Abstract
Breast cancer is a major threat to safety and health of women. The breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) have multi-drug resistance to chemotherapy drugs, which leads to chemotherapy failure. We proposed a strategy of delivery of tumor-killing drugs and a resistance reversal agent, to enhance inhibition of BCSCs. Here, schisandrin B (SchB)/AP NPs are constructed using acid-grafted-poly (β-amino ester) (ATRA-g-PBAE, AP) grafted polymer nanoparticle encapsulated SchB, with pH-sensitive release function. This drug delivery system has good pharmacological properties and can increase the SchB release with the decrease of pH. The NPs showed cytotoxic effects in reversing ATRA resistance to BCSCs. Lysosomal escape was achieved when the nanoparticles were taken up by BCSCs. In addition, we found that NPs may reverse MDR by inhibiting the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and affecting the energy supply of drug efflux. This study provides a nanodelivery therapy strategy that reverses BCSCs multidrug resistance (MDR) and demonstrates that it did so by interfering with cancer cell energy metabolism. Therefore, the co-delivery strategy of ATRA and SchB provides a new option for the treatment of breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in women and has become a serious public health problem in the world today. It has been reported that cancer stem cells are the pivotal cause of malignant tumors [1, 2]. BCSCs are the origin of breast cancer, causing tumors to grow or form new tumor focus. BCSCs have more obvious tumorigenic ability than normal breast cancer cells [3]. Therefore, targeting BCSCs has become a critical approach in the fight against breast cancer.
Peptidyl-prodyl cis-trans isomerase 1 (Pin1) is a tumor-specific enzyme [4]. The overexpression of Pin1 in tumor cells was positively correlated with tumor stem cells progression [5]. Clinical studies have found that the expression level of Pinl can affect the occurrence and prognosis of breast cancer. Pin1 is highly expressed in tumor cells, and the expression level in BCSCs is 30 times higher than in common tumor cells [6, 7]. ATRA is a natural derivative of vitamin A. Wei et al. proved that ATRA could kill tumor cells by inhibiting Pin1 through high-throughput screening experiments [8]. Our previous study found that ATRA showed good toxicity in breast cancer cells, but its toxicity to cancer stem cells was too low [9]. Thus, the inhibition of Pin1 alone is not effective against BCSCs.
BCSCs have strong drug resistance due to the “drug pump” effect of high expression of drug-resistant proteins on their surface. Under the action of drug-resistant proteins, drugs entering cells are expelled from cells, and drug resistance occurs [10, 11]. Importantly, BCSCs were often more resistant to drugs than ordinary tumor cells. ATRA showed lower toxicity in tumor stem cells compared to normal tumor cells, which may be an obstacle to drug resistance [12]. For enhancing the effect of ATRA on breast cancer stem cells (Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7)-induced MS cells were used in this study), it is necessary to load MDR reversal agent to reverse resistance.
Currently, the multidrug resistance mechanism of membrane transporters is critical [13]. ABC transporter-mediated MDR of tumor cells mainly uses the hydrolysis of ATP to obtain energy to expel drugs outside the cells. P-gp is the main component of ABC membrane transporter [14]. P-gp uses the hydrolysis of ATP to obtain energy, and expels drugs entering the cell outside the cell [15]. Many natural products can overcome multidrug resistance, such as quercetin and SchB [16]. SchB has been reported to restore drug sensitivity to MCF-7/MDR1 cell lines containing stable P-gp expression [17]. SchB may increase cytoplasmic drug content by inhibiting P-gp function. SchB has a similar chemical structure to P-gp inhibitors [18]. Notably, in addition to tumor cells, P-gp is expressed in other normal tissues. Therefore, introducing nanotechnology to deliver insoluble SchB to BCSCs efficiently is even more necessary.
Nanoparticles are widely used in cancer treatment as delivery systems to deliver drugs to their destination. In cancer treatment, nanoparticles can be designed as drug delivery systems. Based on the EPR effect, nanocarriers deliver anti-cancer drugs precisely to the tumor site, thereby reducing damage to healthy tissue. Moreover, nanoparticles can also be used to improve the solubility and stability of drugs, prolong the half-life of drugs, and thus enhance the therapeutic effect. Importantly, nanoparticles can combine a variety of therapeutic agents in one, to achieve multi-drug synergies. For example, PBEA is a class of pH-sensitive polymer carrier materials [19]. It can be protonated under acidic conditions, resulting in structural changes, resulting in the release of internal drugs. This characteristic is just suitable for the slightly acidic environment of the tumor cell lysosomes (pH 5.5). Although many literatures have realized resistance reversal, few literatures have designed tumor suppressor drug carrier and reversal agent in the same nanodelivery system and realized energy metabolism intervention, especially targeted delivery of multi-drug reversal agent SchB.
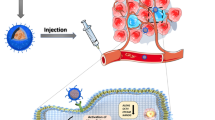
Herein, to reverse BCSCs resistance and enhance the anticancer effect of ATRA, a pH-sensitive polymer loaded with a hydrophobic reversing MDR agent SchB was constructed (Scheme 1). Particularly, the ATRA-g-PBAE was used as a carrier to encapsulate the active molecule SchB to obtain SchB/AP NPs. Passive target delivery of SchB reverses MDR by inhibiting ATPase activity and mitochondrial function affecting P-gp energy supply and transport, which was the novelty of the NPs. The delivery of SchB to reverse BCSCs resistance to ATRA provided a new option for breast cancer treatment. This indicates that SchB/AP NPs have strong application potential in synergistic enhancement of BCSCs inhibition.
Construction of SchB/AP NPs and the mechanism for reversing MDR against BCSCs. The SchB/AP NPs can co-deliver ATRA and SchB into the cells, enabling SchB lysosome escape and responsive release by the pH-sensitive function of the carrier. Importantly, NPs can inhibit the expression of P-gp and weaken the energy metabolism function of cells, ultimately achieving the reversal of MDR.
