Abstract
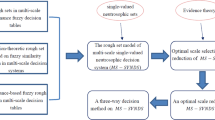
A simplified neutrosophic uncertain linguistic set that integrates quantitative and qualitative evaluation can serve as an extension of both an uncertain linguistic variable and a simplified neutrosophic set. It can describe the real preferences of decision-makers and reflect their uncertainty, incompleteness and inconsistency. This paper focuses on multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problems in which the criteria occupy different priority levels and the criteria values take the form of simplified neutrosophic uncertain linguistic elements. Having reviewed the relevant literatures, this paper develops some generalized simplified neutrosophic uncertain linguistic prioritized weighted aggregation operators and applies them to solve MCDM problems. Finally, an illustrative example is given, and two cases of comparison analysis are conducted with other representative methods to demonstrate the effectiveness and feasibility of the developed approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Mardani A, Jusoh A, Zavadskas EK (2015) Fuzzy multiple criteria decision-making techniques and applications—two decades review from 1994 to 2014. Expert Syst Appl 42(8):4126–4148
Wang XZ, Xing HJ, Li Y, Hua Q, Dong CR, Pedrycz W (2015) A study on relationship between generalization abilities and fuzziness of base classifiers in ensemble learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(5):1638–1654
Wang XZ, Ashfaq RAR, Fu AM (2015) Fuzziness based sample categorization for classifier performance improvement. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 29(3):1185–1196
Wang XZ (2015) Uncertainty in learning from big data-editorial. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(5):2329–2330
Ashfaq RAR, Wang XZ, Huang JZX, Abbas H, He YL (2016) Fuzziness based semi-supervised learning approach for intrusion detection system. Inf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.04.019
He YL, Wang XZ, Huang JZ (2016) Fuzzy nonlinear regression analysis using a random weight network. Inf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.037
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Yue ZL (2014) TOPSIS-based group decision-making methodology in intuitionistic fuzzy setting. Inf Sci 277:141–153
Wang CH, Wang J (2015) A multi-criteria decision-making method based on triangular intuitionistic fuzzy preference information. Intell Autom Soft Comput. doi:10.1080/10798587.2015.1095418
Chen SM, Cheng SH, Chiou CH (2016) Fuzzy multiattribute group decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets and evidential reasoning methodology. Inf Fusion 27:215–227
Martínez L, Ruan D, Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Wang PP (2009) Linguistic decision making: tools and applications. Inf Sci 179(14):2297–2298
Liu PD, Wang YM (2014) Multiple attribute group decision making methods based on intuitionistic linguistic power generalized aggregation operators. Appl Soft Comput 17:90–104
Tian ZP, Wang J, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2015) Multi-criteria decision-making approach based on gray linguistic weighted Bonferroni mean operator. Int Trans Oper Res. doi:10.1111/itor.12220
Zhou H, Wang JQ, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2016) Linguistic hesitant fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making method based on evidential reasoning. Int J Syst Sci 47(2):314–327
Tian ZP, Wang J, Wang JQ, Zhang HY (2016) A likelihood-based qualitative flexible approach with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Cogn Comput. doi:10.1007/s12559-016-9400-1
Chen TY, Chang CH, Lu JFR (2013) The extended QUALIFLEX method for multiple criteria decision analysis based on interval type-2 fuzzy sets and applications to medical decision making. Eur J Oper Res 226(3):615–625
Wang J, Wang JQ, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2016) Multi-criteria group decision making approach based on 2-tuple linguistic aggregation operators with multi-hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Int J Fuzzy Syst 18(1):81–97
Rodríguez RM, Martínez L (2013) An analysis of symbolic linguistic computing models in decision making. Int J Gen Syst 42(1):121–136
Xu ZS (2006) Induced uncertain linguistic OWA operators applied to group decision making. Inf Fusion 7:231–238
Xu ZS (2009) An interactive approach to multiple attribute group decision making with multigranular uncertain linguistic information. Group Decis Negot 18(2):119–145
Liu PD (2013) Some geometric aggregation operators based on interval intuitionistic uncertain linguistic variables and their application to group decision making. Appl Math Model 37(4):2430–2444
Li QX, Zhao XF, Wei GW (2014) Model for software quality evaluation with hesitant fuzzy uncertain linguistic information. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26(6):2639–2647
Smarandache F (1999) A unifying field in logics. Neutrosophy: neutrosophic probability, set and logic. American Research Press, Rehoboth
Wang HB, Smarandache F, Zhang YQ, Sunderraman R (2010) Single valued neutrosophic sets. Multispace Multistruct 4:410–413
Wang HB, Smarandache F, Zhang YQ, Sunderraman R (2005) Interval neutrosophic sets and logic: theory and applications in computing. Hexis, Phoenix
Broumi S, Deli I, Smarandache F (2015) N-valued interval neutrosophic sets and their application in medical diagnosis. Crit Rev Center Math Uncertain Creighton Univ USA 10:46–69
Smarandache F (2013) N-valued refined neutrosophic logic and its applications in physics. Progr Phys 4:143–146
Broumi S, Smarandache F, Maji PK (2014) Intuitionistic neutrosphic soft set over rings. Math Stat 2(3):120–126
Deli I (2015) NPN-soft sets theory and applications. Ann Fuzzy Math Inf 10(6):847–862
Deli I, Broumi S (2015) Neutrosophic soft matrices and NSM-decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(5):2233–2241
Deli I (2015) NPN-soft sets theory and applications. Ann Fuzzy Math Inf 10(6):847–862
Broumi S, Smarandache F (2015) Interval-valued neutrosophic soft rough set. Int J Comput Math. doi:10.1155/2015/232919
Deli I (2015) Interval-valued neutrosophic soft sets and its decision making. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-015-0461-3
Broumi S, Talea M, Bakali A, Smarandache F (2016) Single valued neutrosophic graphs. J N Theory 10:86–101
Broumi S, Talea M, Bakali A, Smarandache F (2016) On bipolar single valued neutrosophic graphs. J N Theory 11:84–102
Broumi S, Smarandache F, Talea M, Bakali A (2016) An introduction to bipolar single valued neutrosophic graph theory. Appl Mech Mater 841:184–191
