Abstract
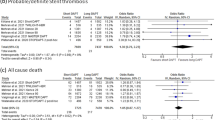
Previously we briefly reported the effect of 1-month dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) for patients with high bleeding risk (HBR) receiving percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in the STOPDAPT-2 trial, but full analysis data have not been available. We conducted post hoc subgroup analysis regarding the effect of very short DAPT for HBR patients in STOPDAPT-2 trial. The primary endpoint was a 1-year composite of cardiovascular (cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, definite stent thrombosis, or stroke) and bleeding (TIMI major/minor bleeding) outcomes. Major secondary endpoints were 1-year cardiovascular composite endpoint and bleeding endpoint. HBR was defined by the academic research consortium (ARC) HBR criteria. Among the 3009 study patients, 1054 (35.0%) were classified as HBR and 1955 (65.0%) were as non-HBR. There were no significant interactions between HBR/non-HBR subgroups and the assigned DAPT group on the primary endpoint (HBR; 3.48% vs. 5.98%, HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.32–1.03, and non-HBR; 1.81% vs. 2.36%, HR 0.78, 95% CI 0.42–1.45; P for interaction = 0.48), the major secondary cardiovascular endpoint (HBR; 3.07% vs. 4.03%, HR 0.77, 95% CI 0.40–1.48, and non-HBR; 1.41% vs. 1.61%, HR 0.89, 95% CI 0.43–1.84; P for interaction = 0.77), and the major secondary bleeding endpoint (HBR; 0.41% vs. 2.71%, HR 0.15, 95% CI 0.03–0.65, and non-HBR; 0.40% vs. 0.85%, HR 0.48, 95% CI 0.14–1.58; P for interaction = 0.22). In conclusion, the effects of 1-month DAPT for the primary and major secondary endpoints were consistent in HBR and non-HBR patients without any significant interactions. The benefit of 1-month DAPT in reducing major bleeding was numerically greater in HBR patients.
Clinical trial registration Short and optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy after everolimus-eluting cobalt–chromium stent-2 [STOPDAPT-2]; NCT02619760.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levine GN, Bates ER, Bittl JA, Brindis RG, Fihn SD, Fleisher LA, et al. 2016 ACC/AHA guideline focused update on duration of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines: an update of the. Circulation. 2016;134:e123–55.
Valgimigli M, Bueno H, Byrne RA, Collet J-P, Costa F, Jeppsson A, et al. 2017 ESC focused update on dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease developed in collaboration with EACTS: the Task Force for dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:213–60.
Urban P, Meredith IT, Abizaid A, Pocock SJ, Carrié D, Naber C, et al. Polymer-free drug-coated coronary stents in patients at high bleeding risk. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2038–47.
Valgimigli M, Patialiakas A, Thury A, McFadden E, Colangelo S, Campo G, et al. Zotarolimus-eluting versus bare-metal stents in uncertain drug-eluting stent candidates. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:805–15.
Varenne O, Cook S, Sideris G, Kedev S, Cuisset T, Carrié D, et al. Drug-eluting stents in elderly patients with coronary artery disease (SENIOR): a randomised single-blind trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10115):41–50.
Watanabe H, Domei T, Morimoto T, Natsuaki M, Shiomi H, Toyota T, et al. Effect of 1-month dual antiplatelet therapy followed by clopidogrel vs 12-month dual antiplatelet therapy on cardiovascular and bleeding events in patients receiving PCI: the STOPDAPT-2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;321:2414–27.
Urban P, Mehran R, Colleran R, Angiolillo DJ, Byrne RA, Capodanno D, et al. Defining high bleeding risk in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2019;140:240–61.
Watanabe H, Domei T, Morimoto T, Natsuaki M, Shiomi H, Toyota T, et al. Very short dual antiplatelet therapy after drug-eluting stent implantation in patients with high bleeding risk: insight from the STOPDAPT-2 trial. Circulation. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.119.043613.
Baber U, Mehran R, Giustino G, Cohen DJ, Henry TD, Sartori S, et al. Coronary thrombosis and major bleeding after PCI with drug-eluting stents risk scores from Paris. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67:2224–34.
Natsuaki M, Morimoto T, Yamaji K, Watanabe H, Yoshikawa Y, Shiomi H, et al. Prediction of thrombotic and bleeding events after percutaneous coronary intervention: CREDO-Kyoto thrombotic and bleeding risk scores. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7:e008708.
