Abstract
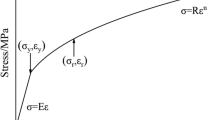
Nanoindentation experiments were carried out at strain rates of 0.05, 0.10, 0.15 and 0.20/s at indentation depths of 1000, 1500 and 2000 nm to investigate the nanomechanical behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The strain rate had little influence on nanohardness, however, nanohardness as well as Young’s modulus gradually decreased with the increase of indentation depth indicating strong indentation size effects. The relation between H2 and 1/h exhibited a good linear relationship, and it is observed that the effect of strain gradient on σ/σ0 is significant at high strain rates according to Nix and Gao strain gradient model. The analysis of plastic behaviour revealed that, strain rates had no significant effect on strain hardening exponent, but had little influence on yield stress.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A proj :
-
Projected Area.nm2
- b :
-
Burgers vector, nm
- C :
-
Loading curvature
- D :
-
Damage Variable
- E* :
-
Reduced Young’s modulus, GPa
- E :
-
Specimen Young’s modulus from Nanoindentation GPa,
- E u :
-
Young’s modulus of undamaged material, GPa
- H :
-
Hardness, GPa
- H 0 :
-
Nanoindentation hardness for a large indentation depth, GPa
- h :
-
Indentation depth, nm
- h* :
-
Characteristic length, nm
- h c :
-
Indenter contact depth, nm
- h m :
-
Max indentation depth, nm
- h r :
-
Reduced indentation depth, nm
- n :
-
Strain Hardening Exponent
- P :
-
Indentation load, mN
- P max :
-
Maximum indentation load, mN
- S :
-
Slope of the unloading curve
- \( \nu_{s} \) :
-
Poisson ratio of the specimen
- \( \nu_{i} \) :
-
Poisson ratio of the indenter
- σ :
-
Flow stress in the presence of a strain gradient, MPa
- σ o :
-
Flow stress in the absence of strain gradient, MPa
- σ y :
-
Yield stress, MPa
- ρ s :
-
Density of statistically stored dislocations,
- μ :
-
Shear modulus, GPa
- θ :
-
Angle between the surface of the indenter and the plane of the specimen surface
- \( \chi \) :
-
Strain gradient
- l ^ :
-
Intrinsic material length scale, µm
- ε :
-
Strain
- ε p :
-
Plastic strain
- γ :
-
Indenter Geometry constant
References
Liu Y, and Ngan A H W, Scripta Mat 44 (2001) 237.
Tekaya A, Labdi S, Benameur T, and Jellad A, J Mater Sci 44 (2009) 4930.
Lee D J, Alloy Compd 480 (2009) 347.
Deng X, Chawla N, Chawla K K, and Koopman M, Acta Mater 52 (2004) 4291.
Swain M V, Mater Sci Eng A 253 (1998) 166.
Venkatesh T A, Van Vliet K J, Giannakopoulos A E, and Suresh S, Scripta Mater 42 (2000) 833
Chollacoop N, Dao M, and Suresh S, Acta Mater 51 (2003) 3713.
Field J S, and Swain M V, J Mater Res 8 (1993) 297.
Field J S, and Swain M V, J Mater Res 10 (1995) 101.
Mayo M J, and Nix W D, Acta Metall 36 (1988) 2183.
Raman V, and Berriche R, J Mater Res 7 (1992) 627.
Poisl W H, Oliver W C, and Fabes B D, J Mater Res 10 (1995) 2024.
Pharr G M, Mater Sci Eng A 253 (1998) 151.
Jang B K, J Alloy Comp 426 (2006) 312.
Montanari B, Costanza G, Tata M E, and Testani C, Mater Charact 59 (2008) 334.
Biswas A, and Majumdar D, J Mater Charact 60 (2009) 513.
Vanderhasten M, Rabet L, and Verlinden B, Mater Des 29 (2008) 1090.
Seshacharyulu T, Medeiros S C, Frazier W G, and Prasad Y V R K, Mater Sci and Engg A 284 (2000) 184.
Kumaraswamy A, and Vekataraman B, Scripta Materialia 54 (2006) 493.
Cai J, Li F, Liu T, and Bo C, Mater charact 62 (2011) 287.
Mcekhaney K W, Vlasak J J, and Nix W D, J Mater Res 13 (1998) 1300.
Shu J Y, and Fleck N A, Int J Solids Struct 161 (1998) 49.
Nix W D, and Gao H, J Mech Phys Solids 46 (1998) 411.
Oliver W C, and Pharr G M, J Mater Res 7 (1992) 1564.
Ma Q, and Clarke D R, J Mater Res 10 (1995) 853.
Castany P, Pettinari-Sturmel F, Crestou J, Douin J, and Coujou A, Acta Mater 55 (2007) 6284.
Guelorget B, and François M, J Mater Lett 61 (2007) 34.
Dao M, Chollacoop N, Van Vliet K J, Venkatesh T A, and Suresh S, Acta Mat 49 (2001) 3899.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Vice chancellor, DIAT (DU), Pune for granting permission to publish this paper. The help provided by technical staff at Central Manufacturing Technology Institute (CMTI), Bangalore to use the facilities for conducting nanoindentation experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SridharBabu, B., Kumaraswamy, A. & AnjaneyaPrasad, B. Effect of Indentation Size and Strain Rate on Nanomechanical Behavior of Ti-6Al-4VAlloy. Trans Indian Inst Met 68, 143–150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-014-0438-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-014-0438-z