Abstract
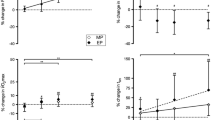
Animal studies have suggested that erythropoietin, besides its well-known hematopoietic effects, can modulate metabolism and prevent fat accumulation. We investigated the effects of repeated injections of recombinant human erythropoietin (EPO) on the balance of substrate oxidation during aerobic exercise in humans. Twelve healthy aerobically trained males received subcutaneously either moderate dose of EPO (50 U/kg, EPO) or saline injections (NaCl 0.9 %, control) three times a week for 4 weeks. Body weight, % fat, maximal aerobic capacity, and substrate utilization during exercise were assessed before and after treatment, while hemoglobin and hematocrit were monitored regularly during the treatment. Carbohydrate and fat oxidation were evaluated via indirect calorimetry, during a submaximal exercise performed at 75 % of the participants’ maximal aerobic capacity (\( \overset{\cdotp }{V}{O}_{2 \max } \)) for 60 min. Results showed that 4 weeks of EPO treatment significantly enhanced fat oxidation (+56 % in EPO versus −9 % in control) during exercise, independent of its effects on hematological parameters or \( \overset{\cdotp }{V}{O}_{2 \max } \). This study shows that EPO can modulate substrate utilization during exercise, leading to enhanced fat utilization and lower use of carbohydrates. This opens new research directions exploring whether systemic EPO levels, in physiological conditions, participate to the modulation of fat oxidation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achten J, Jeukendrup AE (2004) Optimizing fat oxidation through exercise and diet. Nutrition 20:716–727
Borissova AM, Djambazova A, Todorov K, Dakovska L, Tankova T, Kirilov G (1993) Effect of erythropoietin on the metabolic state and peripheral insulin sensitivity in diabetic patients on haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 8:93
Brines M, Grasso G, Fiordaliso F, Sfacteria A, Ghezzi P, Fratelli M, Latini R, Xie Q-W, Smart J, Su-Rick C-J, Pobre E, Diaz D, Gomez D, Hand C, Coleman T, Cerami A (2004) Erythropoietin mediates tissue protection through an erythropoietin and common beta-subunit heteroreceptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:14907–14912
Brooks GA, Mercier J (1994) Balance of carbohydrate and lipid utilization during exercise: the “crossover” concept. J Appl Physiol 76:2253–2261
Christensen B, Nellemann B, Larsen MS, Thams L, Sieljacks P, Vestergaard PF, Bibby BM, Vissing K, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Pedersen SB, Moller N, Nielsen S, Jessen N, Jorgensen JO (2013) Whole body metabolic effects of prolonged endurance training in combination with erythropoietin treatment in humans: a randomized placebo controlled trial. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305:E879–E889
Christensen B, Vendelbo MH, Krusenstjerna-Hafstrøm T, Madsen M, Pedersen SB, Jessen N, Moller N, Jorgensen JOL (2012) Erythropoietin administration acutely stimulates resting energy expenditure in healthy young men. J Appl Physiol 112:1114–1121
Connes P, Bouix D, Py G, Caillaud C, Kippelen P, Brun J-F, Varray A, Prefaut C, Mercier J (2004) Does exercise-induced hypoxemia modify lactate influx into erythrocytes and hemorheological parameters in athletes? J Appl Physiol 97:1053–1058
Connes P, Caillaud C, Mercier J, Bouix D, Casties JF (2004) Injections of recombinant human erythropoietin increases lactate influx into erythrocytes. J Appl Physiol 97:326–332
Connes P, Caillaud C, Simar D, Villard S, Sicart M-T, Audran M (2004) Strengths and weaknesses of established indirect models to detect recombinant human erythropoietin abuse on blood samples collected 48-hr post administration. Haematologica 89:891–892
Connes P, Perrey SP, Varray A, Prefaut C, Caillaud C (2003) Faster oxygen uptake kinetics at the onset of submaximal cycling exercise following 4 weeks recombinant human erythropoietin (r-HuEPO) treatment. Pflugers Arch 447:231–238
Davenport A, King RF, Ironside JW, Will EJ, Davison AM (1993) The effect of treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin on the histological appearance and glycogen content of skeletal muscle in patients with chronic renal failure treated by regular hospital haemodialysis. Nephron 64:89–94
Foskett A, Alnaeeli M, Wang L, Teng R, Noguchi CT (2011) The effects of erythropoietin dose titration during high-fat diet-induced obesity. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:373781
Friedlander AL, Jacobs KA, Fattor JA, Horning MA, Hagobian TA, Bauer TA, Wolfel EE, Brooks GA (2007) Contributions of working muscle to whole body lipid metabolism are altered by exercise intensity and training. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E107–E116
Helge JW, Richter EA, Kiens B (1996) Interaction of training and diet on metabolism and endurance during exercise in man. J Physiol 492(Pt 1):293–306