2 Materials
3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-di- phenytetrazoliumromide (MTT) was from APExBIO Co., Ltd. (Houston, USA). PBS was from BioChannel Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). Cyanine 5.5(Cy5.5) and Coumarin-6 (C6) were from Aladdin Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Lyso-Tracker Green, bicinchoninic acid (BCA), ATPase activity assay kit were from sigma Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Mitochondrial membrane potential JC-1 assay kit was from Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. ATP content activity assay kit was from Grace Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Suzhou, China). FITC-labeled sheep anti-rabbit IgG antibody was from GeneTex Co., Ltd (Beijing, China). P-glycoprotein rabbit antibody was from Zen bioscence (Chengdu, China). Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium F12 (DMEM-F12) was from BDBIO Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China). The cell culture plates were from NEST Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuxi, China). The microwell plates were from CellPro Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China). HAKATA Fetal bovine serum was from Chuanqiu Co., Ltd. (Shanghai China). Human Insulin protein was from ABclonal Technology Co., Ltd. (WuHan, China). The cells culture bottles were from SAINING (Suzhou, China). Cryopreservation was from Sevenbio (Beijing, China). Recombinant human FGFb was from Novoprotein Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
MCF-7 cells (for MS cells formation) were obtained from the BNCC Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Serum-free MS culture medium was prepared by the following: The precise weight of 200 mg bovine serum protein was dissolved in 50 mL DMEM-F12 medium. Then 0.1 mL EGF solution (10 µg/mL), 0.1 mL bFGF solution (10 µg/mL), 0.5 mL antibiotics solution, and 0.5 mL insulin were added. After 0.22 μm filtration membrane, a serum-free medium was obtained.
MCF-7 stem cells (MS cells) were formed in the following way: take MCF-7 cells that have reached the logarithmic growth phase, wash them twice with PBS, and then digest the cells with 2 mL of trypsin. Centrifuge the cells twice, each time throwing away the supernatant before adding serum-free medium. Finally, resuspend the cells in a low-adsorption plate with 4 mL of serum-free MS culture medium. Cells spheroidized at 37 ℃,5% CO2 were observed under a microscope and passaged every 5 days. In our previous experiments, the phenotype of MS cells has been verified by flow cytometry, and the formation of MS cells has been confirmed [18].
3 Method
3.1 The preparation of SchB/AP NPs
ATRA-g-PBAE prodrug polymer was obtained from previous experiments by our research group [9]. PBAE and ATRA-g-PBAE were respectively synthesized by michael and esterification reaction. The EDC·HCl and DMAP were added to the ATRA solution. Then, the PBAE solution was dropped into the mixture and reacted for 48 h. The purification process involved is the use of cold ether to precipitate excess ATRA. Then, to remove the EDC·HCl and DMAP, the fluid was transferred to a dialysis bag for dialysis for 24 h. The final product ATRA-g-PBAE was obtained by vacuum drying. Cy5.5-PBAE was prepared by the same method, only by replacing ATRA with Cy5.5.
SchB/AP NPs were prepared from the solvent volatilization method [20]. Briefly, a certain mass of ATRA-g-PBAE prodrug polymer carrier and SchB (20% carrier mass) were precisely weighed. The organic phase was mixtured by dissolving the carrier and SchB in acetone. According to the experimental design scheme, the organic phases with different carrier concentrations (mg/mL) and the feeding drug (SchB) ratio (%) were prepared. The above organic solution was slowly dripped into 15 mL of 0.5% poloxamer 188 aqueous phase. Then the solution continued stirring at 25 ℃ until the organic solvent evaporated. After filtering through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, the SchB/AP NPs solution with blue opalescent light was obtained. The preparation of C6/AP NPs is the same as the above, only C6 replaced SchB.
3.2 Experimental design of the preparation of the SchB/AP NPs
The factor and level of Central Composite Design Response Surface Model (CCD RSM) were determined according to the preliminary experiment. ATRA-g-PBAE carrier concentration (mg/mL) and the feeding drug (SchB) ratio (%) were set as A and B, respectively. Particle size (Y1) and encapsulation rate (EE) (Y2) were used as response parameters. The NPs were prepared according to the preparation method in Sect. 3.1 for other conditions. Meanwhile, the response surface figure was drawn with the results data, and the optimal scheme was predicted. The experimental design scheme is shown in Table 1.
3.3 The encapsulation efficiency and loading capacity
1 mL of the prepared SchB/AP NPs solution was centrifuged at speed (10,000 rpm) for 60 min. The obtained supernatant was absorbed and methanol was added for demulsification. The solution was further demulsified by an ultrasonic cell crusher. Afterward, the demulsified solution was placed in a 5 mL volumetric bottle and filled with methanol to the scale. The liquid obtained by filtration through a 0.22 μm filter determined the SchB content as Wa. In addition, 1 mL prepared SchB/AP NPs solution was taken for all above operations except centrifugation, and SchB content was determined, denoted as Wb. The centrifugal precipitate above was taken and then its total mass was weighed after vacuum drying, denoted as W. All SchB contents were determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (Shimadzu, 3100, Japan). The EE% and the drug loading capacity (LC)% were computed by the following formula:
3.4 Characterization of the SchB/AP NPs
In order to obtain the appearance of the SchB/AP NPs, the transmission electron microscope (TEM) (JEOL JEM, 4378, Japan) was used to observe the morphology. The specific operation method was as follows: a little SchB/AP NPs solution prepared above was added to the 200-mesh copper net by drops. After 3 min, the excess liquid was absorbed by filter paper. After drying at room temperature, the morphology of the NPs was characterised by TEM.
