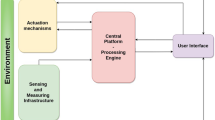
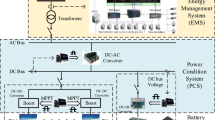
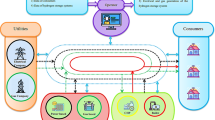
Abstract
With the rapid advancements in technologies like smart grid, network communication, information infrastructures, bidirectional communication medium’s, energy conservation methodologies and diverse techniques, Home area networks (HANs) have undergone a revolutionary change pertaining to various areas of power consumption domains like electricity usage patterns, energy conservation at consumption premises, etc. Under a robust smart grid paradigm, modern home equipped with HEMS contributes significantly towards efficiency improvement, economizing energy usage, reliability, as well as conserving energy for distributed systems. The objective of the paper is to present a comprehensive review covering the various technical and conceptual aspects of efficient power management at home front. A systematic review proposed by several researchers till date in this area is considered. The study focuses on the concepts, technical background, architecture and infrastructure along with various schemes as well as goals including various issues and challenges faced with HEMS systems. The research paper proposes a novel methodology for improvising the home design architecture by incorporating the concept of green building in order to reduce the energy consumption done by a resident at their home front. The concept of HEM systems or SHEMS is not just about proposing new models to save energy, power management, or making energy efficient appliances to be used at home front but also about creating awareness among the consumers and motivating them to participate in the activities related to power conservation in active manner. The study have shown the, impact of various schemes over the peak load reduction with Optimization based residential energy management (OREM) technique showing the reduction in power consumption showing a cut down of about 35% in the overall electricity bill.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pau, G., Collotta, M., Ruano, A., Qin, J.: Smart home energy management. Energies 10(12), 382 (2017)
Aman, S., Simmhan, Y., Prasanna, V.K.: Energy management systems: state of the art and emerging trends. IEEE Commun. Mag. 51(1), 114–119 (2013)
Zipperer, A., Aloise-Young, P.A., Suryanarayanan, S., Roche, R., Earle, L., Christensen, D., Bauleo, P., Zimmerle, D.: Electric energy management in the smart home: perspectives on enabling technologies and consumer behavior. Proc. IEEE 101(11), 2397–2408 (2013)
Asare-Bediako, B., Ribeiro, P.F., Kling, W.L.: Integrated energy optimization with smart home energy management systems. In: 2012 3rd IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT Europe), pp. 1–8 (2012)
Fischer, C.: Feedback on household electricity consumption: a tool for saving energy? Energy Effic. 1(1), 79–104 (2008)
Gellings, C.W.: Power to the people. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 9(5), 52–63 (2011)
Moen, R.L.: Solar energy management system. In: 18th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control including the Symposium on Adaptive Processes, pp. 917–919 (1979)
Capehart, B.L., Muth, E.J., Storin, M.O.: Minimizing residential electrical energy costs using microcomputer energy management systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 6(4), 261–269 (1982)
Rahman, S., Bhatnagar, R.: Computerized energy management systems—why and how. J. Microcomput. Appl. 9(4), 261–270 (1986)
Wacks, K.P.: Utility load management using home automation. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 37(2), 168–174 (1991)
Kidd, C.D., Orr, R., Abowd, G.D., Atkeson, C.G., Essa, I.A., MacIntyre, B., Mynatt, E., Starner, T.E., Newstetter, W.: The aware home: a living laboratory for ubiquitous computing research. In: International Workshop on Cooperative Buildings, pp. 191–198. Springer, Berlin (1999)
Kushiro, N., Suzuki, S., Nakata, M., Takahara, H., Inoue, M.: Integrated residential gateway controller for home energy management system. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(3), 629–636 (2003)
Inoue, M., Higuma, T., Ito, Y., Kushiro, N., Kubota, H.: Network architecture for home energy management system. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(3), 606–613 (2003)
