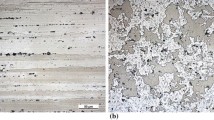
Abstract
Fatigue resistance of structural materials is considered as one of the most important factors in design of structural components for integrity, efficiency and safe functioning under repeated mechanical/thermal loading. Fatigue resistance of structural alloys is characterized in terms of appropriate parameters based on high cycle/low cycle fatigue loading. Fatigue life comprises of two components, number of cycles for crack initiation and for crack propagation. While there is dominant role of the process of crack initiation in high cycle fatigue, low cycle fatigue is controlled by crack propagation. Invariably, fatigue cracks initiate from the surface and surface modification has been used for enhancement of fatigue life, delaying the process of crack initiation. Inducement of compressive residual stress in surface region through shot peening has been one of the most widely used conventional process of enhancing high cycle fatigue life. This paper presents the effect of surface grain refinement, using the novel technique of ultrasonic shot peening, on enhancement of fatigue life of structural alloys at low stress/strain.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tao N R, Sui M L, Lu J, and K Lu, Nanostruct Mater 11 (1999) 433.
Liu G, Lu J, and Lu K, Mater Sci Eng A 286 (2000) 91.
Liu G, Wang S C, Lou X F, Lu J, and Lu K, Scripta Mater 44 (2001) 1791.
Wu X, Tao N, Hong Y, Xu B, Lu J, and Lu K, Acta Mater 50 (2002) 2075.
Lu K, and Lu J, Mater Sci Eng A 375 (2004) 38.
Nalla R K, Altenberger I, Noster U, Liu G Y, Scholtes B, and Ritchie R O, Mater Sci Eng A 355 (2003), 216.
Clauer A H, Laser Shock Peening for Fatigue Resistance, Surface Performance of Titanium, Warrendale (1996), p 217.
Janosch J J, Koneczny H, Debiez S, Statnikov E C, Troufiakov V J, and Mikhee P P, Improvement of Fatigue Strength in Welded Joints (in HSS and in Aluminium Alloys) By Ultrasonic Hammer Peening, Welding in The World, London (1996), p 72.
Jian L, J Mater Sci Technol 15 (1999) 193.
Sonsino C M, Mueller F, and Mueller R, Int J Fatigue 14 (1992) 3.
Umemoto M, Todaka K, and Tsuchiya K, Mater Sci Eng A 375–377 (2004), 899.
Umemoto M, Mater Trans 44 (2003) 1900.
Li J G, Umemoto M, Todaka Y, and Tsuchiya K, Mater Sci Eng A 435–436 (2006) 383.
Lu K, and Lu J, Mater Sci Eng A 375–377 (2004) 38.
Liu G, Lu J, and Lu K, Mater Sci Eng A 286 (2000) 91.
Wu X, Tao N, Hong Y, Xu B, Lu J, and Lu K, Acta Mater 50 (2002) 2075.
Tao N R, Wang Z B, Tong W P, Lu J, and Lu K, Acta Mater 50 (2002) 4603.
Zhang H W, Hei Z K, Liu G, Lu J, and Lu K, Acta Mater 51 (2003) 1871.
Wang K, Tao N R, Liu G, Lu J, and Lu K, Acta Mater 54 (2006) 5281.
Zhu K Y, Vassel A, Brisset F, Lu K, and Lu J, Acta Mater 52 (2004) 4101.
Wu X, Tao N, Hong Y, Liu G, Xu B, Lu J, and Lu K, Acta Mater 53 (2005) 681.
Sun H Q, Shi Y N, Zhang M X, and Lu K, Acta Mater 55 (2007) 975.
Chattopadhyay K, Pandey V, Srinivas N C S, and Singh V, IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 63 (2014) 012017.
Li J, Chen S, Wu X, Soh A, and Lu J, Mater Sci Eng A 527 (2010) 7040.
Cai B, Ma X, Moering J, Zhou H, Yang X, and Zhu X, Mater Sci Eng A 626 (2015) 144.
Yang X, Ma X, Moering J, Zhou H, Wang W, Gong Y, and Zhu X, Mater Sci Eng A 645 (2015) 280.
Kumar S, Rao G S, Chattopadhyay K, Mahobia G S, Srinivas N C S, and Singh V, Mater Design 62 (2014) 76.
Pandey V, Rao G S, Chattopadhyay K, Srinivas N C S, and Singh V, Mater Sci Eng A 647 (2015) 201.
Rai P K, Pandey V, Chattopadhyay K, Singhal L K, and Singh V, J Mater Eng Perf 23 (2014) 4055.
Wu X L, Jiang P, Chen L, Zhang J F, Yuan F P, and Zhu Y T, Mater Res Lett 2 (2014) 185.
Chen X H, Lu J, Lu L, and Lu K, Scr Mater 52 (2005) 1039.
Suresh S, Fatigue of Materials, Cambridge University Press, New York (1991).
Hanlon T, Kwon Y N, and Suresh S, Scr Mater 49 (2003) 675.
Mughrabi H, Hoppel H W and Kautz M, Scr Mater 51 (2004) 807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V., Pandey, V., Kumar, S. et al. Effect of Ultrasonic Shot Peening on Surface Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Structural Alloys. Trans Indian Inst Met 69, 295–301 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0771-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0771-x