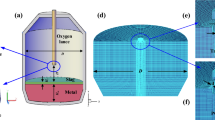
Abstract
Converter steelmaking is the primary steelmaking method because of its fast production rhythm and ability to handle molten iron. Despite its benefits, there are some limitations with this method that cannot be ignored. These limitations include excessive loss of iron by evaporation caused by a high-temperature fire spot zone and uneven melting of lump lime, which leads to an increase in steel consumption and a decrease in steelmaking efficiency. In view of these shortcomings, this study tested the approach of mixing a top-blown O2 lance with CO2. The mixture gas (80%O2 + 20%CO2) was used as a carrier gas to blow CaO powder from the top-blown oxygen lance into a molten bath. Based on the standard κ−ε turbulence model and the discrete particle model, the effects of flow rates of carrier gas on the distribution of gas and CaO powder jets were analyzed by numerical simulation. The simulation results show that the velocity of Cao powder increases with the increase in gas flow rate. The distribution area of Cao powder in radial section is more concentrated, and the deviation distance between Cao powder distribution and pore axis is shorter. At the same time, because of the inertia force of Cao powder, the attenuation speed of carrier gas jet in subsonic region slows down. The interaction between mixed carrier gas and powder is beneficial for the mixture gas and powder to participate in metallurgical reaction.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harada N, Tetsu To Hagane 69(1983) 1010.
Renjie J, Rong Z, and Lixin F, J Univ Sci Technol B (2007).
Xueliang W, Rong Z, and Binglong Z, MS&T2017 USA (2017).
Ming L, Rong Z, and Xinyuan W, Steel Res Int 83 (2012) 11.
Baochen H, Guangsheng W, and Rong Z. J CO2 UTIL 34 (2019) 53.
Liao D S, Sun S, Waterfall S, Boylan K, Pyke N, and Holdridge D, ICS2015 Beijing (2015).
R.Y. Z, TISCO 01(1991) 23.
Buydens J M, Nyssen P, and Knoops S, Metall Res Technol 90 (1993) 53.
Huang Y, and Guo X, The 18th Papers Collection of National Steelmaking Academic Conference (2014).
Carlsson G and Helle L W, Ordnance Mater Sci Eng 02 (1986) 61.
Ishii R, Umeda Y, and Yuhi M, J Fluid Mech 203 (1989) 475.
Singh R P, and Mcnallan M J, Metall Mater Trans B14 (1983) 425.
Miyata M and Higuchi Y, ISIJ Int 57 (2017) 1743.
Liang S B, Chem Eng Commun 197(2010) 1016.
Li Z D, Zhang G Q, Li Z, Zhang Y, and Xu W Y, J Iron Steel Res Int 15 (2008) 44.
Wang H, Zhu R, and Gu Y L, Can Metall Quart 53 (2014) 367.
Lv M, Zhu R, and Wang H, Steel Res Int 84 (2013) 304.
Sun Y H , Liang X T, and Zeng J H, Ironmak Steelmak 44 (2016) 76.
Lu W G, M. Lü, and Pan H T, Iron Steel 49(2014) 36.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their thanks for the support by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 51574021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Zhu, R., Feng, C. et al. Influence of Carrier Gas of Converter Oxygen Lance on Smooth Distribution of O2−CO2−CaO Mixed Jet. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 3027–3035 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02105-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02105-5