Abstract
Objectives
The present study assessed age-related differences in the success of instructed mindful attention and positive reappraisal, as well as trait affect and emotion regulation.
Methods
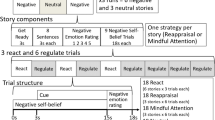
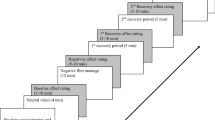
Young and older adults were instructed to regulate their emotions while viewing frightening and amusing films using three separate instructions (just watch, positive reappraisal, or mindful attention). Participants rated the strength of their experience of the target emotion (fear or amusement) and success in following the instruction to regulate. Electrodermal activity was recorded continuously, and facial electromyography measured positive and negative facial expression. Trait measures of affect and emotion regulation were also administered.
Results
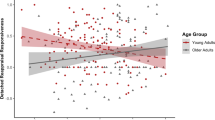
Electrodermal activity provided strong evidence that young adults successfully regulate fear using mindful attention and positive reappraisal relative to a just watch condition. Older adults’ electrodermal activity is was constant across conditions, and lower than young adults’ in the just watch condition, suggesting general hyporeactivity to fear. Subjective data suggest that young, but not older, adults successfully downregulate amusement using mindful attention.
Conclusion
These findings provide some evidence for emotion regulation benefits in young relative to older age. However, these youthful benefits may reflect reduced initial reactivity among older adults.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, P. E., & Henry, J. D. (2009). Subconscious facial expression mimicry is preserved in older adulthood. Psychology and Aging, 24(4), 995–1000. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015789.
Bohlmeijer, E., Ten Klooster, P. M., Fledderus, M., Veehof, M., & Baer, R. (2011). Psychometric properties of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire in depressed adults and development of a short form. Assessment, 18(3), 308–320. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191111408231.
Brady, B., Kneebone, I. I., Denson, N., & Bailey, P. E. (2018). Systematic review and meta-analysis of age-related differences in instructed emotion regulation success. PeerJ, 1–27. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6051.
Brady, B., Kneebone, I. I., & Bailey, P. E. (2019a). Validation of the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire in older community-dwelling adults. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 58(1), 110–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjc.12203.
Brady, B., Kneebone, I. I., & Bailey, P. E. (2019b). Validation of the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire among community-dwelling older Adaults. Mindfulness, 10(3), 529–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-018-0994-0.
Carstensen, L. L., Isaacowitz, D. M., & Charles, S. T. (1999). Taking time seriously: a theory of socioemotional selectivity. American Psychologist, 54(3), 165–181. https://doi.org/10.1037/2F0003-066X.54.3.165.
Charles, S. T., & Carstensen, L. L. (2007). Emotion regulation and ageing. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (pp. 307-327). New York: The Guilford Press.
Cutler, S. J. (2001). Crime (against and by the elderly). In G. L. Maddox (Ed.), The encyclopedia of aging (3rd ed., pp. 260–262). New York: Springer.
de Frias, C. M., & Whyne, E. (2015). Stress on health-related quality of life in older adults: the protective nature of mindfulness. Aging & Mental Health, 19(3), 201–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2014.924090.
Erisman, S. M., & Roemer, L. (2010). A preliminary investigation of the effects of experimentally induced mindfulness on emotional responding to film clips. Emotion, 10(1), 72–82. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017162.
Folkman, S., Lazarus, R. S., Pimley, S., & Novacek, J. (1987). Age differences in stress and coping processes. Psychology and Aging, 2(2), 171–184. https://doi.org/10.1037/0882-7974.2.2.171.
Fredrickson, B. L. (1998). What good are positive emotions? Review of General Psychology, 2(3), 300–319. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.2.3.300.
Geiger, P. J., Boggero, I. A., Brake, C. A., Caldera, C. A., Combs, H. L., Peters, J. R., & Baer, R. A. (2016). Mindfulness-based interventions for older adults: a review of the effects on physical and emotional well-being. Mindfulness, 7(2), 296-307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-015-0444-1.
Gross, J. J. (1998). The emerging field of emotion regulation: an integrative review. Review of General Psychology, 2, 271–299. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.2.3.271.
Gross, J. J. (2015). Emotion regulation: current status and future prospects. Psychological Inquiry, 26, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/1047840X.2014.940781.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85(2), 348–362. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.85.2.348.
Hofer, M., & Allemand, M. (2017). Dispositional and situational emotion regulation in younger and older adults. GeroPsych: The Journal of Gerontopsychology and Geriatric Psychiatry, 30, 109–118. https://doi.org/10.1024/1662-9647/a000171.
Hohaus, L. C., & Spark, J. (2013). Getting better with age: do mindfulness & psychological well-being improve in old age? European Psychiatry, 28, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-9338(13)77295-X.
Hsieh, S., Schubert, S., Hoon, C., Mioshi, E., & Hodges, J. R. (2013). Validation of the Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination III in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 36(3-4), 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1159/000351671.
Isaacowitz, D. M., Livingstone, K. M., & Castro, V. L. (2017). Aging and emotions: experience, regulation, and perception. Current Opinion in Psychology, 17, 79–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.06.013.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1994). Wherever you go, there you are: mindfulness meditation in everyday life. New York: Hyperion Press
Khoury, B., Lecomte, T., Fortin, G., Masse, M., Therien, P., Bouchard, V., et al. (2013). Mindfulness-based therapy: a comprehensive meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(6), 763–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2013.05.005.
