DE (2002) The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annu Rev Med 53:409–435
Bhatt MP, Lim YC, Ha KS (2014) C-peptide replacement therapy as an emerging strategy for preventing diabetic vasculopathy. Cardiovasc Res 104:234–244
Bruce CR, Mertz VA, Heigenhauser GJ, Dyck DJ (2005) The stimulatory effect of globular adiponectin on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation is impaired in skeletal muscle from obese subjects. Diabetes 54:3154–3160
Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B (2005) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 release is higher in visceral than subcutaneous human adipose tissue (AT): implication of macrophages resident in the AT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:2282–2289
Buettner R, Scholmerich J, Bollheimer LC (2007) High-fat diets: modeling the metabolic disorders of human obesity in rodents. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15:798–808
Caimari A, Oliver P, Keijer J, Palou A (2010) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells as a model to study the response of energy homeostasis-related genes to acute changes in feeding conditions. OMICS 14:129–141
Cao H, Maeda K, Gorgun CZ, Kim HJ, Park SY, Shulman GI, Kim JK, Hotamisligil GS (2006) Regulation of metabolic responses by adipocyte/macrophage fatty acid-binding proteins in leptin-deficient mice. Diabetes 55:1915–1922
Clement K, Langin D (2007) Regulation of inflammation-related genes in human adipose tissue. J Intern Med 262:422–430
Chalkley SM, Hettiarachchi M, Chisholm DJ, Kraegen EW (2002) Long-term high-fat feeding leads to severe insulin resistance but not diabetes in Wistar rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282:E1231–E1238
Chen A, Mumick S, Zhang C, Lamb J, Dai H, Weingarth D, Mudgett J, Chen H, MacNeil DJ, Reitman ML, Qian S (2005) Diet induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and its impact on obesity. Obes Res 13:1311–1320
de Ferranti S, Mozaffarian D (2008) The perfect storm: obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic consequences. Clin Chem 54:945–955
Deckelbaum RJ, Worgall TS, Seo T (2006) n-3 fatty acids and gene expression. Am J Clin Nutr 83:1520S–1525S
Di Gregorio GB, Yao-Borengasser A, Rasouli N, Varma V, Lu T, Miles LM, Ranganathan G, Peterson CA, McGehee RE, Kern PA (2005) Expression of CD68 and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 genes in human adipose and muscle tissues: association with cytokine expression, insulin resistance, and reduction by pioglitazone. Diabetes 54:2305–2313
Eckel RH, Alberti KG, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ (2010) The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 375:181–183
Fain JN (2010) Release of inflammatory mediators by human adipose tissue is enhanced in obesity and primarily by the nonfat cells: a review. Mediat Inflamm 2010:513948
Ferrante AW Jr (2007) Obesity-induced inflammation: a metabolic dialogue in the language of inflammation. J Intern Med 262:408–414
Furuhashi M, Fucho R, Gorgun CZ, Tuncman G, Cao H, Hotamisligil GS (2008) Adipocyte/macrophage fatty acid-binding proteins contribute to metabolic deterioration through actions in both macrophages and adipocytes in mice. J Clin Invest 118:2640–2650
Furuhashi M, Saitoh S, Shimamoto K, Miura T (2014) Fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4): pathophysiological insights and potent clinical biomarker of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Clin Med Insights Cardiol 8:23–33
Furuhashi M, Tuncman G, Gorgun CZ, Makowski L, Atsumi G, Vaillancourt E, Kono K, Babaev VR, Fazio S, Linton MF, Sulsky R, Robl JA, Parker RA, Hotamisligil GS (2007) Treatment of diabetes and atherosclerosis by inhibiting fatty-acid-binding protein aP2. Nature 447:959–965
Galic S, Oakhill JS, Steinberg GR (2010) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316:129–139
Ghorbani A, Shafiee-Nick R (2015) Pathological consequences of C-peptide deficiency in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 6:145–150
Giorgino F, Laviola L, Eriksson JW (2005) Regional differences of insulin action in adipose tissue: insights from in vivo and in vitro studies. Acta Physiol Scand 183:13–30
