Abstract
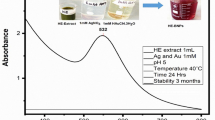
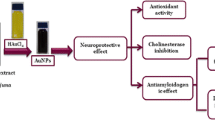
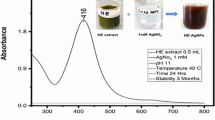
Nanotechnology is contributed to the techniques, which is well known for the production of unique morphology nanoparticles (NPs) through an environmentally satisfactory method. The present research is designed for the production of gold NPs (AuNPs) using Hippeastrum hybridum (HH) extract and then to test the potential of these AuNPs as ex vivo ant-acetyl cholinesterase (anti-AChE) inhibitor. These AuNPs were analyzed by UV-visible spectroscopy, SEM, FT-IR, EDX, and XRD. FT-IR confirmed the functional groups on the AuNPs surface, XRD report showed the crystal AuNPs of 10.72 nm size, SEM showed irregularly shaped morphology of AuNPs with 30 nm size, and EDX analysis confirmed 48.08% Au signal. A significant anti-AChE potential of 131±0.33 μg IC50 was exhibited by these AuNPs. According to Lineweaver-Burk AuNPs inhibit AChE in the non-competitive route (Km remained unchanged, while Vmax decrease from 1.358 to 0.28). Similarly, AuNPs showed no effect against KIapp, while causing an increase in Vmaxiapp value (11 to 23.35) The Km (Michaelis-Menten kinetic constants), KI (dissociation constant), and Ki (inhibitory constant) were reported to be 0.02 mM, 7.32 μg, and 32 μg. So, it is assumed that HH extract holds the potential for the generation of AuNPs that subsequently proved to be an anti-Alzheimer agent.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available as per the requirement of Journal guidelines.
References
Chaloupka, K., Malam, Y., & Seifalian, A. M. (2010). Nanosilver as a new generation of nanoproduct in biomedical applications. Trends in Biotechnology, 28, 580–588.
Ganeshkumar, M., Sathishkumar, M., Ponrasu, T., Dinesh, M. G., & Suguna, L. (2013). Spontaneous ultra fast synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Punica granatum for cancer targeted drug delivery. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 106, 208–216.
Nair, R., Varghese, S. H., Nair, B. G., Maekawa, T., Yoshida, Y., & Kumar, D. S. (2010). Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Science, 179, 154–163.
Kumar, V., Guleria, P., Kumar, V., & Yadav, S. K. (2013). Gold nanoparticle exposure induces growth and yield enhancement in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science of the Total Environment, 461-462, 462–468.
Niraimathi, K. L., Sudha, V., Lavanya, R., & Brindha, P. (2013). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alternanthera sessilis (Linn.) extract and their antimicrobial, antioxidant activities. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 102, 288–291.
Bhat, R., Sharanabasava, V. G., Deshpande, R., Shetti, U., Sanjeev, G., & Venkataraman, A. (2013). Photo-bio-synthesis of irregular shaped functionalized gold nanoparticles using edible mushroom Pleurotus florida and its anticancer evaluation. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology: B, 125, 63–69.
Annamalai, A., Christina, V. L., Sudha, D., Kalpana, M., & Lakshmi, P. T. (2013). Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of Au NPs using Euphorbia hirta L. leaf extract. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 108, 60–65.
Gopinath, K., Gowri, S., Karthika, V., & Arumugam, A. (2014). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from fruit extract of Terminalia arjuna, for the enhanced seed germination activity of Gloriosa superba. Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry, 4, 115.
Inbakandan, D., Kumar, C., Abraham, L. S., Kirubagaran, R., Venkatesan, R., & Khan, S. A. (2013). Silver nanoparticles with anti microfouling effect: A study against marine biofilm forming bacteria. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 111, 636–643.
AshaRani, P. V., Low, K. M. G., PH, M., & Valiyaveettil, S. (2009). Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano, 3, 279–290.
Bhattacharya, R., & Mukherjee, P. (2008). Biological properties of “naked” metal nanoparticles. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 60, 1289–1306.
Pollini, M., Paladini, F., Catalano, M., Taurino, A., Licciulli, A., Maffezzoli, A., & Sannino, A. (2011). Antibacterial coatings on haemodialysis catheters by photochemical deposition of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 22, 2005–2012.