Das, S.K., Roy, N., Roy, A.: Context-aware resource management in multi-inhabitant smart homes: A framework based on Nash H-learning. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2(4), 372–404 (2006)
Ghent, B.A. U.S. Patent 7,110,832. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (2006)
Han, J., Choi, C.S., Lee, I.: More efficient home energy management system based on ZigBee communication and infrared remote controls. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 57(1), 85–89 (2011)
Pipattanasomporn, M., Kuzlu, M., Rahman, S.: An algorithm for intelligent home energy management and demand response analysis. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(4), 2166–2173 (2012)
Di Giorgio, A., Pimpinella, L.: An event driven smart home controller enabling consumer economic saving and automated demand side management. Appl. Energy 96, 92–103 (2012)
Squartini, S., Boaro, M., De Angelis, F., Fuselli, D., Piazza, F.: Optimization algorithms for home energy resource scheduling in presence of data uncertainty. In: 2013 Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), pp. 323–328. IEEE (2013)
Boynuegri, A.R., Yagcitekin, B., Baysal, M., Karakas, A., Uzunoglu, M.: Energy management algorithm for smart home with renewable energy sources. In: 4th International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, pp. 1753–1758. IEEE (2013)
Dittawit, K., Aagesen, F.A.: On adaptable smart home energy systems. In: 2013 Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2013)
Zhou, S., Wu, Z., Li, J., Zhang, X.P.: Real-time energy control approach for smart home energy management system. Elect. Power Compon. Syst. 42(3–4), 315–326 (2014)
Missaoui, R., Joumaa, H., Ploix, S., Bacha, S.: Managing energy smart homes according to energy prices: analysis of a building energy management system. Energy Build. 71, 155–167 (2014)
Shahgoshtasbi, D., Jamshidi, M.M.: A new intelligent neuro–fuzzy paradigm for energy-efficient homes. IEEE Syst. J. 8(2), 664–673 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Zeng, P., Zang, C.: Optimization algorithm for home energy management system based on artificial bee colony in smart grid. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), pp. 734–740. IEEE (2015)
Hong, Y.Y., Chen, C.R., Yang, H.W.: Implementation of demand response in home energy management system using immune clonal selection algorithm. In: 2015 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pp. 3377–3382. IEEE (2015)
Ge, G.E.: BrillionTM Connected Appliances. General Electric. http://www.geappliances.com, http://www.geappliances.com/ge/connected-appliances/ (2018). Accessed 18 Aug 2019
Honda. Honda Smart Home US. http://www.hondasmarthome.com. http://www.hondasmarthome.com/tagged/hems (2018). Accessed 18 Aug 2019
Lujano-Rojas, J.M., Monteiro, C., Dufo-López, R., Bernal-Agustín, J.L.: Optimum residential load management strategy for real time pricing (RTP) demand response programs. Energy Policy 45, 671–679 (2012)
Ha Pham, T.T., Clastres, C., Wurtz, F., Bacha, S., Zamaï, E.: Optimal household energy management and economic analysis: from sizing to operation scheduling. (2008). http://halshs.archives-ouvertes.fr/halshs-00323581/en/
Ha, D.L., Ploix, S., Zamai, E., Jacomino, M.: Tabu search for the optimization of household energy consumption. In: IRI, pp. 86–92 (2006)
Ha, D.L., de Lamotte, F.F., Huynh, Q.H.: Real-time dynamic multilevel optimization for demand-side load management. In: 2007 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, pp. 945-949. IEEE (2007)
Yiyun, T., Can, L., Lin, C., Lin, L.: Research on vehicle-to-grid technology. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Distributed Control and Intelligent Environmental Monitoring, pp. 1013–1016. IEEE (2011)
Kempton, W., Tomić, J.: Vehicle-to-grid power fundamentals: Calculating capacity and net revenue. J. Power Sources 144(1), 268–279 (2005)
Al-Ali, A.R., El-Hag, A., Bahadiri, M., Harbaji, M., El Haj, Y.A.: Smart home renewable energy management system. Energy Procedia 12, 120–126 (2011)
Son, Y.S., Pulkkinen, T., Moon, K.D., Kim, C.: Home energy management system based on power line communication. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 56(3), 1380–1386 (2010)
Kahrobaee, S., Rajabzadeh, R.A., Soh, L.K., Asgarpoor, S.: A multiagent modeling and investigation of smart homes with power generation, storage, and trading features. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(2), 659–668 (2012)