Goran MI, Alderete TL (2012) Targeting adipose tissue inflammation to treat the underlying basis of the metabolic complications of obesity. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser 73:49–60, discussion p61-46
Greenberg AS, Obin MS (2006) Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 83:461S–465S
Hariri N, Thibault L (2010) High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models. Nutr Res Rev 23:270–299
Heilbronn LK, Liu B (2014) Do adipose tissue macrophages promote insulin resistance or adipose tissue remodelling in humans? Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 20:3–13
Heyne A, Kiesselbach C, Sahun I, McDonald J, Gaiffi M, Dierssen M, Wolffgramm J (2009) An animal model of compulsive food-taking behaviour. Addict Biol 14:373–383
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444:860–867
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Bodkin NL, Ortmeyer HK, Arita Y, Hansen BC, Matsuzawa Y (2001) Circulating concentrations of the adipocyte protein adiponectin are decreased in parallel with reduced insulin sensitivity during the progression to type 2 diabetes in rhesus monkeys. Diabetes 50:1126–1133
Im SS, Kwon SK, Kim TH, Kim HI, Ahn YH (2007) Regulation of glucose transporter type 4 isoform gene expression in muscle and adipocytes. IUBMB Life 59:134–145
Jernas M, Palming J, Sjoholm K, Jennische E, Svensson PA, Gabrielsson BG, Levin M, Sjogren A, Rudemo M, Lystig TC, Carlsson B, Carlsson LM, Lonn M (2006) Separation of human adipocytes by size: hypertrophic fat cells display distinct gene expression. FASEB J 20:1540–1542
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K, Ueki K, Tobe K (2006) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 116:1784–1792
Kahn BB, Pedersen O (1992) Tissue-specific regulation of glucose transporters in different forms of obesity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 200:214–217
Kanety H, Hemi R, Ginsberg S, Pariente C, Yissachar E, Barhod E, Funahashi T, Laron Z (2009) Total and high molecular weight adiponectin are elevated in patients with Laron syndrome despite marked obesity. Eur J Endocrinol 161:837–844
Kieffer TJ, Habener JF (2000) The adipoinsular axis: effects of leptin on pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E1–E14
Kim YJ, Park T (2008) Genes are differentially expressed in the epididymal fat of rats rendered obese by a high-fat diet. Nutr Res 28:414–422
Krskova K, Eckertova M, Kukan M, Kuba D, Kebis A, Olszanecki R, Suski M, Gajdosechova L, Zorad S (2012) Aerobic training lasting for 10 weeks elevates the adipose tissue FABP4, Gialpha, and adiponectin expression associated by a reduced protein oxidation. Endocr Regul 46:137–146
Kwon H, Pessin JE (2013) Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:71
Lee JY, Hwang DH (2002) Docosahexaenoic acid suppresses the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in a colon tumor cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298:667–674
Levin BE (2005) Factors promoting and ameliorating the development of obesity. Physiol Behav 86:633–639
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA (2002) Defense of body weight depends on dietary composition and palatability in rats with diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282:R46–R54
Levin BE, Richard D, Michel C, Servatius R (2000) Differential stress responsivity in diet-induced obese and resistant rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R1357–R1364
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Madsen AN, Hansen G, Paulsen SJ, Lykkegaard K, Tang-Christensen M, Hansen HS, Levin BE, Larsen PJ, Knudsen LB, Fosgerau K, Vrang N (2010) Long-term characterization of the diet-induced obese and diet-resistant rat model: a polygenetic rat model mimicking the human obesity syndrome. J Endocrinol 206:287–296
Massiera F, Saint-Marc P, Seydoux J, Murata T, Kobayashi T, Narumiya S, Guesnet P, Amri EZ, Negrel R, Ailhaud G (2003) Arachidonic acid and prostacyclin signaling promote adipose tissue development: a human health concern? J Lipid Res 44:271–279
Michaud A, Boulet MM, Veilleux A, Noel S, Paris G, Tchernof A (2014) Abdominal subcutaneous and omental adipocyte morphology and its relation to gene expression, lipolysis and adipocytokine levels in women. Metabolism 63:372–381