Rajeshkumar, S. (2016). Anticancer activity of eco-friendly gold nanoparticles against lung and liver cancer cells. Journal, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology, 14, 195–202.
Hulla, J. E., Sahu, S. C., & Hayes, A. W. (2015). Nanotechnology: History and future. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 34, 1318–1321.
Ramamurthy, C. H., Padma, M., Samadanam, I. D., Mareeswaran, R., Suyavaran, A., Kumar, M. S., Premkumar, K., & Thirunavukkarasu, C. (2013). The extra cellular synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles and their free radical scavenging and antibacterial properties. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 102, 808–815.
Sher, N., Alkhalifah, D. H. M., Ahmed, M., Mushtaq, N., Shah, F., Fozia, F., Khan, R. A., Hozzein, W. N., & Aboul-Soud, M. A. (2022). Comparative study of antimicrobial activity of silver, gold, and silver/gold bimetallic nanoparticles synthesized by green approach. Molecules, 27, 7895.
Sher, N., Ahmed, M., Mushtaq, N., & Khan, R. A. (2022). Enhancing antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antialzheimer performance of Hippeastrum hybridum (L.) using silver nanoparticles. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 36, e6724.
Sher, N., Ahmed, M., Mushtaq, N., & Khan, R. A. (2020). Calligonum polygonoides reduced nanosilver: A new generation of nanoproduct for medical applications. European Journal of Integrative Medicine, 33, 101042.
Philip, D., Unni, C., Aromal, S. A., & Vidhu, V. K. (2011). Murraya koenigii leaf-assisted rapid green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles, Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 78, 899–904.
Amor, S., Puentes, F., Baker, D., & van der Valk, P. (2010). Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology, 129, 154–169.
Chen, H., Kwong, J. C., Copes, R., Tu, K., Villeneuve, P. J., van Donkelaar, A., Hystad, P., Martin, R. V., Murray, B. J., Jessiman, B., Wilton, A. S., Kopp, A., & Burnett, R. T. (2017). Living near major roads and the incidence of dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis: A population-based cohort study. Lancet, 389, 718–726.
Arsalan, A., Khurram, O., Maimoona, S., Kayser, M., Faiza, R., & Abdul, W. Y. (2013). Dementia in pakistan: national guidelines for clinicians. Pakistan Journal of Neurological Sciences (PJNS), 8, 7–27.
Tan, C. C., Yu, J. T., Tan, M. S., Jiang, T., Zhu, X. C., & Tan, L. (2014). Autophagy in aging and neurodegenerative diseases: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Neurobiology of Aging, 35, 941–957.
Takalo, M., Salminen, A., Soininen, H., Hiltunen, M., & Haapasalo, A. (2013). Protein aggregation and degradation mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases. American Journal of Neurodegenerative Disease, 2, 1–14.
Schliebs, R., & Arendt, T. (2011). The cholinergic system in aging and neuronal degeneration. Behavioural Brain Research, 221, 555–563.
Chen, W. W., Zhang, X., & Huang, W. J. (2016). Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports, 13, 3391–3396.
Johri, A., & Beal, M. F. (2012). Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 342, 619–630.
Butterfield, D. A., Swomley, A. M., & Sultana, R. (2013). Amyloid -peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: Importance in disease pathogenesis and progression. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 19, 823–835.
Ahmed, M., Khan, S. Z., Sher, N., Rehman, Z. U., Mushtaq, N., & Khan, R. A. (2021). Kinetic and toxicological effects of synthesized palladium(II) complex on snake venom (Bungarus sindanus) acetylcholinesterase. Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins Including Tropical Diseases, 27, e20200047.
Solanki, I., Parihar, P., Mansuri, M. L., & Parihar, M. S. (2015). Flavonoid-based therapies in the early management of neurodegenerative diseases. Advances in Nutrition, 6, 64–72.
Racchi, M., Mazzucchelli, M., Porrello, E., Lanni, C., & Govoni, S. (2004). Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: novel activities of old molecules. Pharmacological Research, 50, 441–451.
Öztürk, M. (2012). Anticholinesterase and antioxidant activities of Savoury (Satureja thymbra L.) with identified major terpenes of the essential oil. Food Chemistry, 134, 48–54.
