Abstract
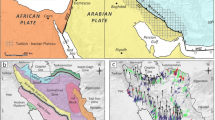
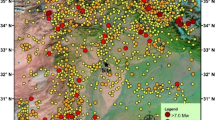
This study aimed to perform a comprehensive Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment (DSHA) to quantify the Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA) values for the Lowari Tunnel region. Twelve thrust faults in the vicinity of the tunnel were evaluated using an updated earthquake catalog from 25AD to 2022. The PGA values were calculated for each thrust fault and compared with the designed value of 0.5 g from the feasibility stage of the tunnel. The study demonstrated that all twelve thrust faults exhibited PGA values below 0.5 g, indicating a low-to-moderate seismic hazard in the region. The maximum PGA value obtained in this study was 0.4 g, which is well below the maximum designed value, indicating that the tunnel is expected to withstand the ground motion values projected to result from high-magnitude earthquakes in the region. These findings hold significant importance as they provide crucial insights into assessing the long-term sustainability of the Lowari Tunnel, situated in one of the world's most seismically active zones.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abrahamson N, Silva W (2008) Summary of the Abrahamson & Silva NGA ground-motion relations. Earthq Spectra 24(1):67–97
Abrahamson NA, Silva WJ, Kamai R (2014) Summary of the ASK14 ground motion relation for active crustal regions. Earthq Spectra 30(3):1025–1055
Ahmad ME, Khan FZ, Ahmad N (2021) Seismic performance assessment of confined adobe masonry structures. NED Univ J Res 18:1–13
Ahmed A, Shahzada K, Ali SM, Khan AN, Shah SAA (2019) Confined and unreinforced masonry structures in seismic areas: validation of macro models and cost analysis. Eng Struct 199:109612
Ansari A, Rao KS, Jain A (2022) Damage assessment of tunnels in seismic prone zone during earthquakes: a part of hazard evaluation. Earthquakes and structures: select proceedings of 7th ICRAGEE 2021. Springer, pp 161–169
Atkinson GM, Boore DM (1995) Ground-motion relations for eastern North America. Bull Seismol Soc Am 85(1):17–30
Aygar EB, Karahan S, Gullu S, Gokceoglu C (2022) Analytical and numerical analyses of the support system for a large-span tunnel in challenging and seismically active ground conditions. Transp Infrastruct Geotechnol 10:1–44
Baeza-Faundez S (2022) Use of deterministic and probabilistic slope stability analyses to evaluate tunnel location in landslide-prone areas. 2022-Mines Theses & Dissertations
Bazzurro P, Allin Cornell C (1999) Disaggregation of seismic hazard. Bull Seismol Soc Am 89(2):501–520
Bilham R (2006) Dangerous tectonics, fragile buildings, and tough decisions. Science 311(5769):1873–1875
Bilham R, Gaur VK, Molnar P (2001) Himalayan seismic hazard. Science 293(5534):1442–1444
Boore DM, Stewart JP, Seyhan E, Atkinson GM (2014) NGA-West2 equations for predicting PGA, PGV, and 5% damped PSA for shallow crustal earthquakes. Earthq Spectra 30(3):1057–1085
Bothara J, Ingham J, Dizhur D (2022) Qualifying the earthquake resilience of vernacular masonry buildings along the Himalayan arc. J Build Eng 52:104339
Burchfiel B, Royden LH (1985) North-south extension within the convergent Himalayan region. Geology 13(10):679–682
Campbell KW, Bozorgnia Y (2003) Updated near-source ground-motion (attenuation) relations for the horizontal and vertical components of peak ground acceleration and acceleration response spectra. Bull Seismol Soc Am 93(1):314–331
Campbell KW, Bozorgnia Y (2014) NGA-West2 ground motion model for the average horizontal components of PGA, PGV, and 5% damped linear acceleration response spectra. Earthq Spectra 30(3):1087–1115
Chatterjee A, Igonin N, Trugman DT (2023) A real-time and data-driven ground-motion prediction framework for earthquake early warning. Bull Seismol Soc Am 113(2):676–689
