Abstract
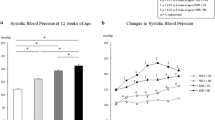
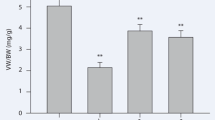
Experimental and clinical evidences suggest that apelin and its receptor APJ are involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular complications. However, the role of apelin/APJ in hypertension is not sufficiently understood. Because chronic kidney diseases lead to hypertension and cardiac failure, we investigated the changes in apelin receptor gene expression in the myocardium and aorta of rat models of kidney disease hypertension. Two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) hypertension was produced by placing a clip around the renal artery. Four and 16 weeks later, blood pressure, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), serum apelin, and angiotensin II were measured. The messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein of APJ were determined by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blotting. Chronic hypertensive rats had approximately 10 times higher LVEDP (P < 0.001). 2K1C decreased serum apelin from 220 ± 11 to 170 ± 10 pg/mL in 16 weeks (P < 0.05). The mRNA expression of APJ significantly decreased in the heart and aorta at 4 weeks. At 16 weeks, the reduction was not significant in the heart but was significant in the aorta. At 4 weeks, the expression of the APJ protein significantly decreased in the heart but not in the aorta. At 16 weeks, APJ protein was significantly decreased only in the aorta. Reduction of serum apelin and downregulation of apelin receptors in both the heart and aorta may play a role in the pathophysiology of hypertension and cardiac failure in 2K1C hypertensive rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnal JF, el Amrani AI, Chatellier G, Ménard J, Michel JB (1993) Cardiac weight in hypertension induced by nitric oxide synthase blockade. Hypertension 22:380–387
Ashley EA, Powers J, Chen M et al (2005) The endogenous peptide apelin potently improves cardiac contractility and reduces cardiac loading in vivo. Cardiovasc Res 65:73–82
Ashley E, Chun HJ, Quertermous T (2006) Opposing cardiovascular roles for the angiotensin and apelin signaling pathways. J Mol Cell Cardiol 41:778–781
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JA, Struhl K (2002) Short protocols in molecular biology. USA Wiley. doi:10.1002/0471140856.txa03as00
Badyal DK, Lata H, Dadhich AP (2003) Animal models of hypertension and effect of drugs. Indian J Pharmacol 35:349–362
Barnes G, Japp AG, Newby DE (2010) Translational promise of the apelin-APJ system. Heart 96(13):1011–1016
Chandrasekaran B, Dar O, McDonagh T (2008) The role of apelin in cardiovascular function and heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 10:725–732
Chun HJ, Ali ZA, Kojima JJ et al (2008) Apelin signaling antagonizes Ang II effects in mouse models of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 118:3343–3354
Dai T, Ramirez-Correa G, Gao WD (2006) Apelin increases contractility in failing cardiac muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 553:222–228
De Falco M, De Luca L, Onori N, Cavallotti I, Artigiano F, Esposito V, De Luca B, Laforgia V, Groeger AM, De Luca A (2002) Apelin expression in normal human tissues. In Vivo 16(5):333–336
De Mota N, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, El Messari S et al (2004) Apelin a potent diuretic neuropeptide counteracting vasopressin actions through inhibition of vasopressin neuron activity and vasopressin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10464–10469
Fukushima H, Kobayashi N, Takeshima H, Koguchi W, Ishimitsu T (2010) Effects of olmesartan on Apelin/APJ and Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway in Dahl rats with end-stage heart failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 55(1):83–88
Goldblatt H, Lynch J, Hanzal RF, Summerville WW (1934) Studies on experimental hypertension: the production of persistent elevation of systolic blood pressure by means of renal ischemia. J Exp Med 59(3):347–379
Hashimoto T, Kihara M, Imai N et al (2007) Requirement of apelin-apelin receptor system for oxidative stress-linked atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol 171:1705–1712
Ishida J, Hashimoto T, Hashimoto Y, Nishiwaki S, Iguchi T, Harada S, Sugaya T, Matsuzaki H, Yamamoto R, Shiota N, Okunishi H, Kihara M, Umemura S, Sugiyama F, Yagami K, Kasuya Y, Mochizuki N, Fukamizu A (2004) Regulatory roles for APJ, a seven-transmembrane receptor related to angiotensin-type 1 receptor in blood pressure in vivo. J Biol Chem 279(25):26274–26279
Iwanaga Y, Kihara Y, Takenaka H, Kita T (2006) Down-regulation of cardiac apelin system in hypertrophied and failing hearts: possible role of angiotensin II-angiotensin type 1 receptor system. J Mol Cell Cardiol 41(5):798–806
