Abstract
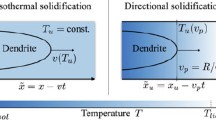
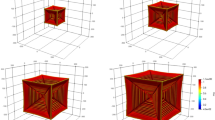
We have presented current ideas towards developing a phase-field model appropriate to the solidification of intermetallic phases. Such simulation presents two main challenges (1) dealing with faceted interfaces and (2) the complex sublattice models used to describe the thermodynamics of such phases. Although models already exist for the simulation of faceted crystals, some of these can be shown to produce highly unrealistic Wulff shapes. The model present here uses a parameterisation of the Wulff shape as a direct input to the model, allowing the simulation of arbitrary crystal shapes. In addition, an anti-trapping current that can be used with arbitrary (including sublattice) thermodynamics is presented. Such anti-trapping currents are vital in the simulation of intermetallic phases where the steep liquidus slope means small deviations in solute partitioning behaviour leading to a significant change in tip undercooling.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
SGTE - Scientific Group Thermodata Europe, see www.sgte.net/en/about-sgte.
Choudhury A, Kellner M, and Nestler B, Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 19 (2015) 287.
Ohno M, Takaki T, and Shibuta Y, Phys Rev E 96 (2017) 33311.
Taylor J E, and Cahn J W, Physica D 112 (1998) 381.
Eggleston J J, McFadden G B, and Voorhees P W, Physica D 150 (2001) 91.
Debierre J-M, Karma A, Celestini F, and Guerin R, Phys Rev E 68 (2003) 041604.
Choi J, Park S-K, Hwang H-Y, and Huh J-Y, Acta Mater 84 (2015) 55.
Abinandanan T A, and Haider F, Philos Mag A 81 (2001) 2457.
Nani E S, and Gururajan M P, Philos Mag 94 (2014) 3331.
Karma A, Phys Rev Lett 87 (2001) 115701.
Galenko P K, Abramova E V, Jou D, Danilov D A, Lebedev V G, and Herlack D M, Phys Rev E 84 (2011) 041143.
Mullis A M, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf 40 (1997) 4085.
Zhang L, Danilova E V, Steinbach I, Medvedev D, and Galenko, P K, Acta Mater 61 (2013) 4155.
Bollada P C, Jimack P K, and Mullis A M, Comput Mater Sci 126 (2016) 426.
Bollada P C, Goodyer C E, Jimack P K, Mullis A M, and Yang F W, J Comput Phys 287 (2015) 130.
Brandt A, Math Comput 31 (1977) 333.
MacNeice P, Olson K M, Mobarry C, de Fainchtein R, and Packer C, Comput Phys Commun 126 (2000) 330.
Redlich O, and Kister A, Ind Eng Chem 40 (1948) 345.
Lengsdorf R, Holland-Moritz D, and Herlach D M, Acta Mater 62 (2009) 365.
Bollada P C, Jimack P K, and Mullis A M, Comput Mater Sci 151 (2018) 338.
Bollada P C, Jimack P K, and Mullis A M, Comput Mater Sci 144 (2018) 76.
Liu R B, Herlach D M, Vandyiousse M, and Greer A L, Metal Mat Trans A 35 (2003) 1067.
Battersby S E, Cochrane R F, and Mullis A M, Mater Sci Eng A 226 (1997) 443.
Battersby S E, Cochrane R F, and Mullis A M, J Mater Sci 34 (1999) 2049.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by EPSRC Innovative Manufacturing Research Hub in Liquid Metal Engineering (LiME), Grant No. EP/N007638/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mullis, A.M., Bollada, P.C. & Jimack, P.K. Simulation of Intermetallic Solidification Using Phase-Field Techniques. Trans Indian Inst Met 71, 2617–2622 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1428-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1428-3