Tsui, K.M., Chan, S.C.: Demand response optimization for smart home scheduling under real-time pricing. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(4), 1812–1821 (2012)
Han, J., Choi, C. S., Park, W. K., & Lee, I. : Green home energy management system through comparison of energy usage between the same kinds of home appliances. In: 2011 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE), pp. 1–4, IEEE (2011)
Son, Y.S., Pulkkinen, T., Moon, K.D., Kim, C.: Home energy management system based on power line communication. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 56(3), 1380–1386 (2010)
Han, J., Choi, C.S., Lee, I.: More efficient home energy management system based on ZigBee communication and infrared remote controls. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 57(1), 85–89 (2011)
Lee, J. I., Choi, C. S., Park, W. K., Han, J. S., & Lee, I. W.: A study on the use cases of the smart grid home energy management system. In ICTC 2011 IEEE pp. 746-750(2011)
Kuzlu, M., Pipattanasomporn, M., Rahman, S.: Hardware demonstration of a home energy management system for demand response applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(4), 1704–1711 (2012)
Dimeas, A., Drenkard, S., Hatziargyriou, N., Karnouskos, S., Kok, K., Ringelstein, J., Weidlich, A.: Smart houses in the smart grid: developing an interactive network. IEEE Electrif. Mag. 2(1), 81–93 (2014)
Mesarić, P., Krajcar, S.: Home demand side management integrated with electric vehicles and renewable energy sources. Energy Build. 108, 1–9 (2015)
Missaoui, R., Joumaa, H., Ploix, S., Bacha, S.: Managing energy smart homes according to energy prices: analysis of a building energy management system. Energy Build. 71, 155–167 (2014)
Asare-Bediako, B., Kling, W.L., Ribeiro, P.F.: Home energy management systems: evolution, trends and frameworks. In: 2012 47th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2012)
Al-Ali, A.R., El-Hag, A., Bahadiri, M., Harbaji, M., El Haj, Y.A.: Smart home renewable energy management system. Energy Procedia 12, 120–126 (2011)
Son, Y.S., Pulkkinen, T., Moon, K.D., Kim, C.: Home energy management system based on power line communication. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 56(3), 1380–1386 (2010)
Van Dam, S.S., Bakker, C.A., Buiter, J.C.: Do home energy management systems make sense? Assessing their overall lifecycle impact. Energy Policy 63, 398–407 (2013)
Yanyu, Z., Peng, Z., Chuanzhi, Z.: Review of home energy management system in smart grid. Power Syst. Protect. Control 42(18), 144–154 (2014)
Han, D.M., Lim, J.H.: Design and implementation of smart home energy management systems based on zigbee. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 56(3), 1417–1425 (2010)
Inoue, M., Higuma, T., Ito, Y., Kushiro, N., Kubota, H.: Network architecture for home energy management system. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(3), 606–613 (2003)
Erol-Kantarci, M., Mouftah, H.T.: Wireless sensor networks for cost-efficient residential energy management in the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2(2), 314–325 (2011)
Hu, Q., Li, F.: Hardware design of smart home energy management system with dynamic price response. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(4), 1878–1887 (2013)
IEA: Renewables information. International Energy Agency 2014. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/energy/renewables-information-2014_renew-2014-en. (2014). Accessed 18 Feb 2019
GENI: Renewable energy potential of small island states. Global Energy Network Institute. https://www.geni.org/globalenergy/library/technical-articles/generation/small-island-nations/renewable-energy-potential-of-small-island-states/Renewable%20Energy%20Potential%20of%20Small%20Island%20States1.pdf (2008). Accessed 18 Feb 2019
Vijayapriya, T., Kothari, D.P.: Smart grid: an overview. Smart Grid Renew. Energy 2(04), 305–311 (2011)
The Reegle Portal. https://www.reeep.org/policy-and-regulation-overview-country. Accessed 18 Aug 2019
Dena—German energy agency. Bruttostromerzeugung in Deutschland. https://www.auswaertiges-amt.de/blob/610620/5d9bfec0ab35695b9db548d10c94e57d/the-german-energiewende-data.pdf; https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Branchen-Unternehmen/Energie/Erzeugung/Tabellen/bruttostromerzeugung.html (2012). Accessed 20 Aug 2019