Hojman P, Brolin C, Gissel H, Brandt C, Zerahn B, Pedersen BK, Gehl J (2009) Erythropoietin over-expression protects against diet-induced obesity in mice through increased fat oxidation in muscles. PLoS One 4:e5894
Juel C, Thomsen JJ, Rentsch RL, Lundby C (2007) Effects of prolonged recombinant human erythropoietin administration on muscle membrane transport systems and metabolic marker enzymes. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:41–44
Katz O, Stuible M, Golishevski N, Lifshitz L, Tremblay ML, Gassmann M, Mittelman M, Neumann D (2010) Erythropoietin treatment leads to reduced blood glucose levels and body mass: insights from murine models. J Endocrinol 205:87–95
Khedr E, El-Sharkawy M, Abdulwahab S, Eldin EN, Ali M, Youssif A, Ahmed B (2009) Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin on insulin resistance in hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int 13:340–346
Lundby C, Hellsten Y, Jensen MBF, Munch AS, Pilegaard H (2008) Erythropoietin receptor in human skeletal muscle and the effects of acute and long-term injections with recombinant human erythropoietin on the skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 104:1154–1160
Mak RH (1996) Correction of anemia by erythropoietin reverses insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia in uremia. Am J Physiol 270:F839–F844
Mak RH (1998) Metabolic effects of erythropoietin in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 12:660–665
Martin WH, Dalsky GP, Hurley BF, Matthews DE, Bier DM, Hagberg JM, Rogers MA, King DS, Holloszy JO (1993) Effect of endurance training on plasma free fatty acid turnover and oxidation during exercise. Am J Physiol 265:E708–E714
Millet GP, Candau RB, Barbier B, Busso T, Rouillon JD, Chatard JC (2002) Modelling the transfers of training effects on performance in elite triathletes. Int J Sports Med 23:55–63
Peronnet F, Massicotte D (1991) Table of nonprotein respiratory quotient: an update. Can J Sport Sci 16:23–29
Phillips SM, Green HJ, Tarnopolsky MA, Heigenhauser G, Hill RE, Grant SM (1996) Effects of training duration on substrate turnover and oxidation during exercise. J Appl Physiol 81:2182–2191
Romijn JA, Coyle EF, Hibbert J, Wolfe RR (1992) Comparison of indirect calorimetry and a new breath 13C/12C ratio method during strenuous exercise. Am J Physiol 263:E64–E71
Rundqvist H, Rullman E, Sundberg CJ, Fischer H, Eisleitner K, Ståhlberg M, Sundblad P, Jansson E, Gustafsson T (2009) Activation of the erythropoietin receptor in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Endocrinol 161:427–434
Shuai H, Zhang J, Zhang J, Xie J, Zhang M, Yu Y, Zhang L (2011) Erythropoietin protects pancreatic β-cell line NIT-1 cells against cytokine-induced apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling. Endocr Res 36:25–34
Teng R, Gavrilova O, Suzuki N, Chanturiya T, Schimel D, Hugendubler L, Mammen S, Yver DR, Cushman SW, Mueller E, Yamamoto M, Hsu LL, Noguchi CT (2011) Disrupted erythropoietin signalling promotes obesity and alters hypothalamus proopiomelanocortin production. Nat Commun 2:520
Thomsen JJ, Rentsch RL, Robach P, Calbet JAL, Boushel R, Rasmussen P, Juel C, Lundby C (2007) Prolonged administration of recombinant human erythropoietin increases submaximal performance more than maximal aerobic capacity. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:481–486
Tuzcu A, Bahceci M, Yilmaz E, Bahceci S, Tuzcu S (2004) The comparison of insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients treated with and without recombinant human erythropoietin. Horm Metab Res 36:716–720
van Loon LJ (2004) Use of intramuscular triacylglycerol as a substrate source during exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 97:1170–1187
Xu B, G-h D, Liu H, Wang Y-q W, H-w JH (2005) Recombinant human erythropoietin pretreatment attenuates myocardial infarct size: a possible mechanism involves heat shock protein 70 and attenuation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Ann Clin Lab Sci 35:161–168
Yeo WK, Carey AL, Burke L, Spriet LL, Hawley JA (2011) Fat adaptation in well-trained athletes: effects on cell metabolism. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 36:12–22
Acknowledgments
The study has been conducted in the Clinical Physiology Department, Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire, Montpellier, France. The authors thank Ray Patton from the University of Sydney for his contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caillaud, C., Connes, P., Ben Saad, H. et al. Erythropoietin enhances whole body lipid oxidation during prolonged exercise in humans. J Physiol Biochem 71, 9–16 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0374-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0374-8