Abstract
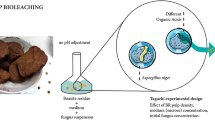
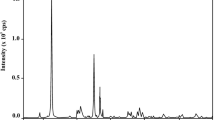
The demand for high-value metals and therefore metal prices are increasing rapidly due to the use of technological devices in construction and operation. The limited or lack of mineral resources of metals has increased the importance of studies on metal extraction from secondary sources such as mine waste. Hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical methods for metal extraction are not applicable due to their cost, environmental risks, and lower efficiency. Biological methods may be a suitable alternative because they are low cost, environmentally friendly, and effective at low metal contents. In this study, bioleaching for the extraction of Li, Rb, and Cs from clay-containing boron waste (BW) was investigated. BW was bioleached with Aspergillus niger (A. niger) in a growth medium in a shaking incubator at 30 °C and 125 rpm, and the pH, organic acids, and metal concentrations in the leaching liquid were measured at specific time intervals. The concentrations of Li, Rb, and Cs extracted during the 31 days were 298.7, 149, and 390 mg kg−1, respectively. The bioleaching residue was determined by FTIR and SEM–EDS analysis. Characterization of the residue revealed interactions between the metals and the metabolites secreted by the fungus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saxena N, Int J Lat Tren Eng Technol 6 (2015) 255.
Fazzo L, Minichilli F, Santoro M, Ceccarini A, Della S M, Bianchi F, Comba P, and Martuzzi M, Environ Health 16 (2017) 1.
Şensöz H, Sayın Z E, Savaş M, and Erdoğan Y, J Sci Eng 21 (2021) 1460. https://doi.org/10.35414/akufemubid.933125
Ertan B, and Erdoğan E, Powder Technol 295 (2016) 254.
Helvacı C, Mordoğan H, Çolak M, and Gündoğan İ, Int Geol Rev 46 (2004) 177.
Helvacı C, 71st Geological Congress of Turkey (2018) 265.
Ertan B, Pamukkale U J Eng Sc 26 (2020) 1267.
Jaskula B W, Lithium. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries 703 (2021) 648.
European Commission, Study on the EU’s list of Critical Raw Materials – Final Report (2020) https://doi.org/10.2873/11619.
Li H, Eksteen J, and Kuang G, Hydrometallurgy 189 (2019) 105129
Tuck C C, Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 703 (2022) 648.
Clearfield A, Solvent Extr Ion Exc 18 (2000) 655.
Naidu G, Loganathan P, Jeong S, Johir A H, Phuong To V H, Kandasamy J, and Vigneswaran S, Chem Eng J 306 (2016) 31.
Wang J, Che D, and Qin W, Chin J Chem Eng 23 (2013) 1110.
Yan Q, Li X, Wang Z, Wu X, Guo H, Hu Q, and Wang J, Hydrometallurgy 117 (2012) 116.
Bharadwaj A, and Ting Y P, Adv Mat Res 825 (2013) 280.
Bertrand J C, Caumette P, Lebaron P, Matheron R, Normand P, Sime-Ngando T, Environ Microbiol: Fundamentals and Applications, (Eds.). (2015), Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer, (pp. 659-753).
Srichandan H, Mohapatra R K, Parhi P K, and Mishra S, Hydrometallurgy 189 (2019) 105122
Anjum F, Shahid M, and Akcil A, Hydrometallurg 117 (2012) 1.
Burgstaller W, and Schinner F, J Biotechnol 27 (1993) 91.
Mulligan C N, Kamali M, and Gibbs B F, J Hazard Mater 110 (2004) 77.
Schuster E, Dunn-Coleman N S, Frisvad J C, and van Dijck P, Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59 (2002) 426.
Santhiya D, and Ting Y, J Biotechnol 121 (2006) 62.
Ren W X, Li P J, Geng Y, and Li X J, J Hazard Mater 167 (2009) 164.
Qu Y, Lian B, Mo B, and Liu C, Hydrometallurgy 136 (2013) 71.
Bindschedler S, Bouquet T Q T V, Job D, Joseph E, and Junier P, Adv Appl Microbiol 99 (2017) 53.
Sheel A, and Pant D, Bioresour Technol 247 (2018) 1189.
Alavi N, Partovi K, Majlessi M, Rashidi M, and Alimohammadi M, Bioresour Technol Rep 15 (2021) 100768
Faraji F, Golmohammadzadeh R, Rashchi F, and Alimardani N, J Environ Manag 217 (2018) 775.
Rasoulnia P, and Mousavi S M, Bioresour Technol 216 (2016) 729.
Li G, Sun J, Li F, Wang Y, and Li Q, Miner Eng 180 (2022) 107493
Keshavarz S, Faraji F, Rashchi F, and Mokmeli M, J. Environ. Manage 285 (2021) 112153
Bahaloo-Horeh N, and Mousavi S M, Waste Manag 60 (2017) 666.
Welch S A, Barker W W, and Banfield J F, Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63 (1999) 1405.
Gadd G M, Adv Microb Physiol 41 (1999) 47.
Goldberg R N, Kishore N, and Lennen R M, J Phys Chem Ref Data 31 (2002) 231.
Budavari S. The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals Drugs and Biologicals. 11th ed. centennial ed. Merck, 1989, 699 pp. ISBN: 978-0911910285.
Santos A, Yustos P, Quintanilla A, Ruiz G, and Garcia-Ochoa F, Appl Catal B Envir 61 (2005) 323.
Yang Q, Bin L, Binbin M, and Congqiang L, Hydrometallurgy 136 (2013) 71.
Sun L, and Qiu K, Waste Manag 32 (2012) 1575.
Bahaloo-Horeh N, Mousavi S M, and Shojaosadati S A, J Power Sources 320 (2016) 257.
Acknowledgement
The author would like to thank Prof. Dr. Arzu Görmez from Erzurum Technical University, Erzurum, Turkey, for providing fungal culture.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Dumlupinar University under grant number 2021–2041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ertan, B. Extraction of High-value Metals from Boron Waste by Bioleaching Using Aspergillus niger. Trans Indian Inst Met 76, 3137–3145 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03013-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03013-0