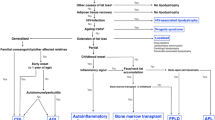
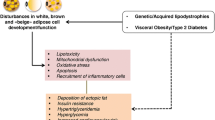
Abstract
Lipodystrophy encompass a group of heterogeneous disorders consisting in marked reduction, absence, and/or the redistribution of adipose tissue. Lipodystrophy is frequently complicated with severe insulin resistance, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and fatty liver. Anatomically, lipodystrophies can be partial or generalized. Etiologically, they can be congenital or acquired. Lipodystrophy diagnosis can be challenging, and it has been suggested that partial forms can be easily misdiagnosed as common central obesity with associated metabolic syndrome. Conventional insulin-sensitizing approaches usually fail to fully ameliorate insulin resistance in lipodystrophic patients. Leptin replacement is an approved therapy for the metabolic complications of congenital generalized lipodystrophy. Novel nutritional interventions are promising complementary approaches for treating lipodystrophy metabolic complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal AK, Garg A (2002) A novel heterozygous mutation in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma gene in a patient with familial partial lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:408–411
Andrés V, González JM (2009) Role of A-type lamins in signaling, transcription, and chromatin organization. J Cell Biol 187:945–957
Asilmaz E, Cohen P, Miyazaki M, Dobrzyn P, Ueki K, Fayzikhodjaeva G, Soukas AA, Kahn CR, Ntambi JM, Socci ND, Friedman JM (2004) Site and mechanism of leptin action in a rodent form of congenital lipodystrophy. J Clin Investig 113:414–424
Berardinelli W (1954) An undiagnosed endocrinometabolic syndrome: report of 2 cases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 14:193–204
Cao H, Hegele RA (2000) Nuclear lamin A/C R482Q mutation in Canadian kindreds with Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet 9:109–112
Chong AY, Lupsa BC, Cochran EK, Gorden P (2010) Efficacy of leptin therapy in the different forms of human lipodystrophy. Diabetologia 53:27–35
Colca JR, McDonald WG, Waldon DJ, Leone JW, Lull JM, Bannow CA, Lund ET, Mathews WR (2004) Identification of a novel mitochondrial protein (“mitoNEET”) cross-linked specifically by a thiazolidinedione photoprobe. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 286:E252–E260
Cortés VA, Cautivo KM, Rong S, Garg A, Horton JD, Agarwal AK (2014) Leptin ameliorates insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in Agpat2−/− lipodystrophic mice independent of hepatocyte leptin receptors. J Lipid Res 55:276–288
Cortes VA, Smalley SV, Goldenberg D, Lagos CF, Hodgson MI, Santos JL (2014) Divergent metabolic phenotype between Two sisters with congenital generalized lipodystrophy due to double AGPAT2 homozygous mutations. A clinical, genetic and in silico study. PLoS One 9:e87173
de Medeiros D, Rocha E, Dantas Leite L, de Fatima Paiva Baracho M, Goretti do Nascimento Santos M, de Araujo DM, Cavalcante Franca M, da Silva CA, das Gracas Almeida M, Rezende AA, Marchini JS, Brandao-Neto J (2010) Effect of diet intervention and oral zinc supplementation on metabolic control in Berardinelli-Seip syndrome. Ann Nutr Metab 57:9–17
Decaudain A, Vantyghem MC, Guerci B, Hecart AC, Auclair M, Reznik Y, Narbonne H, Ducluzeau PH, Donadille B, Lebbe C, Bereziat V, Capeau J, Lascols O, Vigouroux C (2007) New metabolic phenotypes in laminopathies: LMNA mutations in patients with severe metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:4835–4844
Domingo P, Gutierrez Mdel M, Gallego-Escuredo JM, Torres F, Mateo GM, Villarroya J, de los Santos I, Domingo JC, Villarroya F, Del Rio L, Estrada V, Giralt M (2014) Effects of switching from stavudine to raltegravir on subcutaneous adipose tissue in HIV-infected patients with HIV/HAART-associated lipodystrophy syndrome (HALS). A clinical and molecular study. PLoS One 9:e89088
Dunnigan MG, Cochrane MA, Kelly A, Scott JW (1974) Familial lipoatrophic diabetes with dominant transmission. A new syndrome. Q J Med 43:33–48
Dutour A, Roll P, Gaborit B, Courrier S, Alessi MC, Tregouet DA, Angelis F, Robaglia-Schlupp A, Lesavre N, Cau P, Levy N, Badens C, Morange PE (2011) High prevalence of laminopathies among patients with metabolic syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 20:3779–3786
Ebihara K, Kusakabe T, Hirata M, Masuzaki H, Miyanaga F, Kobayashi N, Tanaka T, Chusho H, Miyazawa T, Hayashi T, Hosoda K, Ogawa Y, DePaoli AM, Fukushima M, Nakao K (2007) Efficacy and safety of leptin-replacement therapy and possible mechanisms of leptin actions in patients with generalized lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:532–541
