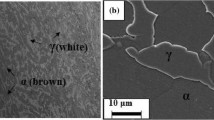
Abstract
Duplex stainless steels (DSSs) are prone to formation of various secondary phases in their microstructure upon exposure to high temperatures which can lead to degradation in their engineering performance. The present work was aimed to study the effect of a wide range of isothermal treatments (475°–1050 °C) on the impact toughness and corrosion resistance besides microstructure, ferrite content and microhardness of gas tungsten arc (GTA) welded 2205 DSS. It was observed that the isothermal exposure at 850 °C for 2 h led to maximum ferrite content reduction, imparted maximum hardening, caused maximum embrittlement of the weld metal (203 J → 2 J) and HAZ (204 J → 3 J) regions of the weldment besides causing maximum degradation in the pitting corrosion resistance. Corresponding to the aging condition of 475 °C/20 h, reduction in the ferrite content was not much, however, a significant increase in the microhardness along with severe loss in the toughness of the weld metal (203 J → 6 J) occurred, but the HAZ region was relatively tolerant (204 J → 54 J) against loss of toughness. In general, impact and corrosion properties were highly sensitive to degradation at 850 °C. Hence it can be inferred that the amount of ferrite content reduction cannot be directly correlated with the extent of hardening, decrease in the toughness and corrosion resistance; as such, changes will be primarily governed by the type of secondary precipitation which is temperature and exposure duration-dependent in the case of DSS welds.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh J, and Shahi A S, Trans Ind Inst Met 72 (2019) 1497.
Haddad N I A, The development of microstructure in duplex stainless steel welds, Doctoral dissertation, University of Cambridge, (1990).
Charles J, Why and where duplex stainless steels. Duplex stainless Steels’ 97 (1997) 345.
Brozda J, and Lomozik M, Welding International 16 (2002) 5.
Practical Guidelines for the Fabrication of Duplex Stainless Steel, IMOA (2014) Third Edition, ISBN 978-1-907470-09-7.
Alvarez-Armas I, Degallaix-Moreuil S (Ed.), Duplex stainless steels, ISTE Ltd. and Wiley (2009) ISBN 978-1-84821-137-7.
Olsson J, and Snis M, Desalination 205 (2007) 104.
Hoffman J P, J S Afr Inst Min Metall, 86 (1986) 433.
Thorvaldsson T, Eriksson H, Kutka J, and Salwén A, Influence of microstructure on mechanical properties of a duplex stainless steel. Stainless Steel’84, Chalmers University of Technology, (1984) 101–105.
Fargas G, Anglada M, and Mateo A, J Mater Process Techn 209 (2009) 1770.
Miodownik A P, and Saunders N, Mater Sci Techn 18 (2002) 861.
Redjaimia A, Metauer G, and Gantois M, Decomposition of Delta Ferrite in an Fe–22 Cr–5 Ni–3 Mo–0. 03 C Duplex Stainless Steel. A Morphological and Structural Study; In Proceedings of the Duplex Stainless Steels (’91); Beaune 1 (1991) 119–126.
Josefsson B, Nilsson J O, and Wilson A, Phase transformations in duplex steels and the relation between continuous cooling and isothermal heat treatment. Duplex Stainless Steels’91, 1 (1991) 67–78.
Nilsson J O, Mater Sci Techn 8 (1992) 685.
Chen T H, Weng K L, and Yang J R, Mater Sci Eng A 338 (2002) 259.
Hoffmeister H and Lothongkum G, Quantitative effects of nitrogen contents and cooling cycles on δ-γ transformation, chromium nitride precipitation and pitting corrosion after weld simulation of duplex stainless steels. In: Proceedings of the fourth international conference on duplex stainless steels 2 (1994) 80–89.
Kotecki Demian J, Soldag. Insp. 15 (2010) 336.
El Koussy M R, El Mahallawi I S, Khalifa W, Al Dawood M M, and Bueckins M, Mater Sci Techn 20 (2004) 375.
Jebaraj A V, and Ajaykumar L, Proc Eng 64 (2013) 456.
Badji R, Bouabdallah M, Bacroix B, Kahloun C, Belkessa B, and Maza H, Mater Charac 59 (2008) 447.
Badji R, Bouabdallah M, Bacroix B, Kahloun C, Bettahar K, and Kherrouba N, Mater Sci Eng A 496 (2008) 447.
Kashiwar A, Vennela N P, Kamath S L, and Khatirkar R K, Mater Charac 74 (2012) 55.
Ghosh S K, and Mondal S, Mater Charac 59 (2008) 1776.
Escriba D M, Materna-Morris E, Plaut R L, and Padilha A F, Mater Charac 60 (2009) 1214.
Örnek C, Burke M G, Hashimoto T, and Engelberg D L, Metall and Mat Trans A 48 (2017) 1653.
Wilms M E, Gadgil V J, Krougman J M, and Kolster B H, Mater High Temp 9 (1991) 160.
Singh J, and Shahi A S, J Mater Process Tech 272 (2019) 137.
Singh J, and Shahi A S, J Manuf Process 50 (2020) 581.
Taban E, and Kaluc E, Weld World 55 (2011) 48.
ASTM G48 Standard Test Methods for Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steels and Related Alloys by Use of Ferric Chloride Solution.
Fu W, Yang Y S, Guo J J, and Tong W H, Mater Sci Techn 24 (2008) 941.
Verma J, and Taiwade R V, J Manuf Process 25 (2017) 134.
Fourie J W, and Robinson F P A, J S Afr Inst Min Metall 90 (1990) 59.
Zhang Z, Jing H, Xu L, Han Y, and Zhao L, Mater Des 109 (2016) 670.
Hosseini V A, Hurtig K, and Karlsson L, Weld World 64 (2020) 283.
Atamert S, and King J E, J Mater Sci Lett 12 (1993) 1144.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the infrastructural support extended in the form of testing facilities by Welding Metallurgy Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sant Longowal Institute of Engineering and Technology, Longowal, Sangrur-148106 (Punjab), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Singh, J. & Shahi, A.S. Investigation on Aging-Induced Degradation of Impact Toughness and Corrosion Performance of Duplex Stainless Steel Weldment. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 2747–2765 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02070-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02070-z