Mukherjee, P. K., Kumar, V., Mal, M., & Houghton, P. J. (2007). Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from plants. Phytomedicine, 14, 289–300.
Stevens, P. F. (2016). Asparagales: Amaryllidoideae. Angiosperm Phylogeny Website version. 3, 10531.
Wang, Y., Chen, D., He, X., Shen, J., Xiong, M., Wang, X., Zhou, D., & Wei, Z. (2018). Revealing the complex genetic structure of cultivated amaryllis (Hippeastrum hybridum) using transcriptome-derived microsatellite markers. Scientific Reports, 8, 10645.
Peterson, M. E., & Patricia, A. T. (2006). Small animal toxicology. Elsevier Health Sciences, 643–663.
Prasad, K. S., & Savithramma, N. (2015). Biosynthesis and validation of silver nanoparticles from Nymphaea caerulea American Journal of Advanced. Drug Delivery, 3, 149–159.
Gopinath, K., Kumaraguru, S., Bhakyaraj, K., Mohan, S., Venkatesh, K. S., Esakkirajan, M., Kaleeswarran, P., Alharbi, N. S., Kadaikunnan, S., Govindarajan, M., Benelli, G., & Arumugam, A. (2016). Green synthesis of silver, gold and silver/gold bimetallic nanoparticles using the Gloriosa superba leaf extract and their antibacterial and antibiofilm activities. Microbial Pathogenesis, 101, 1–11.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. D., Andres, V., Jr., & Feather-Stone, R. M. (1961). A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochemical Pharmacology, 7, 88–95.
Pereira, M. E., Adams, A. I. H., & Silva, N. S. (2004). 2,5-Hexanedione inhibits rat brain acetylcholinesterase activity in vitro. Toxicology Letters, 146, 269–274.
Lineweaver, H., & Burk, D. (1934). The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 56, 658–666.
Hofstee, B. H. (1952). On the evaluation of the constants Vm and KM in enzyme reactions. Science, 116, 329–331.
Dowd, J. E., & Riggs, D. S. (1965). A comparison of estimates of michaelis-menten kinetic constants from various linear transformations. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 240, 863–869.
Cornish-Bowden, A., & Cárdenas, M. L. (1991). Hexokinase and ‘glucokinase’ in liver metabolism. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 16, 281–282.
Dixon, M., & Webb, E. C. (1964). Enzymes. Longmans.
Sher, N., Ahmed, M., Mushtaq, N., & Khan, R. A. (2022). Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles from the extract of Heliotropium eichwaldi L. and their effect as antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anti-cholinesterase. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 37, e6950.
Adebayo, E. A., Ibikunle, J. B., Oke, A. M., Lateef, A., Azeez, M. A., Oluwatoyin, A. O., AyanfeOluwa, A. V., Blessing, O. T., Comfort, O. O., & Adekunle, O. O. (2019). Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of silver, gold and silver-gold alloy nanoparticles phytosynthesized using extract of Opuntia ficus-indica. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 58, 313–326.
Armendariz, V., Herrera, I., Peralta-videa, J. R., Jose-yacaman, M., Troiani, H., Santiago, P., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2004). Size controlled gold nanoparticle formation by Avena sativa biomass: use of plants in nanobiotechnology. Journal of Nanoparticle Research Journal of Recent Sciences, 6, 377–382.
Ajitha, B., Ashok Kumar Reddy, Y., & Sreedhara Reddy, P. (2015). Enhanced antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size by pH variation. Powder Technology, 269, 110–117.
Park, Y., Hong, Y. N., Weyers, A., Kim, Y. S., & Linhardt, R. J. (2011). Polysaccharides and phytochemicals: a natural reservoir for the green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnology, 5, 69–78.
Rai, A., Singh, A., Ahmad, A., & Sastry, M. (2006). Role of halide ions and temperature on the morphology of biologically synthesized gold nanotriangles. Langmuir, 22, 736–741.
Pastoriza-Santos, I., & Liz-Marzan, L. M. (2002). Formation of PVP-protected metal nanoparticles in DMF. Langmuir, 18, 2888–2894.
Palaniappan, P., Sathishkumar, G., & Sankar, R. (2015). Fabrication of nano-silver particles using Cymodocea serrulata and its cytotoxicity effect against human lung cancer A549 cells line. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 138, 885–890.