Broumi S, Talea M, Bakali A, Smarandache F (2016) Interval valued neutrosophic graphs. SISOM Conference
Broumi S, Talea M, Smarandache F, Bakali A (2016) Single valued neutrosophic graphs: degree, order and size. FUZZ IEEE Conference, p 8
Liu PD, Chu YC, Li YW, Chen YB (2014) Some generalized neutrosophic number Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to group decision making. Int J Fuzzy Syst 16(2):242–255
Şahin R, Liu PD (2015) Maximizing deviation method for neutrosophic multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-1995-8
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Wang J, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2016) Simplified neutrosophic sets and their applications in multi-criteria group decision-making problems. Int J Syst Sci 47(10):2342–2358
Broumi S, Smarandache F (2014) Correlation coefficient of interval neutrosophic set. Appl Mech Mater 436:511–517
Zhang HY, Ji P, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2015) An improved weighted correlation coefficient based on integrated weight for interval neutrosophic sets and its application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Int J Comput Intell Syst 8(6):1027–1043
Şahin R, Liu PD (2016) Correlation coefficient of single-valued neutrosophic hesitant fuzzy sets and its applications in decision making. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-2163-x
Broumi S, Deli I (2016) Correlation measure for neutrosophic refined sets and its application in medical diagnosis. Palestine J Math 5(1):135–143
Majumdar P, Samant SK (2014) On similarity and entropy of neutrosophic sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26(3):1245–1252
Tian ZP, Zhang HY, Wang J, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2015) Multi-criteria decision-making method based on a cross-entropy with interval neutrosophic sets. Int J Syst Sci. doi:10.1080/00207721.2015.1102359
Şahin R (2015) Cross-entropy measure on interval neutrosophic sets and its applications in multicriteria decision making. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-2131-5
Wu XH, Wang JQ, Peng JJ, Chen XH (2016) Cross-entropy and prioritized aggregation operator with simplified neutrosophic sets and their application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Int J Fuzzy Syst. doi:10.1007/s40815-016-0180-2
Ye J (2015) Improved cosine similarity measures of simplified neutrosophic sets for medical diagnoses. Artif Intell Med 63(3):171–179
Şahin R, Küçük A (2015) Subsethood measure for single valued neutrosophic sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 29(2):525–530
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2014) An outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with simplified neutrosophic sets. Appl Soft Comput 25:336–346
Zhang HY, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2016) An outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with interval-valued neutrosophic sets. Neural Comput Appl 27(3):615–627
Zhang HY, Ji P, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2016) A neutrosophic normal cloud and its application in decision-making. Cogn Comput. doi:10.1007/s12559-016-9394-8
Ye J (2015) An extended TOPSIS method for multiple attribute group decision making based on single valued neutrosophic linguistic numbers. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(1):247–255
Ye J (2014) Some aggregation operators of interval neutrosophic linguistic numbers for multiple attribute decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 27(5):2231–2241
Ma YX, Wang JQ, Jing Wang WuXH (2016) An interval neutrosophic linguistic multi-criteria group decision-making method and its application in selecting medical treatment options. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2203-1
Ye J (2015) Multiple attribute group decision making based on interval neutrosophic uncertain linguistic variables. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-015-0382-1
Broumi S, Ye J, Smarandache F (2015) An extended TOPSIS method for multiple attribute decision making based on interval neutrosophic uncertain linguistic variables. Neutrosophic Sets Syst 8:23–32
Broumi S, Smarandache F (2015) Single valued neutrosophic trapezoid linguistic aggregation operators based multi-attribute decision making. Bull Pure Appl Sci Math Stat 33(2):135–155
Yager RR (2008) Prioritized aggregation operators. Int J Approx Reason 48(1):263–274
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Verdegay JL (1996) A model of consensus in group decision-making under linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets Syst 79(1):73–87
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E (2000) Linguistic decision analysis: steps for solving decision problems under linguistic information. Fuzzy Sets Syst 115(1):67–82
Xu ZS (2006) A note on linguistic hybrid arithmetic averaging operator in multiple attribute decision-making with linguistic information. Group Decis Negot 15(6):593–604
Bao GY, Lian XL, He M, Wang LL (2010) Improved two-tuple linguistic representation model based on new linguistic evaluation scale. Control Decis 25(5):780–784
Kahneman D, Tversky A (1979) Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 47(2):263–291
Ye J (2014) A multicriteria decision-making method using aggregation operators for simplified neutrosophic sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26(5):2459–2466
Tian ZP, Wang J, Wang JQ, Zhang HY (2016) Simplified neutrosophic linguistic multi-criteria group decision-making approach to green product development. Group Decis Negot. doi:10.1007/s10726-016-9479-5
Yager RR (2004) Choquet aggregation using order inducing variables. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 12(1):69–88
Zhou H, Wang JQ, Zhang HY (2016) Multi-criteria decision-making approaches based on distance measures for linguistic hesitant fuzzy sets. J Oper Res Soc. doi:10.1057/jors.2016.41
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions that improved the paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71571193 and 71431006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Zp., Wang, J., Zhang, Hy. et al. Multi-criteria decision-making based on generalized prioritized aggregation operators under simplified neutrosophic uncertain linguistic environment. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 9, 523–539 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0552-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0552-9