Abstract
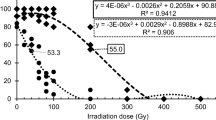
The ionizing radiation methods, including X-rays, gamma rays, and neutrons to create variation is well established and used in major crops. Many seed-propagated crops with homozygous parents such as barley, rice, and tomato are resilant to the higher level of damage to chromosomal DNA during mutation induction, followed by repair. In order to improve oil content and other agronomic traits, we treated Camelina sativa Crantz with diverse levels of gamma ray and neutron beam. Overall, 300 Gy of gamma ray and at 50 Gy of neutron beam treated C. sativa showed better agronomic traits. 400 Gy of gamma rays and 200 Gy of fast neutron treatments increased almost four times more oil content than non-treated seeds. In conclusion, our results provide a rapid and economical means to improve agronomic characters of camelina in breeding programs. This is undoubtedly highly valuable, pre-breeding material especially for high oil content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agegenehu M, Honermeier B. 1997. Effects of seeding rates and nitrogen fertilization on seed yield, seed quality and yield components of false flax (Camelina sativa Crtz.). Die Bodenkultur 8: 15–20
Ahloowalia BS, Maluszynski M. 2001. Induced mutations—A new paradigm in plant breeding. 2001. Euphytica 118: 67–73
Gehringer A, Friedt W, Lühs W, Snowdon RJ. 2006. Genetic mapping of agronomic traits in false flax (Camelina sativa subsp. sativa). Genome 49: 1555–1563
Hutcheon C, Ditt RF, Beilstein M, Comai L, Schroeder J, Goldstein E, Shewmaker CK, Nguyen T, De Rocher J, Kiser J. 2010. Polyploid genome of Camelina sativa revealed by isolation of fatty acid synthesis genes. BMC Plant Biol. 10: 233
Jacobsen E, Schouten HJ. 2007. Cisgenesis strongly improves introgression breeding and induced translocation breeding of plants. Trends Biotechnol. 25:219–223
Jain SM. Mutagenesis in crop improvement under the climate change. 2010. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 15: 88–106
Kramer CY. 1956. Extension of multiple range tests to group means with unequal numbers of replications. Biometrics. 12: 307–10
Li W, Huang L, Gill BS. 2008. Recurrent deletions of puroindoline genes at the grain hardness locus in four independent lineages of polyploid wheat. Plant Physiol. 146: 200–212
Marshall I, Bianchi M. 1983. Micronucleus induction in Vicia faba and Trifolium pratense. Radiobiologia 14: 480–485
Misset MT. 1992. Meiotic abnormalities during microsporogensis and low fertility in prostrate ecotypes of Ulex species (Papilionoideae, Genisteae). Can. J. Bot. 70: 1223–1227
Momiyama M, Koshiba, T, Furukawa K, Kamiya Y, Satô M. 1999. Effects of gamma irradiation on elongation and indole-3-acetic acid level of maize (Zea mays) coleoptiles. Environ. Exp. Bot. 41: 131–143
Stadler LJ. 1929. Chromosome number and the mutation rate in Avena and Triticum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 15: 876–881
Taguchi TN, Tatara A, Eguchi H, Tano S. 1994. Effects of low-dose gamma-irradiation on the root apical meristem of barley. Environ. Mut. Res. Commun. 16: 205–209
Vollmann J, Eynck C. 2015. Camelina as a sustainable oilseed crop: Contributions of plant breeding and genetic engineering. Biotechnol. J. 10: 525–535
Walsh KD, Puttick DM, Hills MJ, Yang RC, Hall LM. 2012. First report of outcrossing rates in camelina [Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz], a potential platform for bioindustrial oils. Can. J. Plant Sci. 92: 681–685
Zaka R, Chenal C, Misset MT. 2004. Effects of low doses of short-term gamma irradiation on growth and development through two generations of Pisum sativum. Sci. Total Environ. 20: 121–129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, Y.S., Silva, R.R., Park, M. et al. Radiation-Induced Breeding in Camelina Sativa. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 22, 17–20 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-018-0249-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-018-0249-0