The particle size and size distribution of SchB/AP NPs were determined by the Marvin particle size analyzer (Marvin, 2900, US). One drop of the NPs solution was added to the size cell. Finally, the average size and particle size distribution were recorded. The same method was used to measure the zeta potential.
3.5 In Vitro SchB release
The optimal preparation of SchB/AP NPs was put into the given dialysis bags (Mw = 3,500). Moreover, the free SchB acted as the control group. Dialysis bags were transferred to 50 mL PBS solution containing 0.5% (m/w) polysorbate 80 at pH 5.5, 6.8, and 7.4. Water bath oscillations at 37 ℃ were used, samples were taken at different times. The sample solution was determined by the concentration of SchB by HPLC. The cumulative release was depicted and the cumulative release curve was plotted in accordance with following formula:
where, Er, Ve, Ci, V0, Cn and mdrug, were the cumulative release of SchB, the displaced volume of PBS, the concentration at the ith sampling (µg/mL), release medium volume (mL), the concentration at the nth sampling (µg/mL) and SchB content in drug-loaded NPs (mg), respectively.
3.6 Serum stability of the SchB/AP NPs
The SchB/AP NPs were placed in serum contained DMEM at 37 ℃ to investigate the stability of the NPs. The mixture was shaken in a shaker, and 1 mL of the sample was aspirated at 0, 6, 12, 36, 24 and 48 h for particle size determination. The particle size was measured according to the particle size determination method in Sect. 3.4.
3.7 The parameter of HPLC
The SchB was measured by HPLC fitted with a Prominence LC-20AD at 220 nm. The experimental result was detected on a Diamonsil C18 column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm). The mobile phase A and B were respectively 15% phosphoric acid aqueous solution and 85% methanol. Moreover, the flow rate was 0.8 mL /min. Measured method of SchB concentration section “3.3 and 3.5” was according to those conditions above.
3.8 In vitro cytotoxicity
In vitro cytotoxicity was detected by MTT. MS cells were seeded in 96 wells at a density of 7 × 103 cells per well and incubated at 37 ℃ for 24 h at 5% CO2 in an incubator. The free solution of the drug was a blank control group. The pharmaceutical solution was taken into certain wells in the experimental group. Cell culture grade 0.05% DMSO was added to the wells to aid dissolution. Each concentration was made three parallel while leaving blank wells. After that, the cell culture plates were placed in the incubator for 48 h. Finally, the absorbance value was detected at 490 nm with a multifunctional microplate reader (JD-SY96A, JingDao, China). The IC50 at which the reversal agent SchB was added to certain wells was denoted as IC50 (A/S). The Reversal Factor (RF) was calculated according to the following formula:
3.9 Cellular uptake of the SchB/AP NPs
To verify the cellular uptake performance of the carriers of the NPs, Cy5.5-g-PBAE NPs were used to replace ATRA-g-PBAE NPs. Besides, to testify the cellular uptake ability of SchB /AP NPs, C6/AP NPs were used instead SchB /AP NPs. The NPs preparation method was referred to the Part 3.1. MS cells were digested and seeded in 6-well cell culture plates at a density of 2.5 × 104. C6/AP and Cy5.5-g-PBAE NPs were diluted in the serum-free medium that were added to the wells and incubated for 0.5, 2 and 4 h, respectively. Pre-chilled PBS was added at the end of the incubation to stop cell uptake. PBS washed the cells twice to remove drug interference and then placed them under a fluorescence microscope (Laika, 5699, Germany) to observe cell uptake. Finally, flow cytometry (Beckman, CytoFLEX, China) was used to determine the intensity of cells fluorescence at different times.
3.10 Lysosome co-localization
Coverslips were placed in 6-well plates, and MS cells were seeded on them at 105 cells/well. After overnight culture, 2 mL Cy5.5-g-PBAE NPs solution was added into each well and incubated for 0.5, 1 and 2 h. Intracellular lysosomes were labeled with 200 µL Lyso-Tracker Green lysosome fluorescent probe. After 30 min of incubation, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and placed under confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) (Olympus, FV3000, Germany) to observe the intracellular drug delivery of MS cells.
3.11 The mechanism of MS cells reversing MDR
3.11.1 Determination of P-gp expression
MS cells with strong growth were incubated for 24 h. After 24 h incubation in the incubator, 2 ml PBS was washed twice. The cells incubated without drug solution were set as the control group, and the cells incubated with different preparation groups were set as the experimental group. After 12 h incubation, centrifuge to collect the cells and wash twice with cold PBS. And the rabbit anti-human P-gp primary antibody was added and incubated at 4 ℃ protected from light. Then the mixture was centrifuged to remove unbound antibodies. Then, the already diluted FITC-labeled sheep anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody was added to the centrifuge tube for staining. After 30 min of incubation at 4 ℃ in the dark, the mixture was centrifuged and discarded the supernatant. The excess fluorescent substance was removed by PBS cleaning, and the expression of P-gp was detected by fluorescent microplate reader. The excitation wavelength is 488 nm and the maximum emission wavelength is 525 nm. It is detected by the FL1 channel of flow cytometry.
3.11.2 Assay of intracellular protein content
The Bicinchoninic acid (BCA) method was to detect the protein concentration of MS cells in preparation for the ATPase activity assay and ATP content. Single-cell suspensions of logarithmically grown MS cells were collected and seeded in cell culture plates. After 24 h of incubation, the cells were rinsed twice with normal saline to prevent contamination of the sample with phosphorus. The solution of three different preparation groups was added into different holes respectively, and the blank medium without drugs was the control group. After 2 h of incubation, MS cells were resuspended in 0.3 mL saline. The cells were disrupted using a cell disruptor and diluted 3-fold with normal saline for assay. The protein concentration of samples was calculated by constructing the protein standard curve.
