Abstract
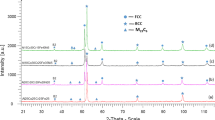
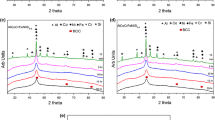
TiAlNiCr, TiAlNiCrCo, TiAlNiCrFe, TiAlNiCrCoFe, TiAlNiCo, TiAlNiFe and TiAlNiCoFe high-entropy alloys were processed through mechanical alloying followed by spark plasma sintering (SPS). All the alloys develop a BCC (Cr-/Cr–Fe-rich) structure after mechanical alloying. Sintering at high temperature promotes the formation of one more BCC phase which is of NiAl type. Phase evolution after mechanical alloying and SPS was studied using X-ray diffraction. Composition of the phases was analysed using energy-dispersive spectroscopy, and microstructural characterisation was done using back-scattered electron images. Characterisation studies done on the alloys confirm the presence of BCC phases. Alloys without Cr develop a single BCC peak after SPS compared to alloys with Cr.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, Gan J Y, Chin T S, Shun T T, Tsau C H, and Chang S Y, Adv Eng Mater 6 (2004), 299.
Miracle D B, and Senkov O N, Acta Materialia, 122 (2017).
Jiang S, Lin Z, Xu H, and Sun Y, J Alloys Compd 741 (2018), 826.
Lindner T, Löbel M, Mehner T, Dietrich D, and Lampke T, Metals (Basel) 7 (2017), 162.
Hou J, Zhang M, Ma S, Liaw P K, Zhang Y, and Qiao J, Mater Sci Eng A 707 (2017), 593.
Moravcik I, Cizek J, Zapletal J, Kovacova Z, Vesely J, Minarik P, Kitzmantel M, Neubauer E, Dlouhy I, Mater Des 119 (2017), 141.
Singh S, Wanderka N, Kiefer K, Siemensmeyer K, and Banhart J, Ultramicroscopy 111 (2011), 619.
Fu Z, Chen W, Fang S, and Li X, Mater Sci Eng A 597 (2014), 204.
Salishchev G A, Tikhonovsky M A, Shaysultanov D G, Stepanov N D, Kuznetsov A V, Kolodiy I V, Tortika A S, and Senkov O N, J Alloys Compd 591 (2014), 11.
Zhang L, Zhou D, and Li B, Mater Lett 216 (2018), 252.
Wang Z, Guo S, Wang Q, Liu Z, Wang J, Yang Y, and Liu C T, Intermetallics 53 (2014), 183.
Chen Z, Chen W, Wu B, Cao X, Liu L, and Fu Z, Mater Sci Eng A 648 (2015), 217.
Miedema A R, de Boer F R, and Boom R, Calphad 1 (1977), 341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand Sekhar, R., Bakshi, S.R. Microstructural Evolution of Ti–Al–Ni (Cr,Co,Fe)-Based High-Entropy Alloys Processed Through Mechanical Alloying. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 1427–1430 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01596-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01596-1