Kannel WB (1996) Blood pressure as a cardiovascular risk factor: prevention and treatment. J Am Med Assoc 275:1571–1576
Kazemi-Bajestani SMR, Patel VB, Wang W, Oudit GY (2012) Targeting the ACE2 and apelin pathways are novel therapies for heart failure: opportunities and challenges. Cardiol Res Pract. doi:10.1155/2012/823193
Ladeiras-Lopes R, Ferreira-Martins J, Leite-Moreira AF (2008) The apelinergic system: the role played in human physiology and pathology and potential therapeutic applications. Arq Bras Cardiol 90:343–349
Levy D, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Kannel WB, Ho KK (1996) The progression from hypertension to congestive heart failure. J Am Med Assoc 275:1557–1562
Losano GA (2005) On the cardiovascular activity of apelin. Cardiovasc Res 65:8–9
Marone M, Mozzetti S, Ritis DD, Pierelli L, Scambia G (2001) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis to assess the expression levels of multiple transcripts from the same sample. Biol Proced Online 3:19–25
Martinez-Maldonado M (1991) Pathophysiology of renovascular hypertension. Hypertension 17:707–719
Mitchell BM, Wallerath T, Forstermann U (2007) Animal models of hypertension. Methods Mol Med 139:105–111
Najafipour H, Ferrell WR (1993) Sympathetic innervation and β-adrenoceptor profile of blood vessels in the posterior region of the rabbit knee joint. Exp Physiol 78:625–637
Najafipour H, SoltaniHekmat A, Nekooian AA, Esmaeli-Mahani S (2012) Apelin receptor expression in ischemic and non-ischemic kidneys and cardiovascular responses to apelin in chronic two‐kidney–one‐clip hypertension in rats. Regul Pept 178:43–50
O’Carroll AM, Selby TL, Palkovits M, Lolait SJ (2000) Distribution of mRNA encoding B78/apj, the rat homologue of the human APJ receptor, and its endogenous ligand apelin in brain and peripheral tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492:72–80
O’Carrol AM, Lolait SJ, Harris LE, Pope GR (2013) The apelin receptor APJ: journey from an orphan to a multifaceted regulator of homeostasis. J Endocrinol 219:R13–R35
Sadjadi J, Puttaparthi K, Welborn MB III, Rogers TE, Moe O, Clagett GP, Turnage RH, Levi M, Modrall JG (2002) Up regulation of autocrine-paracrine renin-angiotensin systems in chronic reno-vascular hypertension. J Vasc Surg 36(2):386–392
Soltani Hekmat A, Najafipour H, Nekooian AA, Esmaeli-Mahani S, Javanmardi K (2011) Cardiovascular responses to apelin in two-kidney–one-clip hypertensive rats and its receptor expression in ischemic and non-ischemic kidneys. Regul Pept 172(1–3):62–68
Szokodi I, Tavi P, Földes G, Voutilainen-Myllylä S, Ilves M, Tokola H, Pikkarainen S, Piuhola J, Rysä J, Tóth M, Ruskoaho H (2002) Apelin, the novel endogenous ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, regulates cardiac contractility. Circ Res 91:434–440
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R, Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Fujino M (1998) Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251:471–476
Xiao-Hua Y, Tang Z-B, Liu L-J, Qian H, Tang S-L, Zhang D-W, Tian G-P, Tang C-K (2014) Apelin and its receptor APJ in cardiovascular diseases. Clin Chim Acta 248(1):1–8
Zhang J, Ren CX, Qi YF, Lou LX, Chen L, Zhang LK, Wang X, Tang C (2006) Exercise training promotes expression of apelin and APJ of cardiovascular tissues in spontaneously hypertensive rats 79:1153–9
Zhong JC, Huang DY, Liu GF, Jin HY, Yang YM, Li YF, Song XH, Du K (2005) Effects of all-trans retinoic acid on orphan receptor APJ signaling in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Cardiovasc Res 65(3):743–750
Zile MR, Gaasch WH, Carroll JD, Feldman MD, Aurigemma GP, Schaer GL, Ghali JK, Liebson PR (2001) Heart failure with a normal ejection fraction: is measurement of diastolic function necessary to make the diagnosis of diastolic heart failure? Circulation 104(7):779–782
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Iran National Science Foundation—INSF (Grant No. 92029227) and the Physiology Research Center of Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran. The authors are thankful to Zahra Kordestani and Sara Araghsoltan from the Kerman Physiology Research Center and Zahra Hajializadeh from the Kerman Neuroscience Research Center for their technical support in laboratory tests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Najafipour, H., Vakili, A., Shahouzehi, B. et al. Investigation of changes in apelin receptor mRNA and protein expression in the myocardium and aorta of rats with two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) Goldblatt hypertension. J Physiol Biochem 71, 165–175 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0394-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0394-z