Gandotra S, Le Dour C, Bottomley W, Cervera P, Giral P, Reznik Y, Charpentier G, Auclair M, Delepine M, Barroso I, Semple RK, Lathrop M, Lascols O, Capeau J, O'Rahilly S, Magre J, Savage DB, Vigouroux C (2011) Perilipin deficiency and autosomal dominant partial lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med 364:740–748
Garg A (2011) Lipodystrophies: genetic and acquired body fat disorders. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:3313–3325
Goldenberg D, Santos JL, Hodgson MI, Cortes VA (2014) Novel physiological and therapeutic implications of leptin. Rev Med Chil 142:738–747
Halberg N, Wernstedt-Asterholm I, Scherer PE (2008) The adipocyte as an endocrine cell. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 37:753
Herbst KL, Tannock LR, Deeb SS, Purnell JQ, Brunzell JD, Chait A (2003) Kobberling type of familial partial lipodystrophy: an underrecognized syndrome. Diabetes Care 26:1819–1824
Ishii J, Abe M, Kubo M, Sumimoto T, Hamada M, Hiwada K, Kokubu T, Osawa G (1989) Total lipodystrophy with heart failure and renal failure: report of a case. Jpn J Med 28:534–537
Javor ED, Cochran EK, Musso C, Young JR, Depaoli AM, Gorden P (2005) Long-term efficacy of leptin replacement in patients with generalized lipodystrophy. Diabetes 54:1994–2002
Javor ED, Moran SA, Young JR, Cochran EK, DePaoli AM, Oral EA, Turman MA, Blackett PR, Savage DB, O'Rahilly S, Balow JE, Gorden P (2004) Proteinuric nephropathy in acquired and congenital generalized lipodystrophy: baseline characteristics and course during recombinant leptin therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3199–3207
Khalife WI, Mourtada MC, Khalil J (2008) Dilated cardiomyopathy and myocardial infarction secondary to congenital generalized lipodystrophy. Tex Heart Inst J 35:196–199
Kobberling J, Willms B, Kattermann R, Creutzfeldt W (1975) Lipodystrophy of the extremities. A dominantly inherited syndrome associated with lipatrophic diabetes. Humangenetik 29:111–120
Levy M, Thaiss CA, Katz MN, Suez J, Elinav E (2014) Inflammasomes and the microbiota-partners in the preservation of mucosal homeostasis. Semin Immunopathol 36:261–274
Maguire M, Lungu A, Gorden P, Cochran E, Stratton P (2012) Pregnancy in a woman with congenital generalized lipodystrophy: leptin’s vital role in reproduction. Obstet Gynecol 119:452–455
McDuffie JR, Riggs PA, Calis KA, Freedman RJ, Oral EA, DePaoli AM, Yanovski JA (2004) Effects of exogenous leptin on satiety and satiation in patients with lipodystrophy and leptin insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:4258–4263
McNally M, Mannon RB, Javor ED, Swanson SJ, Hale DA, Gorden P, Kirk AD (2004) Successful renal transplantation in a patient with congenital generalized lipodystrophy: a case report. Am J Transplant 4:447–449
Minokoshi Y, Kim YB, Peroni OD, Fryer LG, Muller C, Carling D, Kahn BB (2002) Leptin stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 415:339–343
Misra A, Garg A (2003) Clinical features and metabolic derangements in acquired generalized lipodystrophy: case reports and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 82:129–146
Misra A, Peethambaram A, Garg A (2004) Clinical features and metabolic and autoimmune derangements in acquired partial lipodystrophy: report of 35 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 83:18–34
Miyamoto L, Ebihara K, Kusakabe T, Aotani D, Yamamoto-Kataoka S, Sakai T, Aizawa-Abe M, Yamamoto Y, Fujikura J, Hayashi T, Hosoda K, Nakao K (2012) Leptin activates hepatic 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase through sympathetic nervous system and α1-adrenergic receptor: A potential mechanism for improvement of fatty liver in lipodystrophy by leptin. J Biol Chem 287:40441–40447
Montenegro RM Jr, Montenegro AP, Fernandes MI, de Moraes RR, Elias J Jr, Gouveia LM, Muglia VF, Foss MC, Moreira AC, Martinelli CE Jr (2002) Triglyceride-induced diabetes mellitus in congenital generalized lipodystrophy. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 15:441–447
Musso C, Javor E, Cochran E, Balow JE, Gorden P (2006) Spectrum of renal diseases associated with extreme forms of insulin resistance. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:616–622
Naska A, Trichopoulou A (2014) Back to the future: the Mediterranean diet paradigm. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 24:216–219