3.11.3 Measurement of ATPase activity
MS cells of logarithmic growth stage were collected and washed with normal saline 3 times. A drug-free medium was added into the culture hole as the control group. Three different preparation solutions were added to the other groups. The value of Na+-K+-ATPase, Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and T-ATPase were measured respectively. After incubation for 24 h, the supernatant was taken for ATPase activity determination. The absorbance value of 636 nm was measured. To calculate the activity of Na+-K+-ATPase, Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and T-ATPase, the ATPase content was calculated according to the following formula.
Where, the A1, A2, A3, A0 and C0, were determination group absorbance, standard group absorbance, blank group absorbance, control group absorbance and protein concentration of sample to be tested.
3.11.4 Assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm)
MS cells were inoculated into 6-well plates with 5 × 104 cells per well and cultured for 24 h. Then, the solution of three formulations was added. In addition, drug - free medium was added into the culture hole as the control group. After incubation for 2 h, the cells were re-suspended in 500 µL of 10 µg/mL JC-1 working solution and incubated at 37 ℃ for 20 min. Finally, the cells were washed twice with JC-1 staining solution and suspended in 500 µL buffer solution. The values of red fluorescence (λex = 525 nm / λem = 590 nm) and green fluorescence (λex = 490 nm / λem = 530 nm) were observed and determined by fluorescence microplate.
3.11.5 Assay of ATP content
ATP content was determined by ATP colorimetric assay kit. MS cells were cultivated with medium containing blank group and preparation group solutions, then incubated for 2 h. Subsequently, the ATP working solution was added and measured the absorbance value. In the other part of the sample, the protein content of the cells was through BCA method, and the ATP concentration was converted into the form of nmoL/mg protein to eliminate the error caused by the different number of cells per well. The absorbance of the treated samples was measured by the microplate reader. ATP1 was the measured data of the experimental group, and ATP2 was the measured data of the control group. The relative ATP activity is calculated as follows:
3.12 Statistical analyses
The experiment was repeated 3 times and the results are reported as mean ± SD (standard deviation). The experimental design and data processing of CCD-RSM was completed by Design Export 11. The analysis of experimental data was made using GraphPad Prism 11. The Student’ s t-test between 2 groups or more was with ANOVA test when more than 3 groups. Significance at *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 was acceptable.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Optimization result of the SchB/AP NPs
RSM has been widely used in process optimization schemes, including the preparation of nanoparticles. As a means of experimental design, CCD is often used in conjunction with RSM (CCD RSM) to optimize the formulation of NPs preparation. CCD RSM was used to optimize the preparation of SchB /AP NPs. The experimental data were fitted with multiple linear and second-degree polynomial regression, and the results were as follows:
The response surface in Fig. 1 was obtained by fitting the equation. Figure 1a is the change in particle size caused by factors A (carrier concentration) and B (feeding drug ratio), and Fig. 1b is the change of EE caused by factors A and B. It can be seen Fig. 1a that particle size gradually decreases and then increases with the increase of A and B. As shown in Fig. 1b, EE increased first and then decreased with the rise in values of A and B. The reason is that after the concentration of the carrier was too high, the organic phase was opposed to dispersing evenly in the water phase, and agglomeration occurred [21]. As the feeding drug ratio was too high, the carriers could not carry more SchB, resulting in the decline of EE. Thus, carrier concentration and feeding drug ratio should be maintained at a medium level to obtain lower particle size and higher EE. Finally, according to the software prediction, the optimal conditions are as follows: carrier concentration was 22.78 mg/mL, and feeding drug ratio was 19.32%. The optimal particle size is 146.5 nm and the EE is 73.89%. The best prescription verification results of SchB/AP NPs prepared by the optimal scheme were as follows: the particle size was 135.1 ± 0.96 nm, the LC was 5.01 ± 0.15%, the EE was 80.68 ± 1.15%. The actual result is similar to the size and EE predicted by the software.
Typically, the size of nanoparticles is designed to be around 100–200 nm. This is due to the presence of the enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR), which means that the capillary epithelial cells near the tumor cells are not tightly arranged, resulting in pore sizes between 100 and 200 nm, while the capillary vessels in normal tissues are extremely tightly arranged [22]. Therefore, the nanoparticles will be selectively enriched in the tumor area.
4.2 Characterization of the SchB /AP NPs
As shown in Fig. 2a, the TEM of SchB/AP NPs could be seen from the figure that the NPs were spherical-likeand monodisperse. The result showed that the hydrophobic ATRA-g-PBAE could condense into spherical form under the influence of hydrophobic action, and the stronger the hydrophobic action was, the smaller the particle size was. Monodisperse nanoparticles indicate that there is no aggregation between particles, which is extremely important for the distribution of nanoparticles in vivo [23]. Figure 2b shows the particle size distribution, which showed a particle size of 134.97 ± 0.25 nm. The results of the two characterization methods are consistent and similar to the size obtained by the optimal scheme. Thus, the SchB/AP NPs prepared by the optimal scheme have good pharmaceutical properties.
Sufficiently small particle size is beneficial to NPs to be passively targeted to the tumor and enriched within the tumor under the EPR effect [24]. The EPR effect relies on the high vascular permeability and low lymphatic outflow of solid tumors to achieve passive targeting and long-term retention of nanoparticles at the tumor site.
4.3 In Vitro SchB release
To realize the study of drug release by NPs in tumor cells, pH 7.4, 6.8 and 5.5 were selected to simulate the pH of normal physiology in vivo, tumor microenvironment and the lysosomes, respectively [13, 25]. The release curves of SchB/AP NPs in different pH release media were shown in Fig. 2c. Free SchB was rapidly released from the dialysis bag to the medium solution within 12 h, indicating that the dialysis bag had minimal effect on the release of SchB. Within 48 h, the release of SchB reached 80% at pH 5.5. At pH 6.8, SchB release was finally 30%.