Mikuska L, Vrabcova M, Lackovicova L, Ukropec J, Hegedusova N, Slavkovsky P, Hubka P, Mravec B (2013) Long-term liquid nutrition intake and development of obesity: differences between young and adult rats. Endocr Regul 47:85–92
Morris MJ, Chen H, Watts R, Shulkes A, Cameron-Smith D (2008) Brain neuropeptide Y and CCK and peripheral adipokine receptors: temporal response in obesity induced by palatable diet. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:249–258
Muhlhausler BS, Cook-Johnson R, James M, Miljkovic D, Duthoit E, Gibson R (2010) Opposing effects of omega-3 and omega-6 long chain polyunsaturated Fatty acids on the expression of lipogenic genes in omental and retroperitoneal adipose depots in the rat. J Nutr Metab. doi:10.1155/2010/927836
Mullen KL, Smith AC, Junkin KA, Dyck DJ (2007) Globular adiponectin resistance develops independently of impaired insulin-stimulated glucose transport in soleus muscle from high-fat-fed rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E83–E90
Naderali EK, Estadella D, Rocha M, Pickavance LC, Fatani S, Denis RG, Williams G (2003) A fat-enriched, glucose-enriched diet markedly attenuates adiponectin mRNA levels in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Clin Sci (Lond) 105:403–408
Ota H, Furuhashi M, Ishimura S, Koyama M, Okazaki Y, Mita T, Fuseya T, Yamashita T, Tanaka M, Yoshida H, Shimamoto K, Miura T (2012) Elevation of fatty acid-binding protein 4 is predisposed by family history of hypertension and contributes to blood pressure elevation. Am J Hypertens 25:1124–1130
Palou M, Priego T, Sanchez J, Rodriguez AM, Palou A, Pico C (2009) Gene expression patterns in visceral and subcutaneous adipose depots in rats are linked to their morphologic features. Cell Physiol Biochem 24:547–556
Papa PC, Seraphim PM, Machado UF (1997) Loss of weight restores GLUT 4 content in insulin-sensitive tissues of monosodium glutamate-treated obese mice. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 21:1065–1070
Paulsen SJ, Jelsing J, Madsen AN, Hansen G, Lykkegaard K, Larsen LK, Larsen PJ, Levin BE, Vrang N (2010) Characterization of beta-cell mass and insulin resistance in diet-induced obese and diet-resistant rats. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18:266–273
Pou KM, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Vasan RS, Maurovich-Horvat P, Larson MG, Keaney JF Jr, Meigs JB, Lipinska I, Kathiresan S, Murabito JM, O'Donnell CJ, Benjamin EJ, Fox CS (2007) Visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue volumes are cross-sectionally related to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 116:1234–1241
Queipo-Ortuno MI, Escote X, Ceperuelo-Mallafre V, Garrido-Sanchez L, Miranda M, Clemente-Postigo M, Perez-Perez R, Peral B, Cardona F, Fernandez-Real JM, Tinahones FJ, Vendrell J (2012) FABP4 dynamics in obesity: discrepancies in adipose tissue and liver expression regarding circulating plasma levels. PLoS One 7:e48605
Rajala MW, Scherer PE (2003) Minireview: the adipocyte—at the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology 144:3765–3773
Ravussin E, Smith SR (2002) Increased fat intake, impaired fat oxidation, and failure of fat cell proliferation result in ectopic fat storage, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 967:363–378
Reseland JE, Haugen F, Hollung K, Solvoll K, Halvorsen B, Brude IR, Nenseter MS, Christiansen EN, Drevon CA (2001) Reduction of leptin gene expression by dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Lipid Res 42:743–750
Riccardi G, Giacco R, Rivellese AA (2004) Dietary fat, insulin sensitivity and the metabolic syndrome. Clin Nutr 23:447–456
Rodriguez A, Catalan V, Becerril S, Gil MJ, Mugueta C, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Fruhbeck G (2008) Impaired adiponectin-AMPK signalling in insulin-sensitive tissues of hypertensive rats. Life Sci 83:540–549
Ryo M, Nakamura T, Kihara S, Kumada M, Shibazaki S, Takahashi M, Nagai M, Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T (2004) Adiponectin as a biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. Circ J 68:975–981
Sampey BP, Vanhoose AM, Winfield HM, Freemerman AJ, Muehlbauer MJ, Fueger PT, Newgard CB, Makowski L (2011) Cafeteria diet is a robust model of human metabolic syndrome with liver and adipose inflammation: comparison to high-fat diet. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19:1109–1117