Oral EA, Simha V, Ruiz E, Andewelt A, Premkumar A, Snell P, Wagner AJ, DePaoli AM, Reitman ML, Taylor SI, Gorden P, Garg A (2002) Leptin-replacement therapy for lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med 346:570–578
Paik JH, Kollipara R, Chu G, Ji H, Xiao Y, Ding Z, Miao L, Tothova Z, Horner JW, Carrasco DR, Jiang S, Gilliland DG, Chin L, Wong WH, Castrillon DH, DePinho RA (2007) FoxOs are lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell 128:309–323
Petersen KF, Oral EA, Dufour S, Befroy D, Ariyan C, Yu C, Cline GW, DePaoli AM, Taylor SI, Gorden P, Shulman GI (2002) Leptin reverses insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in patients with severe lipodystrophy. J Clin Invest 109:1345–1350
Rother KI, Brown RJ (2013) Novel forms of lipodystrophy: why should we care? Diabetes Care 36:2142–2145
Saito I, Saruta T, Iyori S, Sakaguchi H (1977) The renal lesion associated with total lipodystrophy. J Am Geriatr Soc 25:175–178
Seip M (1959) Lipodystrophy and gigantism with associated endocrine manifestations. A new diencephalic syndrome? Acta Paediatr 48:555–574
Shastry S, Delgado MR, Dirik E, Turkmen M, Agarwal AK, Garg A (2010) Congenital generalized lipodystrophy, type 4 (CGL4) associated with myopathy due to novel PTRF mutations. Am J Med Genet Part A 152A:2245–2253
Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Ikemoto S, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1999) Leptin reverses insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in mice with congenital lipodystrophy. Nature 401:73–76
Simha V, Rao S, Garg A (2008) Prolonged thiazolidinedione therapy does not reverse fat loss in patients with familial partial lipodystrophy, Dunnigan variety. Diabetes Obes Metab 10:1275–1276
Simha V, Szczepaniak LS, Wagner AJ, DePaoli AM, Garg A (2003) Effect of leptin replacement on intrahepatic and intramyocellular lipid content in patients with generalized lipodystrophy. Diabetes Care 26:30–35
Strickland LR, Guo F, Lok K, Garvey WT (2013) Type 2 diabetes with partial lipodystrophy of the limbs: a new lipodystrophy phenotype. Diabetes Care 36:2247–2253
Subramanyam L, Simha V, Garg A (2010) Overlapping syndrome with familial partial lipodystrophy, Dunnigan variety and cardiomyopathy due to amino-terminal heterozygous missense lamin A/C mutations. Clin Genet 78:66–73
Tam CS, Lecoultre V, Ravussin E (2012) Brown adipose tissue: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Circulation 125:2782–2791
Tsiodras S, Poulia K-A, Yannakoulia M, Chimienti SN, Wadhwa S, Karchmer AW, Mantzoros CS (2009) Adherence to Mediterranean diet is favorably associated with metabolic parameters in HIV-positive patients with the highly active antiretroviral therapy-induced metabolic syndrome and lipodystrophy. Metabolism 58:854–859
Turčinov D, Stanley C, Rutherford G, Novotny T, Begovac J (2009) Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of body-shape changes in Croatian patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy. Eur J Epidemiol 24:267–274
Unger RH, Scherer PE (2010) Gluttony, sloth and the metabolic syndrome: a roadmap to lipotoxicity. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:345–352
Ursich MJ, Fukui RT, Galvao MS, Marcondes JA, Santomauro AT, Silva ME, Rocha DM, Wajchenberg BL (1997) Insulin resistance in limb and trunk partial lipodystrophy (type 2 Kobberling-Dunnigan syndrome). Metabolism 46:159–163
Villarroya F, Domingo P, Giralt M (2005) Lipodystrophy associated with highly active anti-retroviral therapy for HIV infection: the adipocyte as a target of anti-retroviral-induced mitochondrial toxicity. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:88–93
Visser ME, Kropman E, Kranendonk ME, Koppen A, Hamers N, Stroes ES, Kalkhoven E, Monajemi H (2011) Characterisation of non-obese diabetic patients with marked insulin resistance identifies a novel familial partial lipodystrophy-associated PPAR gamma mutation (Y151C). Diabetologia 54:1639–1644
Weir-Mitchell S (1885) Singular case of absence of adipose matter in upper half of the body. Am J Med Sci 90:105–106
Yano M, Yamamoto T, Nishimura N, Gotoh T, Watanabe K, Ikeda K, Garan Y, Taguchi R, Node K, Okazaki T, Oike Y (2013) Increased oxidative stress impairs adipose tissue function in sphingomyelin synthase 1 null mice. PLoS One 8:e61380
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortés, V.A., Fernández-Galilea, M. Lipodystrophies: adipose tissue disorders with severe metabolic implications. J Physiol Biochem 71, 471–478 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0404-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0404-1