IRENA: Feed-in tariff specifications, features, amendments, and current and future challenges in Cyprus. Int. Renew Energy Agency. https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Events/2013/Jan/12/Country-Case-Study—Cyprus—George-Partasides.pdf?la=en&hash=750CFE0334B2E484D2ABF80BE2358F0F02FD8A4F. (2013)
The reegle portal. https://www.reeep.org/china-2014. Accessed 20 Aug 2019
Alvarez, R., Araque, J., Sierra, J.: A novel smart home energy management system: architecture and optimization model. Ind. J. Sci. Technol. 10(26), 1–8 (2017)
Tiptipakorn, S., Lee, W.J.: A residential consumer-centered load control strategy in real-time electricity pricing environment. In: 2007 39th North American Power Symposium, pp. 505-510. IEEE (2000)
Yu, T., Kim, D.S., Son, S.Y.: Optimization of scheduling for home appliances in conjunction with renewable and energy storage resources. Int. J. Smart Home 7(4), 261–272 (2013)
Zhu, Z., Lambotharan, S., Chin, W.H., Fan, Z.: Overview of demand management in smart grid and enabling wireless communication technologies. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 19(3), 48–56 (2012)
Flick, T., Morehouse, J.: Securing the smart grid: next generation power grid security. Elsevier, USA (2010)
Ancillotti, E., Bruno, R., Conti, M.: The role of communication systems in smart grids: Architectures, technical solutions and research challenges. Comput. Commun. 36(17–18), 1665–1697 (2013)
Denmark Wind Power Output. https://www.wsj.com/articles/denmarks-wind-power-output-rises-to-record-in-first-half-1409750563. Accessed 22 Aug 2019)
Basit, A., Hansen, A.D., Altin, M., Sørensen, P., Gamst, M.: Wind power integration into the automatic generation control of power systems with large-scale wind power. J. Eng. 10, 538–545 (2014)
REN21 Renewables 2011: global status report. https://www.ren21.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/GSR2011_Full-Report_English.pdf. (2011). Accessed 25 Aug 2019
The World Wind Energy Association. Half-year Report. WWEA. https://wwindea.org/blog/2016/10/10/wwea-half-year-report-worldwind-wind-capacity-reached-456-gw/. (2014). Accessed 26 Aug 2019
Raadal, H.L., Gagnon, L., Modahl, I.S., Hanssen, O.J.: Life cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the generation of wind and hydro power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(7), 3417–3422 (2011)
Torriti, J.: Price-based demand side management: assessing the impacts of time-of-use tariffs on residential electricity demand and peak shifting in Northern Italy. Energy 44(1), 576–583 (2012)
Asadinejad, A., Tomsovic, K.: Optimal use of incentive and price based demand response to reduce costs and price volatility. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 144, 215–223 (2017)
Erol-Kantarci, M., Mouftah, H.T.: Wireless sensor networks for cost-efficient residential energy management in the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2(2), 314–325 (2011)
Han, J., Choi, C.S., Lee, I.: More efficient home energy management system based on ZigBee communication and infrared remote controls. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 57(1), 85–89 (2011)
Mahmood, A., Ullah, M.N., Razzaq, S., Basit, A., Mustafa, U., Naeem, M., Javaid, N.: A new scheme for demand side management in future smart grid networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 32, 477–484 (2014)
Erol-Kantarci, M., Mouftah, H.T.: Wireless sensor networks for domestic energy management in smart grids. In: 2010 25th Biennial Symposium on Communications, pp. 63–66. IEEE (2010)
Pedrasa, M.A.A., Spooner, T.D., MacGill, I.F.: Coordinated scheduling of residential distributed energy resources to optimize smart home energy services. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 1(2), 134–143 (2010)
Lujano-Rojas, J.M., Monteiro, C., Dufo-López, R., Bernal-Agustín, J.L.: Optimum residential load management strategy for real time pricing (RTP) demand response programs. Energy Policy 45, 671–679 (2012)
Rezaee, Y., Sedaghati, A.: Optimal operation strategy of power systems in the presence of smart grids and electric vehicles. Majlesi J. Mechatr. Syst. 6(4), 31–40 (2018)
Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., Xu, G., Zhang, Q., Krundel, L.: Home energy management with PSO in smart grid. In: 2014 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), pp. 1666–1670. IEEE (2014)
