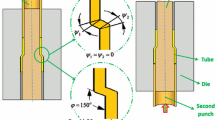
Abstract
In this study, ultra-fine grained (UFG) Cu–Zn tubes were produced by parallel tubular channel angular pressing (PTCAP) process and the effects of the number of passes on the microstructure, mechanical properties and fracture behavior were investigated. The results showed that the yield and the ultimate strengths of the processed UFG tube increased about four and two folds compared to the coarse grain counterparts due to grains refinement. The notable increase in the strength achieved after the first pass of the PTCAP process and further passes of the process only have a minor effect on the tube properties which may be due to the grain size saturation. However, the tube ductility reduced drastically after the PTCAP processing. Hardness of the PTCAP processed tube was increased compared to the annealed one according to Hall–Petch relationship which reports the hardness in terms of grain size. The strength, hardness and ductility were decreased after two passes PTCAP as a result of the formation of microvoids during the further straining through three passes. Microstructural investigations show a notable decrease in the grain size.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valiev R Z, Islamgaliev R K, Alexandrov I V, Prog Mater Sci, 45 (2000) 103.
Zehetbauer M, Stüwe H, Vorhauer A, Schafler E, Kohout J, Adv Eng Mater, 5 (2003) 330.
Langdon T G, Mater Sci Eng: A, 462 (2007) 3.
Zhilyaev A, Langdon T, Prog Mater Sci, 53 (2008) 893.
Saito Y, Utsunomiya H, Tsuji N, Sakai T, Acta Mater, 47 (1999) 579.
Segal V, Mater Sci Eng: A, 197 (1995) 157.
Orlov D, Raab G, Lamark T T, Popov M, Estrin Y, Acta Mater, 59 (2011) 375.
Ferrasse S, Segal V, Kalidindi S, Alford F, Mater Sci Eng: A, 368 (2004) 28.
Xu C, Furukawa M, Horita Z, Langdon T G, Acta Mater, 53 (2005) 749.
Zhao Y H, Liao X Z, Jin Z, Valiev R Z, Zhu Y T, Acta Mater, 52 (2004) 4589.
Eizadjou M, Manesh H D, Janghorban K, J Alloys Compd, 474 (2009) 406.
Terada D, Inoue S, Tsuji N, J Mater Sci, 42 (2007) 1673.
Wei Q, Zhang H, Schuster B, Ramesh K, Valiev R, Kecskes L, Dowding R, Magness L, Cho K, Acta Mater, 54 (2006) 4079.
Faraji G, Babaei A, Mashhadi M M, Abrinia K, Mater Lett, 77 (2012) 82.
Faraji G, Mashhadi M M, Kim H S, Mater Lett, 65 (2011) 3009.
Faraji G, Mashhadi M M, Bushroa A R , Babaei A, Mater Sci Eng A, 563 (2013) 193.
Mesbah M, Faraji G, Bushroa A R, Mater Sci Eng A, 590 (2014) 289.
Afrasiab M, Faraji G, Tavakkoli V, Mashhadi M M, Bushroa A R, Mater Sci Eng: A, 599 (2014) 141.
Kim W, An C, Kim Y, Hong S, Scripta Mater, 47 (2002) 39.
Ghasemi-Nanesa H, Nili-Ahmadabadi M, Mirsepasi A, Zamani C, Met Mater Int, 20 (2014) 201.
Valiev R Z, LangdonT G, Prog Mater Sci, 51 (2006) 881.
Pasebani S, Toroghinejad M R, Mater Sci Eng A, 527 (2010) 491.
Subramanya Sarma V, Sivaprasad K, Sturm D, Heilmaier M, Mater Sci Eng: A, 489 (2008) 253.
Suryadi S, Napitupulu R, Priadi D, Suhadi A, Siradj E S, Adv Mater Res, 789 (2013) 373.
Tavakkoli V, Afrasiab M, Faraji G, Mashhadi M M, Mater Sci Eng: A, 625 (2015) 50.
Shaarbaf M, Toroghinejad M R, Mater Sci Eng: A, 473 (2008) 28.
Sharififar M, Mousavi S A A A, Mater Sci Eng: A, 594 (2014) 118.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afrasiab, M., Faraji, G., Tavakkoli, V. et al. The Effects of the Multi-pass Parallel Tubular Channel Angular Pressing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Cu–Zn Tubes. Trans Indian Inst Met 68, 873–879 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0524-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0524-x