The pH of the lysosomes of tumor cells is 5.5, and experimental results show that the drug is rapidly released at this acidity. PBAE is a pH-sensitive polymer, which can undergo strong protonation under acidic lysosomal conditions [26]. At the same time, the protonation causes abundant chloride ions and water molecules to flow into the lysosome, resulting in osmotic pressure increasing and e lysosome rupturing [27]. Accordingly, after the nanoparticles are protonated in the lysosome, the released drugs SchB can be quickly dispersed into the cytoplasm and take effect.
4.4 Serum stability of the SchB/AP NPs
The stability of NPs in blood circulation is the primary condition for the passive targeting of NPs to tumor sites through EPR effects. Drugs are expected to have more excellent stability in the blood to maintain a longer duration of action in the body. To investigate the stability of the SchB/AP NPs, the NPs were placed in the medium containing serum for a total of 48 h. In Fig. 2d, the size of the NPs changed little within 48 h. This was indicated that SchB/AP NPs had weak interaction with serum proteins and showed a stable state.
The strong stability of SchB/AP NPs in serum may be because the NPs were not adsorbed by the proteins in serum and maintained a stable nanostructure. The stability of the nanoparticles ensures that the injected nanoparticles do not accumulate or precipitate in the blood circulation, thus maintaining their properties and drug activity. In addition, stable nanoparticles can achieve multiple functions: long circulation in the body, better-targeting ability, toxic side effects reduction, and therapeutic effect improvement [28].
4.5 In vitro cytotoxicity
The inhibitory effects of the free SchB group and SchB/AP NPs on the proliferation of MS cells were shown in Table 2. The inhibitory effect of SchB/AP NPs (IC50: 10.54 ± 1.29 µg/mL) on MS cells was slightly smaller than that of free SchB (IC50: 7.31 ± 1.12 µg/mL).
This difference was explained by in vitro release results: the different cytotoxic effects of NPs and free groups were caused by the incomplete release of SchB in NPs within 48 h. Even though free SchB is highly toxic, free drugs are difficult to dissolve in water and lack an effective target site for accumulation in the body. In this case, the drug cannot effectively achieve the toxic effects of MS cells. It is worth noting that the IC50 (13.43 ± 0.65 µg/mL) of MCF-7 cells administered with AP NPs was significantly increased compared with the IC50 in MS cells previously reported by our research group. The drug resistance of MS cells is many times stronger than that of MCF-7 cells, and strong drug resistance is an important reason for the reduction of toxicity [29].
Li et al. used Vitamin E derivatives as drug resistance reversal agents to treat drug-resistant cancer cells together with chemotherapy drugs. They found that chemotherapy drugs were less toxic in resistant cancer cells than in normal cancer cells. Studies have found that the VE derivatives, while inhibiting the activity of drug-resistant cells, can reduce drug resistance and play a stronger inhibitory role [30]. Therefore, after loading SchB, NPs have great potential to reverse MDR and enhance the effect of ATRA on Pin1 inhibition.
4.6 Cellular uptake of the SchB/AP NPs
The uptake of Cy5.5-g-PBAE NPs and C6/AP NPs by MS cells was detected by fluorescence microscopy. In Fig. 3a and b, the fluorescence intensity was low within 0.5 h, and the amount of drug in the cell was minimal. When incubation time reached 2 h, enhanced red fluorescence intensity could be observed due to partial drug entry into cells. At 4 h, the fluorescence intensity in the cell was strengthened, and the amount of drug entering the cell increased. This proved that drug intake of MS cells was a time-dependent behavior with the extension of incubation time.
To demonstrate that the encapsulated drug can be transported into the cell through the carrier, the uptake of C6/AP NPs at different times was detected. C6 is similar to SchB in hydrophobic properties and can replace SchB as an encapsulated fluorescent drug. The green fluorescence intensity in MS cells also increased with the extension of incubation time.
Compared with free C6, nanoparticle-encapsulsated C6 showed excellent uptake performance. Li et al. incubated cells with free C6 and loaded C6 nanoparticles respectively, and found that weak fluorescence of free C6 could be observed only after 4 h, while the NPs group showed obvious green light within 1 h [31]. Nanocarriers can transfer hydrophobic molecules into cells more rapidly and release molecules into the cytoplasm with pH sensitivity. Compared with drug molecules, nano-loaded drug particles can increase the accumulation of local drug concentrations in tumor cells, increase bioavailability, and thus have higher therapeutic potential.
4.7 Lysosome co-localizationIn
Fig. 3c, weak yellow fluorescence appeared in 0.5 h. This indicated that the color of Lyso-Tracker Green coincidated with Cy5.5. At 2 h, the red fluorescence increased significantly, and the yellow fluorescence was more obvious. However, the intracellular yellow fluorescence was significantly weaker in MS cells treated with chloroquine. Chloroquine is a drug that disrupts the acidic environment of the lysosome, thereby raising the pH of the lysosome. Therefore, chloroquine interfered with the release of acid-responsive drugs in lysozyme.
The results of the above uptake experiments have proved that blank NPs can carry SchB for cell uptake. The ingested NPs enter the early endosome and then the lysosome. Since PBAE is pH-sensitive, protonation of PBAE will cause lysosome rupture and further escape release [32].