Rao AK, Pratt C, Berke A, Jaffe A, Ockene I, Schreiber TL, et al. Thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) trial-Phase I: hemorrhagic manifestations and changes in plasma fibrinogen and the fibrinolytic system in patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and streptokinase. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988;11:1–11.
Mehran R, Rao SV, Bhatt DL, Gibson CM, Caixeta A, Eikelboom J, et al. Standardized bleeding definitions for cardiovascular clinical trials: a consensus report from the bleeding academic research consortium. Circulation. 2011;123:2736–47.
The GUSTO investigators. An international randomized trial comparing four thrombolytic strategies for acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:673–82.
Cutlip DE, Windecker S, Mehran R, Boam A, Cohen DJ, Van Es GA, et al. Clinical end points in coronary stent trials: a case for standardized definitions. Circulation. 2007;115:2344–51.
Kimura T, Morimoto T, Nakagawa Y, Tamura T, Kadota K, Yasumoto H, et al. Antiplatelet therapy and stent thrombosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circulation. 2009;119:987–95.
Kimura T, Morimoto T, Furukawa Y, Nakagawa Y, Kadota K, Iwabuchi M, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of sirolimus-eluting stents versus bare-metal stents in real world clinical practice in Japan. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2011;26:234–45.
Sianos G, Morel M-A, Kappetein AP, Morice M-C, Colombo A, Dawkins K, et al. The SYNTAX Score: an angiographic tool grading the complexity of coronary artery disease. EuroIntervention. 2005;1:219–27.
CAPRIE Steering Committee. A randomised, blinded, trial of clopidogrel versus aspirin in patients at risk of ischaemic events (CAPRIE). Lancet. 1996;348:1329–39.
Capodanno D, Mehran R, Valgimigli M, Baber U, Windecker S, Vranckx P, et al. Aspirin-free strategies in cardiovascular disease and cardioembolic stroke prevention. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15:480–96.
Généreux P, Giustino G, Witzenbichler B, Weisz G, Stuckey TD, Rinaldi MJ, et al. Incidence, predictors, and impact of post-discharge bleeding after percutaneous coronary intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66:1036–45.
Valgimigli M, Costa F, Lokhnygina Y, Clare RM, Wallentin L, Moliterno DJ, et al. Trade-off of myocardial infarction vs. bleeding types on mortality after acute coronary syndrome: lessons from the Thrombin Receptor Antagonist for Clinical Event Reduction in Acute Coronary Syndrome (TRACER) randomized trial. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:804–10.
Taguchi I, Iimuro S, Iwata H, Takashima H, Abe M, Amiya E, et al. High-dose versus low-dose pitavastatin in Japanese patients with stable coronary artery disease (REAL-CAD). Circulation. 2018;137:1997–2009.
LaRosa JC, Grundy SM, Waters DD, Shear C, Barter P, Fruchart J-C, et al. Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1425–35.
Onuma Y, Kimura T, Räber L, Magro M, Girasis C, Van Domburg R, et al. Differences in coronary risk factors, procedural characteristics, mortality and stent thrombosis between two all-comers percutaneous coronary intervention registries from Europe and Japan: a patient-level data analysis of the Bern-Rotterdam and j-Cypher. EuroIntervention. 2015;11:533–40.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the members of Research Institute for Production Development handling a series of large clinical trials and the co-investigators for exaggeratedly enrolling patients, collecting follow-up data, or adjudicating clinical events.
Funding
STOPDAPT-2 was funded by Abbott Vascular Japan. The study sponsor is not involved in the implementation of the study, data collection, event fixation and statistical analysis. However, approval of the study sponsor should be obtained for presentation in scientific meetings and submission of papers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Koichi Nakao has received a speaker honorarium from Sanofi and Daiichi-Sankyo. Kenji Ando has received a speaker honorarium from Japan Lifeline, Medtronic Japan, Terumo, and Biotronik Japan. Kengo Tanabe has received a speaker honorarium from Kaneka Medix. Yuji Ikari received a research grant from Abbott Vascular Japan. Yoshihisa Nakagawa has received a speaker honorarium from Daiichi-Sankyo, Bayer Yakuhin, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Takeshi Kimura acts in an advisory role in Abbott Vascular Japan and received a research grant from Daiichi-Sankyo. Others have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, H., Domei, T., Morimoto, T. et al. Details on the effect of very short dual antiplatelet therapy after drug-eluting stent implantation in patients with high bleeding risk: insight from the STOPDAPT-2 trial. Cardiovasc Interv and Ther 36, 91–103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-020-00651-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-020-00651-9