Abstract
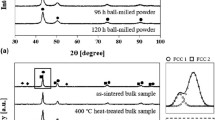
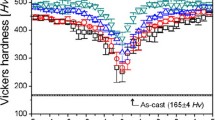
Two-phase microstructure was realized in CoCrFeMnNi system using a combination of ball milling and spark plasma sintering at 1273 K. Microstructure consisted of finer average grain size with broader grain size distribution, complex solid solution phases (a major face-centered cubic phase and a minor body-centered cubic phase) with very close lattice constants, dislocations and nano twins. A high hardness of 6.3 GPa and a negative strain rate sensitivity (with no associated serrated flow) of − 0.0206 were observed. Various interactions between dislocations and grain boundaries/interphase boundaries/twin boundaries, prevailing atomic level complex chemistry in the lattices, interfaces and dislocation cores might be the reasons for the observed flow characteristics. Dislocation–solute atom interactions observed in conventional dilute alloys that have resulted in negative strain rate sensitivity and dynamic strain aging may not be operating in the present alloy system under the given set of test conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, Gan J Y, Chin T S, Shun T T, Tsua C H, and Chang S Y, Adv Eng Mater 6 (2004) 299.
Cantor B, Chang I T H, Knight P, and Vincent A J B, Mater Sci Eng A 375–377 (2004) 213.
Murty B S, Yeh J W, Ranganathan S, and Bhattacharjee P P, High-Entropy Alloys, Elsevier, Amsterdam (2019).
Gao M C, Yeh J W, Liaw P K, and Zhang Y., High-Entropy Alloys, Springer, Berlin (2016).
Miracle D B, and Senkov O N, Acta Mater 122 (2017) 448.
Zhao Y, Lee D H, Seok M Y, Lee J A, Phaniraj M P, Suh J Y, Ha H Y, Kim J Y, Ramamurty U, and Jang J I, Scr Mater 135 (2017) 54.
Lee D H, Choi I C, Yang G, Lu Z, Kawasaki M, Ramamurty U, Schwaiger R, and Jang J I, Scr Mater 156 (2018) 129.
Gludovatz B, Hohenwarter A, Catoor D, Chang E H, George E P, and Ritchie R O, Science 345 (2014) 1153.
Zhang Z, Mao M M, Wang J, Gludovatz B, Zhang Z, Mao S X, George E P, Yu Q, and Ritchie R O, Nat Commun 6 (2015), 10143.
Koch C C, J Mater Res 32 (2017) 3435.
Vaidya M, Muralikrishna G M, and Murty B S, J Mater Res 34 (2019) 664.
Joo S H, Kato H, Jang M J, Moon J, Kim E B, Hong S J, and Kim H S, J Alloys Compd 698 (2017) 591.
Ganji R S, Karthik P S, Rao K B S, and Rajulapati K V, Acta Mater 125 (2017) 58.
Kocks U F, Argon A S, and Ashby M F, Prog Mater Sci 19 (1975) 1.
Wei Q, Cheng S, Ramesh K T, and Ma E, Mater Sci Eng A 381 (2004) 71.
Varam S, Narayana P V S L, Prasad M D, Chakravarty D, Rajulapati K V, and Bhanu Sankara Rao K, Phil Mag Lett 94 (2014) 582.
Varam S, Rajulapati K V, Bhanu Sankara Rao K, Scattergood R O, Murty K L, and Koch C C. Metall Mater Trans A 45 (2014) 5249.
Komarasamy M, Alagarsamy K, and Mishra R S, Intermetallics 84 (2017) 20.
Yasuda H Y, Shigeno K, and Nagase T, Scr Mater 108 (2015) 80.
Maier-Kainer V, Schuh B, George E P, Clemens H, and Hohenwarter A, J Mater Res 32 (2017) 2658.
Basu S, Li Z, Pradeep K G, and Raabe D, Front Mater 5 (2018) 30.
Dieter G E, Mechanical Metallurgy, Third Edition, McGraw Hill Education (India), Bangalore (2013) p 311.
Bhanu Sankara Rao K, Kalluri S, Halford G R, and McGaw M A, Scr Metall Mater 32 (1995) 493.
Cottrell A H, and Bilby B A, Proc Phys Soc Lond A 62 (1949) 49.
Picu R C, Acta Mater 52 (2004), 3447.
Yoshida S, Bhattacharjee T, Bai Y, and Tsuji N, Scr Mater 134 (2017) 33.
Lu L, Schwaiger R, Shan Z W, Dao M, Lu K, and Suresh S, Acta Mater 53 (2005) 2169.
Acknowledgements
The experimental facilities used in this work at University of Hyderabad were supported by various schemes i.e., DST-PURSE, DST-FIST and Central Facility for Nanotechnology, funded by the Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abhijit, A., Varghese, J., Chalavadi, P. et al. Negative Strain Rate Sensitivity in Two-Phase Nanocrystalline CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy with Broader Grain Size Distribution Studied by Nanoindentation. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 2861–2867 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01762-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01762-5