4.8 The mechanism of MS cells reversing MDR
4.8.1 Effect on the expression of drug-resistant protein P-gp
The results were shown in Fig. 4a, after MS cells were treated with ATRA-g-PBAE NPs group, there was no significant change in the produce of P-gp compared with the blank group. However, the expression of P-gp in MS cells treated with free ATRA + SchB decreased significantly (p < 0.01). Compared with the control group, the expression of P-gp was significantly reduced (p < 0.01) after treatment with SchB/AP NPs group. And the expression of P-gp, after free ATRA + SchB intervened, was similar to SchB/AP NPs group.
It has been reported that the chemical structure of SchB is similar to that of P-gp inhibitors and has been shown to inhibit P-gp expression [18]. Therefore, SchB/AP NPs has an approximate effect on reducing P-gp expression with free SchB.
P-gp is not only expressed in tumor tissues, but also widely distributed in other organs [33]. If the MDR reversing agent is combined with other P-gp, it will lead to the occurrence of drug side effects on the body. Hence, the use of pH-sensitive carrier encapsulation of SchB reversers is an effective way to improve drug targeting and reduce side effects.
4.8.2 Measurement of ATPase activity
The effects of SchB/AP NPs on Na+-K+-ATPase, Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and total ATPase (T-ATPase) activity were shown in Fig. 4b. Compared with control group and ATRA-g-PBAE NPs group, Na+-K+-ATPase, Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and T-ATPase activity in SchB and SchB/AP NPs groups were significantly decreased (p < 0.05). Mitochondria are crucial organelles and energy metabolism centers of cells, and their inner membrane is rich in enzymes related to energy metabolism, such as ATPase [34]. ATPase can hydrolyze ATP for the transport of P-gp to achieve energy supply [35, 36]. The ATPase activity of drug-loaded NPs was significantly lower than that of blank NPs. This suggests that SchB can reverse MDR by inhibiting ATPase activity and affecting P-gp energy supply and transport. However, the rate of passive diffusion of the free ATRA and SchB into the cells is different, and MS cells still maintain some resistance [37]. Therefore, the SchB/AP NPs group showed a stronger inhibitory effect.
Among them, Na+-K+-ATPase can promote ATP decomposition and maintain the balance of Na + and K + concentrations inside and outside cells, which can form resting potentials. Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase can maintain intracellular energy stability by catalyzing ATP hydrolysis. When the activity of Na+-K+-ATPase and Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase decreases, the internal and external flow of Na+ and Ca2+ of tumor cells decreases, resulting in abnormal transport function of tumor cells, and also interferes with mitochondrial uptake of Ca2+, which in turn causes abnormal energy metabolism in tumor cells [38]. Hence, the drug efflux function of MS cells could suppressed by SchB/AP NPs.
4.8.3 Assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential
The effects of AP NPs, free ATRA + SchB and SchB/AP NPs on ΔΨm are exhibited in Fig. 4c. Compared with the control group, ΔΨm decreased slightly after ATRA-g-PBAE NPs were incubated. Free ATRA and SchB, and SchB/AP NPs can significantly reduce ΔΨm in MS cells. Among them, the ΔΨm in the SchB/AP NPs group decreased significantly compared with the free drug group (p < 0.05).
JC-1 can determine the state of mitochondria and is a pivotal dye for detecting mitochondrial potential [39]. As the ΔΨm decreases, JC-1 was transferred from the mitochondrial matrix to the cytoplasm, and JC-1 changed from red fluorescence to green fluorescence [40]. A decrease in ΔΨm indicates that mitochondrial function has been disrupted and cannot release sufficient energy [41]. In the state of energy scarcity, various cells behaviors were blocked, especially P-gp mediated efflux. Furthermore, a decrease in ΔΨm indicated that cell death was about to occur. Free drugs captured by lysosomes are easily degraded under the action of their acidic environment and enzymes, resulting in reduced efficacy or even loss of efficacy [42]. It was due to the fact that after NPs co-deliver ATRA and SchB to MS cells, the intracellular concentration of ATRA was maintained by SchB and exerted cytotoxic effects.
4.8.4 Assay of ATP content
The change in intracellular ATP content after incubation in different groups was shown in Fig. 4d. Taking the control group as 100%, the ATP content of the other groups was calculated by the ratio respectively. MS cells experienced a slight decrease in ATP content after being given vector blank NPs. Compared with the free drug group, SchB/AP NPs caused a significant difference in ATP content reduction (p < 0.01). Moreover, the ATP content of cells from free drug was significantly lower than that from ATRA-g-PBAE NPs, indicating that the participation of SchB was a significant factor affecting the ATP content.
The transport of drugs requires the consumption of a large amount of ATP, so it causes a large amount of ATP production in cells. Especially for drug-resistant cells, P-gp-mediated cell excretion comes from rich ATP content [43]. The significant decrease in ATP may be due to SchB promoting the uptake process of NPs by cells, and intracellular ATP is consumed in large quantities. Moreover, SchB/AP NPs can inhibit cells activity, so the mitochondrial function is likewise inhibited [44]. Therefore, SchB/AP NPs have a significant ability to reverse the effect of MDR and have tremendous therapeutic potential for MS cells.
5 Conclusion
In summary, we successfully constructed a novel dual-drug co-delivery SchB/AP NPs by grafting ATRA on PBAE and encapsulated MDR reversal agent SchB. We used CCD RSM to optimize the preparation of NPs, the SchB/AP NPs with good pharmaceutical properties were obtained. Because PBAE is a pH-sensitive carrier, the NPs has fast-release behavior and lysosomal escape ability at the same acidity as lysosome. Hopefully, we found that NPs was significantly cytotoxic and showed a reversal of cellular resistance to ATRA. In addition, we found that the effect of NPs reversing MDR may be accomplished by inhibiting P-gp and interfering with cellular energy metabolism. SchB/AP NPs, which reverse MDR based on co-delivery strategy to enhance the killing ability of cancer cells, provide a new strategy and research idea for anti-BCSCs resistance-related research.