Patel, K., Khosla, A.: Home energy management systems in future smart grid networks: a systematic review. In: 2015 1st International Conference on Next Generation Computing Technologies (NGCT), pp. 479–483. IEEE (2015)
NRC: Survey of household energy use 2007. Technical report. Natural Resources Canada. http://oee.nrcan.gc.ca/Publications/statistics/sheu07/pdf/sheu07.pdf. (2010). Accessed 26 Aug 2019
NRC: Energy use data handbook 1990–2010. http://oee.nrcan.gc.ca/publications/statistics/handbook2010/handbook2013.pdf. Accessed 27 Aug 2019
Molderink, A., Bakker, V., Bosman, M.G., Hurink, J.L., Smit, G.J.: Management and control of domestic smart grid technology. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 1(2), 109–119 (2010)
Clastres, C., Pham, T.H., Wurtz, F., Bacha, S.: Ancillary services and optimal household energy management with photovoltaic production. Energy 35(1), 55–64 (2010)
Costanzo, G.T., Zhu, G., Anjos, M.F., Savard, G.: A system architecture for autonomous demand side load management in smart buildings. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(4), 2157–2165 (2012)
Agnetis, A., De Pascale, G., Detti, P., Vicino, A.: Load scheduling for household energy consumption optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(4), 2364–2373 (2013)
Mazen, R., Radwan, M., Abdel-Samiea, M.: Utilization of biomass energy in high-rise buildings. In: 2013 4th International Youth Conference on Energy (IYCE), pp. 1–3. IEEE (2013)
Molderink, A., Bakker, V., Bosman, M.G., Hurink, J. L., Smit, G.J.: Domestic energy management methodology for optimizing efficiency in smart grids. In: 2009 IEEE Bucharest PowerTech, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2009)
The NEED project, Biomass. http://www.need.org/Files/curriculum/infobook/BiomassS.pdf. (2012) Accessed 25 Aug 2019
Carpio, M., Zamorano, M., Costa, M.: Impact of using biomass boilers on the energy rating and CO2 emissions of Iberian Peninsula residential buildings. Energy Build. 66, 732–744 (2013)
Berković-Šubić, M., Rauch, M., Dović, D., Andrassy, M.: Primary energy consumption of the dwelling with solar hot water system and biomass boiler. Energy Convers. Manag. 87, 1151–1161 (2014)
Huang, Y., Wang, Y.D., Rezvani, S., McIlveen-Wright, D.R., Anderson, M., Hewitt, N.J.: Biomass fuelled trigeneration system in selected buildings. Energy Convers. Manag. 52(6), 2448–2454 (2011)
Corno, F., Razzak, F.: Intelligent energy optimization for user intelligible goals in smart home environments. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(4), 2128–2135 (2012)
Oureilidis, K.O., Bakirtzis, E.A., Demoulias, C.S.: Frequency-based control of islanded microgrid with renewable energy sources and energy storage. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 4(1), 54–62 (2016)
Chen, X., Wei, T., Hu, S.: Uncertainty-aware household appliance scheduling considering dynamic electricity pricing in smart home. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(2), 932–941 (2013)
Chen, C., Wang, J., Kishore, S.: A distributed direct load control approach for large-scale residential demand response. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 29(5), 2219–2228 (2014)
US Department of Energy. Benefits of demand response in electricity markets and recommendations for achieving them: a report to the United State Congress pursuant to section 1252 of the Energy Policy Act of 2005. https://eetd.lbl.gov/sites/all/files/publications/report-lbnl-1252d.pdf. Accessed 25 Aug 2019
Nacer, A., Marhic, B., Delahoche, L.: Smart home, smart hems, smart heating: an overview of the latest products and trends. In: 2017 6th International Conference on Systems and Control (ICSC), pp. 90–95. IEEE (2017)
Khan, J.Y., Chen, D., Hulin, O.: Enabling technologies for effective deployment of internet of things (IoT) systems. Aust. J. Telecommun. Digit. Econ. (2014). https://doi.org/10.18080/ajtde.v2n4.65
Arbaz, A., Waqas, M., Shehzad, K., Mahmood, A.: Home energy management and knapsack technique in smart grid environment. In: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies (ICEET). Lahore, Pakistan (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahapatra, B., Nayyar, A. Home energy management system (HEMS): concept, architecture, infrastructure, challenges and energy management schemes. Energy Syst 13, 643–669 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-019-00364-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-019-00364-w