Kunzmann, U., Kappes, C., & Wrosch, C. (2014). Emotional aging: a discrete emotions perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00380.
Labouvie-Vief, G. (2009). Dynamic integration theory: Emotion, cognition, and equilibrium in later life. In V. L. Bengston, D. Gans, N. M. Pulney, & M. Silverstein (Eds.), Handbook of theories of aging (pp. 277–293). New York: Springer Publishing Company. https://doi.org/10.1037/11882-009
Labuschagne, I., Pedder, D. J., Henry, J. D., Terrett, G., & Rendell, P. G. (2020). Age differences in emotion regulation and facial muscle reactivity to emotional films. Gerontology, 66(1), 74–84. https://doi.org/10.1159/000501584.
Lalot, F., Delplanque, S., & Sander, D. (2014). Mindful regulation of positive emotions: a comparison with reappraisal and expressive suppression. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 243–252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00243.
Lohani, M., & Isaacowitz, D. M. (2014). Age differences in managing response to sadness elicitors using attentional deployment, positive reappraisal and suppression. Cognition and Emotion, 28(4), 678–697. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2013.853648.
Mackinnon, A., Jorm, A. F., Christensen, H., Korten, A. E., Jacomb, P. A., & Rodgers, B. (1999). A short form of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule: evaluation of factorial validity and invariance across demographic variables in a community sample. Personality and Individual Differences, 27(3), 405–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(98)00251-7.
Mallya, S., & Fiocco, A. J. (2016). Effects of mindfulness training on cognition and well-being in healthy older adults. Mindfulness, 7(2), 453-465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-015-0468-6.
Nowlan, J. S., Wuthrich, V. M., & Rapee, R. M. (2015). Positive reappraisal in older adults: a systematic literature review. Aging and Mental Health, 19, 475–484. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2014.954528.
Pavlov, S. V., Reva, N. V., Loktev, K. V., Tumyalis, A. V., Korenyok, V. V., & Aftanas, L. I. (2014). The temporal dynamics of cognitive reappraisal: cardiovascular consequences of downregulation of negative emotion and upregulation of positive emotion. Psychophysiology, 51, 178–186. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12159.
Pedder, D. J., Terrett, G., Bailey, P. E., Henry, J. D., Ruffman, T., & Rendell, P. G. (2016). Reduced facial reactivity as a contributor to preserved emotion regulation in older adults. Psychology and Aging, 31(1), 114–125. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0039985.
Prakash, R. S., De Leon, A. A., Patterson, B., Schirda, B. L., & Janssen, A. L. (2014). Mindfulness and the ageing brain: a proposed paradigm shift. Frontiers in Ageing Neuroscience, 6, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00120.
Prakash, R. S., Hussain, M. A., & Schirda, B. (2015). The role of emotion regulation and cognitive control in the association between mindfulness disposition and stress. Psychology and Aging, 30(1), 160–171. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0038544
Raes, A. K., Bruyneel, L., Loeys, T., Moerkerke, B., & De Raedt, R. (2013). Mindful attention and awareness mediate the association between age and negative affect. The Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 70(2), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbt074.
Rand, D. G., Kraft-Todd, G., & Gruber, J. (2015). The collective benefits of feeling good and letting go: positive emotion and (dis)inhibition interact to predict cooperative behavior. PloS One, 10(1), e0117426. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117426.
Reed, A. E., Chan, L., & Mikels, J. A. (2014). Meta-analysis of the age-related positivity effect: age differences in preferences for positive over negative information. Psychology and Aging, 29(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0035194.
Rejeski, W. J. (2008). Mindfulness: reconnecting the body and mind in geriatric medicine and gerontology. The Gerontologist, 48(2), 135–141. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/48.2.135.
Sheppes, G., & Gross, J. J. (2011). Is timing everything? Temporal considerations in emotion regulation. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 15, 319–331. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088868310395778.
Shiota, M. N., & Levenson, R. W. (2009). Effects of ageing on experimentally instructed detached reappraisal, positive reappraisal, and emotional behavior suppression. Psychology & Aging, 24(4), 890–900. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017896.
Slutsky, J., Rahl, H., Lindsay, E. K., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Mindfulness, emotion regulation, and social threat. In J. C. Karremans & E. K. Papies (Eds.), Mindfulness in Social Psychology (pp. 79–93). New York: Routledge.
Teper, R., Segal, Z. V., & Inzlicht, M. (2013). Inside the mindful mind: how mindfulness enhances emotion regulation through improvements in executive control. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 22, 449–454. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721413495869.
Vieillard, S., Harm, J., & Bigand, E. (2015). Expressive suppression and enhancement during music-elicited emotions in younger and older adults. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 7, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00011.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063 - 1070.
Funding
This study was funded by the Australian Research Council (grant number DP200100876).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BB: designed and executed the study, completed the data analyses, and wrote the paper. CG: collaborated with the analysis and interpretation of physiological data. IK: collaborated with the design and writing of the study. EW: provided coding expertise that was applied to complex physiological data collection, data extraction and artefact correction. PB: collaborated with the design and writing of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Western Sydney University IRB committee (approval number H11503) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brady, B., Gonsalvez, C., Kneebone, I.I. et al. Age-related differences in instructed positive reappraisal and mindful attention. Mindfulness 12, 646–658 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01523-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01523-2