Although the nano drug delivery system has shown excellent tumor targeted therapy effect. However, there are still limitations to our nanocarriers [45]. First, the loading efficiency of the carrier to the drug needs to be improved. Second, in vivo safety and biocompatibility have not been fully verified. Third, the mechanism of interaction between nanocarriers and tumor cells is still unclear and needs further study. We will explore these limitations in further research to overcome these obstacles. Besides, there are still many challenges in the clinical transformation of nanoparticles [46]. For example, the complexity of tumor biology and the scale of production quality control are important obstacles. In addition, the safety and biocompatibility of nanomaterials require more in-depth research and analysis, and long-term toxicity in vivo also needs to be studied.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to some reasons but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Pan L, Han J, Lin M. Targeting breast cancer stem cells directly to treat refractory breast cancer. Front Oncol. 2023;13: 981247.
Wu Y, Shum HCE, Wu K, Vadgama J. From interaction to intervention: how mesenchymal stem cells affect and target triple-negative breast cancer. Biomedicines. 2023;11(4): 1182.
Itoo AM, Paul M, Ghosh B, Biswas S. Oxaliplatin delivery via chitosan/vitamin E conjugate micelles for improved efficacy and MDR-reversal in breast cancer. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;282: 119108.
Krishnan N, Titus MA, Thapar R. The prolyl isomerase pin1 regulates mRNA levels of genes with short half-lives by targeting specific RNA binding proteins. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1): e85427.
Wang JZ, Liu BG, Zhang Y. Pin1-based diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for breast cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2015;93:28–35.
Wulf GM, Ryo A, Wulf GG, Lee SW, Niu T, Petkova V, Lu KP. Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1. EMBO J. 2001;20(13):3459–72.
Luo ML, Gong C, Chen CH, et al. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 acts downstream of miR200c to promote cancer stem-like cell traits in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014;74(13):3603–16.
Wei S, Kozono S, Kats L, Nechama M, Li W, Guarnerio J, Luo M, You MH, Yao Y, Kondo A, Hu H, Bozkurt G, Moerke NJ, Cao S, Reschke M, Chen CH, Rego EM, Lo-Coco F, Cantley LC, Lee TH, Wu H, Zhang Y, Pandolfi PP, Zhou XZ, Lu KP. Active Pin1 is a key target of all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia and breast cancer. Nat Med. 2015;21(5):457–66.
Li W, Gong H, Fu Y, Sun J, Wang Y. Novel pH-sensitive nanoparticles based on prodrug strategy to delivery all-trans retinoic acid for breast cancer. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;219: 112838.
Liu H, Song Y, Qiu H, et al. Downregulation of FOXO3a by DNMT1 promotes breast cancer stem cell properties and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27(3):966–83.
Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(10):755–68.
Pan Y, Ma X, Liu C, Xing J, Zhou S, Parshad B, Schwerdtle T, Li W, Wu A, Haag R. Retinoic acid-loaded dendritic polyglycerol-conjugated gold nanostars for targeted photothermal therapy in breast cancer stem cells. ACS Nano. 2021;15(9):15069–84.
Johnstone RW, Cretney E, Smyth MJ. P-glycoprotein protects leukemia cells against caspasedependent but not caspase-independent, cell death. Blood. 1999;93(3):1075–85.
Juliano RL, Ling V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976;455(1):152–62.
Fritz F, Howard EM, Hoffman MM, et al. Evidence for altered ion transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae overexpressing human MDR 1 protein. Biochemistry. 1999;38(13):4214–26.
Zang X, Cheng M, Zhang X, Chen X. Quercetin nanoformulations: a promising strategy for tumor therapy. Food Funct. 2021;12(15):6664–81.
Li L, Wang T, Xu ZL, Yu Y, Chen W, Chen F. [Effects of schisandrin B on reversing multidrug resistance in human breast cancer cells transfected with mdr1 gene]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005;85(23):1633–7.
Li X, Zhao Y, Gong S, Song T, Ge J, Li J, Zhang J, Fu K, Zheng Y, Ma L. Schisandrin B ameliorates acute liver injury by regulating EGFR-mediated activation of autophagy. Bioorg Chem. 2023;130: 106272.
Li W, Xu Q, Wang Y, Chen D. Poly(β-amino esters)-based barriers for tumor targeted delivery system. Acta Pharm Sin. 2015;50(4):434–9.
Li W, Zhang X, Nan Y, Jia L, Sun J, Zhang L, Wang Y. Hyaluronidase and pH dual-responsive nanoparticles for targeted breast cancer stem cells. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 760423.
Zhang H, Xue Q, Zhou Z, He N, Li S, Zhao C. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and hydroxychloroquine via chitosan/alginate nanoparticles for blocking autophagy and enhancing chemotherapy in breast cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14: 1176232.
Andreotti AM, Goiato MC, Moreno A, Nobrega AS, Pesqueira AA, dos Santos DM. Influence of nanoparticles on color stability, microhardness, and flexural strength of acrylic resins specific for ocular prosthesis. Int J Nanomed. 2014;9:5779–87.
Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, Farokhzad OC. Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(1):20–37.
Zhao Q, Chen J, Zhang Z, Xiao C, Zeng H, Xu C, Yang X, Li Z. Modulating tumor mechanics with nanomedicine for cancer therapy. Biomater Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3bm00363a.
Gao N, Fu Y, Gong H, Liu H, Li W. Hyaluronic acid and cholecalciferol conjugate based nanomicelles: synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxicity against MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Carbohydr Res. 2022;522: 108706.
Sang R, Fan R, Deng A, Gou J, Lin R, Zhao T, Hai Y, Song J, Liu Y, Qi B, Du G, Cheng M, Wei G. Degradation of hexokinase 2 blocks glycolysis and induces GSDME-Dependent pyroptosis to amplify immunogenic cell death for breast cancer therapy. J Med Chem. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00118.