Darroudi, M., Ahmad, M. B., Zamiri, R., Zak, A. K., Abdullah, A. H., & Ibrahim, N. A. (2011). Time-dependent effect in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 6, 677–681.
Balavandy, S. K., Shameli, K., Biak, D. R., & Abidin, Z. Z. (2014). Stirring time effect of silver nanoparticles prepared in glutathione mediated by green method. Chemistry Central Journal, 8, 11.
Gao, Y., Huang, Q., Su, Q., & Li, R. (2014). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles at room temperature using kiwifruit juice. An International Journal for Rapid Communication, 47, 790–795.
Baer, D. R. (2011). Surface characterization of nanoparticles: Critical needs and significant challenges. Journal of surface analysis, 17, 163–169.
Bhatnagar, I., Mahato, K., Ealla, K. K. R., Asthana, A., & Chandra, P. (2018). Chitosan stabilized gold nanoparticle mediated self-assembled gliP nanobiosensor for diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 110, 449–456.
Dauthal, P., & Mukhopadhyay, M. (2016). Noble metal nanoparticles: Plant-mediated synthesis, mechanistic aspects of synthesis, and applications. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 55, 9557–9577.
Syed, B., Karthik, N., Bhat, P., Bisht, N., Prasad, A., Satish, S., & Prasad, M. N. N. (2019). Phyto-biologic bimetallic nanoparticles bearing antibacterial activity against human pathogens. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 31, 798–803.
Dada, A. O., Inyinbor, A. A., Idu, E. I., Bello, O. M., Oluyori, A. P., Adelani-Akande, T. A., Okunola, A. A., & Dada, O. (2018). Effect of operational parameters, characterization and antibacterial studies of green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Tithonia diversifolia. PeerJ, 6, e5865.
Femi-Adepoju, A. G., Dada, A. O., Otun, K. O., Adepoju, A. O., & Fatoba, O. P. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using terrestrial fern (Gleichenia Pectinata (Willd.) C. Presl.): characterization and antimicrobial studies. Heliyon, 5, e01543.
Khan, F. A., Zahoor, M., Jalal, A., & Rahman, A. U. (2016). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using Ziziphus nummularia leaves aqueous extract and their biological activities. Journal of Nanomaterials, 1, 1–8.
Sharififar, F., Moshafi, M. H., Shafazand, E., & Koohpayeh, A. (2012). Acetyl cholinesterase inhibitory, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of three dietary medicinal plants. Food Chemistry, 130, 20–23.
Orhan, I. E., Senol, F. S., Ercetin, T., Kahraman, A., Celep, F., Akaydin, G., Sener, B., & Dogan, M. (2013). Assessment of anticholinesterase and antioxidant properties of selected sage (Salvia) species with their total phenol and flavonoid contents. Industrial Crops and Products, 41, 21–30.
Sher, N., Ahmed, M., Mushtaq, N., & Khan, R. A. (2022). Enhancing antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antialzheimer performance of Hippeastrum hybridum (L.) using silver nanoparticles. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 36, 6724.
Dorosti, N., & Jamshidi, F. (2016). Plant-mediated gold nanoparticles by Dracocephalum kotschyi as anticholinesterase agent: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of anticancer and antibacterial activity. Journal of Applied Biomedicine, 14, 235–245.
Songül, K., Mehmet, K., & Ceyda, S. K. (2019). Antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities of Heliotropium dolosum, H. lasiocarpum and H. hirsutissimum growing in Turkey. Journal of Science and Technology, 12, 1381–1391.
Funding
The present study was supported by the higher education commission of Pakistan via project no. 20-2171/NRPU/R&D/HEC/13/5610.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NS, MA, and NM performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent To Participate
The study was approved by the Departmental Ethical Approval Committee Ref No: Biotech/Ethic/110.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Research Involving Humans and Animals Statement
None.
Informed Consent
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sher, N., Ahmed, M. & Mushtaq, N. Plant-Based Synthesis of AuNPs Using Hippeastrum hybridum (L.): Their Ex vivo Anti-acetylcholinesterase Property. BioNanoSci. 13, 1766–1778 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01227-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01227-6