Seino Y, Yamamoto T, Koh G (1992) Insulin and glucose transporter gene expression in obesity and diabetes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 200:210–213
Semple RK, Halberg NH, Burling K, Soos MA, Schraw T, Luan J, Cochran EK, Dunger DB, Wareham NJ, Scherer PE, Gorden P, O'Rahilly S (2007) Paradoxical elevation of high-molecular weight adiponectin in acquired extreme insulin resistance due to insulin receptor antibodies. Diabetes 56:1712–1717
Seraphim PM, Nunes MT, Machado UF (2001) GLUT4 protein expression in obese and lean 12-month-old rats: insights from different types of data analysis. Braz J Med Biol Res 34:1353–1362
Sevilla L, Guma A, Enrique-Tarancon G, Mora S, Munoz P, Palacin M, Testar X, Zorzano A (1997) Chronic high-fat feeding and middle-aging reduce in an additive fashion Glut4 expression in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 235:89–93
Trayhurn P, Wood IS (2004) Adipokines: inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr 92:347–355
Ukropec J, Penesova A, Skopkova M, Pura M, Vlcek M, Radikova Z, Imrich R, Ukropcova B, Tajtakova M, Koska J, Zorad S, Belan V, Vanuga P, Payer J, Eckel J, Klimes I, Gasperikova D (2008) Adipokine protein expression pattern in growth hormone deficiency predisposes to the increased fat cell size and the whole body metabolic derangements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:2255–2262
Van Heek M, Compton DS, France CF, Tedesco RP, Fawzi AB, Graziano MP, Sybertz EJ, Strader CD, Davis HR Jr (1997) Diet-induced obese mice develop peripheral, but not central, resistance to leptin. J Clin Invest 99:385–390
Woods SC, D'Alessio DA, Tso P, Rushing PA, Clegg DJ, Benoit SC, Gotoh K, Liu M, Seeley RJ (2004) Consumption of a high-fat diet alters the homeostatic regulation of energy balance. Physiol Behav 83:573–578
Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Rushing PA, D'Alessio D, Tso P (2003) A controlled high-fat diet induces an obese syndrome in rats. J Nutr 133:1081–1087
Xu A, Wang Y, Xu JY, Stejskal D, Tam S, Zhang J, Wat NM, Wong WK, Lam KS (2006) Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein is a plasma biomarker closely associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Clin Chem 52:405–413
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 112:1821–1830
Yang ZH, Miyahara H, Takeo J, Katayama M (2012) Diet high in fat and sucrose induces rapid onset of obesity-related metabolic syndrome partly through rapid response of genes involved in lipogenesis, insulin signalling and inflammation in mice. Diabetol Metab Syndr 4:32
Ye J (2008) Regulation of PPARgamma function by TNF-alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:405–408
Yosten GL, Maric-Bilkan C, Luppi P, Wahren J (2014) Physiological effects and therapeutic potential of proinsulin C-peptide. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 307:E955–E968
Yu R, Kim CS, Kwon BS, Kawada T (2006) Mesenteric adipose tissue-derived monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 plays a crucial role in adipose tissue macrophage migration and activation in obese mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14:1353–1362
Zeyda M, Stulnig TM (2009) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance--a mini-review. Gerontology 55:379–386
Zhang M, Zhu W, Li Y (2014) Small molecule inhibitors of human adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (FABP4). Med Chem 10:339–347
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by European Regional Development Fund Research and Development Grant (ITMS 26240120015). The grant support had no role in the design, analysis, or writing of this article. We wish to thank Dr. Goldstein of ScienceDocs (www.sciencedocs.com/) for the editing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Livia Mikuska and Michaela Vrabcova participated equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikuska, L., Vrabcova, M., Tillinger, A. et al. Chronic liquid nutrition intake induces obesity and considerable but reversible metabolic alterations in Wistar rats. J Physiol Biochem 72, 225–243 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0472-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0472-x