Davatgaran-Taghipour Y, Masoomzadeh S, Farzaei MH, Bahramsoltani R, Karimi-Soureh Z, Rahimi R, Abdollahi M. Polyphenol nanoformulations for cancer therapy: experimental evidence and clinical perspective. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:2689–702.
Fang F, Wang S, Song Y, Sun M, Chen WC, Zhao D, Zhang J. Continuous spatiotemporal therapy of a full-API nanodrug via multi-step tandem endogenous biosynthesis. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):1660.
Li W, Sun J, Zhang X, Jia L, Qiao M, Zhao X, Hu H, Chen D, Wang Y. Synthesis and characterization of pH-responsive PEG-poly (β-amino ester) block copolymer micelles as drug carriers to eliminate cancer stem cells. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(2): 111.
Li Z, Qiu L, Chen Q, Hao T, Qiao M, Zhao H, Zhang J, Hu H, Zhao X, Chen D, Mei L. pH-sensitive nanoparticles of poly(L-histidine)-poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate for anti-tumor drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:137–50.
Li WQ, Wu JY, Xiang DX, Luo SL, Hu XB, Tang TT, Sun TL, Liu XY. Micelles loaded with puerarin and modified with triphenylphosphonium cation possess mitochondrial targeting and demonstrate enhanced protective effect against isoprenaline-induced H9c2 cells apoptosis. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:8345–60.
Chen Q, Shan T, Liang Y, Xu Y, Shi E, Wang Y, Li C, Wang Y, Cao M. A biomimetic phototherapeutic nanoagent based on bacterial double-layered membrane vesicles for comprehensive treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Mater Chem B. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3tb02046k.
Ma L, Ruan L, Liu H, Yang H, Feng Y. ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism is associated with leukemia susceptibility: evidence from a meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 2015;8:1009–15.
Harazono Y, Kho DH, Balan V, et al. Extracellular galectin-3 programs multidrug resistance through Na+/K+-ATPase and P-glycoprotein signaling. Oncotarget. 2015;6(23):19592–604.
Krstić D, Krinulović K, Vasić V. Inhibition of Na+/K(+)-ATPase and mg(2+)-ATPase by metal ions and prevention and recovery of inhibited activities by chelators. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2005;20(5):469–76.
Loo TW, Clarke DM. Recent progress in understanding the mechanism of P-glycoproteinmediated drug efflux. J Membr Biol. 2005;206(3):173–85.
Chen M, Li W, Zhang X, Dong Y, Hua Y, Zhang H, Gao J, Zhao L, Li Y, Zheng A. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of SN-38 nanocrystals with different particle sizes. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:5487–500.
Fan M, Zhang J, Tsai CW, Orlando BJ, Rodriguez M, Xu Y, Liao M, Tsai MF, Feng L. Structure and mechanism of the mitochondrial Ca2 + uniporter holocomplex. Nature. 2020;582(7810):129–33.
Xu F, Li M, Qian Q, Chen L, Yang Y, Ji TF, Li JG. β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin suppresses proliferation and induces ROS-based mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human melanoma cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2023;13:1–15.
De Toni L, Cosci I, Sabovic I, Di Nisio A, Guidolin D, Pedrucci F, Finocchi F, Dall’Acqua S, Foresta C, Ferlin A, Garolla A. Membrane cholesterol inhibits progesterone-mediated sperm function through the possible involvement of ABHD2. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11): 9254.
Wang Z, Cui J, Li D, Ran S, Huang J, Chen G. Morin exhibits a neuroprotective effect in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model via TFEB/AMPK-mediated mitophagy. Phytomedicine. 2023;116: 154866.
Wang R, Yin C, Liu C, Sun Y, Xiao P, Li J, Yang S, Wu W, Jiang X. Phenylboronic acid modification augments the lysosome escape and antitumor efficacy of a cylindrical polymer brush-based prodrug. J Am Chem Soc. 2021;143(49):20927–38.
Wang C, Zhang J, Wei X, Yang M, Ma W, Yu R, Liu M, Jiang T. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of marine lissodendrins B analogues as modulators of ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance. Mar Drugs. 2023;21(5): 314.
Mukerabigwi JF, Tang R, Cao Y, Mohammed F, Zhou Q, Zhou M, Ge Z. Mitochondria-targeting polyprodrugs to overcome the drug resistance of cancer cells by self-amplified oxidation-triggered drug release. Bioconjug Chem. 2023;34(2):377–91.
Li K, Cai X, Fan Y, Jin M, Xie Y, Jing Z, Zang X, Han Y. Codelivery of Que and BCL-2 siRNA with Lipid-Copolymer Hybrid Nanocomplexes for Efficient Tumor Regression. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(8):4805–4820.
Oh H, Jeong E, Lee JS, Kim J, Lee D, Kim BS, Sung D, Koo H, Choi WI, Tae G. ROS-responsive PEGylated ferrocene polymer nanoparticles with improved stability for tumor-selective chemotherapy and imaging. Mater Today Bio. 2023;22: 100774.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science Foundation Project of Heilongjiang Province of China [No. LH2021H098]; National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 82074025]; the Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program; Self-funded Project of Science and Technology Plan of Harbin Science and Technology Bureau [No. 2022ZCZJNS049] and Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine graduate innovative research project [No. 2023yjscx011].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by WL, YF, JS, YW. HG and RY were cooperatively help experiments. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YF and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Fu, Y., Sun, J. et al. Construction and in vitro evaluation of pH-sensitive nanoparticles to reverse drug resistance of breast cancer stem cells. Discov Onc 15, 21 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-024-00873-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-024-00873-w