Chen Z, Shi C, Li T, Yuan Y (2012) Damage characteristics and influence factors of mountain tunnels under strong earthquakes. Nat Hazards 61(2):387–401
Chen X, Shen J, Bao X, Wu X, Tang W, Cui H (2023) A review of seismic resilience of shield tunnels. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 136:105075
Chiou BS-J, Youngs RR (2014) Update of the Chiou and Youngs NGA model for the average horizontal component of peak ground motion and response spectra. Earthq Spectra 30(3):1117–1153
Danciu L, Şeşetyan K, Demircioglu M, Gülen L, Zare M, Basili R et al (2018) The 2014 earthquake model of the Middle East: seismogenic sources. Bull Earthq Eng 16:3465–3496
Dowding CH, Rozan A (1978) Damage to rock tunnels from earthquake shaking. J Geotech Eng Div 104(2):175–191
Ekström G, Nettles M, Dziewoński A (2012) The global CMT project 2004–2010: centroid-moment tensors for 13,017 earthquakes. Phys Earth Planet Inter 200:1–9
Geoconsult/Typsa (2005) Bid documents. II-A, 109-121
Idriss I (2014) An NGA-West2 empirical model for estimating the horizontal spectral values generated by shallow crustal earthquakes. Earthq Spectra 30(3):1155–1177
Jaramillo CA (2017) Impact of seismic design on tunnels in rock-case histories. Undergr Space 2(2):106–114
Kazmi AH, Jan MQ (1997) Geology and tectonics of Pakistan. Graphic publishers, West Chicago
Khan S, Waseem M, Khan MA, Ahmed W (2018) Updated earthquake catalogue for seismic hazard analysis in Pakistan. J Seismol 22(4):841–861
Lisa M, Khan SA, Khwaja AA (2004) Focal mechanism study of north Potwar deformed zone, Pakistan. Acta Seismol Sin 17(3):255–261
McGuire RK (1995) Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis and design earthquakes: closing the loop. Bull Seismol Soc Am 85(5):1275–1284
National Highway Board Pakistan, P. E. I. N. Y., London, The Hague (1988) Lowari Tunnel, Final Feasibility Report. Part I, 252
Petersen MD, Moschetti MP, Powers PM, Mueller CS, Haller KM, Frankel AD et al (2015) The 2014 United States national seismic hazard model. Earthq Spectra 31(1_suppl):S1–S30
Rossetto T, Peiris N (2009) Observations of damage due to the Kashmir earthquake of October 8, 2005 and study of current seismic provisions for buildings in Pakistan. Bull Earthq Eng 7(3):681–699
Roy N, Sarkar R (2017) A review of seismic damage of mountain tunnels and probable failure mechanisms. Geotech Geol Eng 35(1):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-016-0091-x
Schirripa Spagnolo G, Mercuri M, Billi A, Carminati E, Galli P (2021) The segmented campo felice normal faults: seismic potential appraisal by application of empirical relationships between rupture length and earthquake magnitude in the Central Apennines, Italy. Tectonics 40(7):e2020TC006465
Searle MP, Khan MA, Fraser JE, Gough SJ, Jan MQ (1999) The tectonic evolution of the Kohistan-Karakoram collision belt along the Karakoram Highway transect, north Pakistan. Tectonics 18(6):929–949
Şeşetyan K, Danciu L, Demircioğlu Tümsa MB, Giardini D, Erdik M, Akkar S et al (2018) The 2014 seismic hazard model of the Middle East: overview and results. Bull Earthq Eng 16:3535–3566
Shrestha R, Li X, Yi L, Mandal AK (2020) Seismic damage and possible influencing factors of the damages in the Melamchi tunnel in Nepal due to Gorkha earthquake 2015. Geotech Geol Eng 38:5295–5308
Sun B, Deng M, Zhang S, Wang C, Cui W, Li Q et al (2023) Optimal selection of scalar and vector-valued intensity measures for improved fragility analysis in cross-fault hydraulic tunnels. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 132:104857
Tahirkheli RK (1979) Geology of kohistan, karakoram, himalaya, northern. Geol Bull Univ Peshawar 11:1–30
Wang X, Pan C (2022) Review of seismic damage characteristics and influence factors of mountain tunnels. Arab J Geosci 15(6):478
Wang T-T, Kwok O-LA, Jeng F-S (2021) Seismic response of tunnels revealed in two decades following the 1999 Chi–Chi earthquake (Mw 7.6) in Taiwan: a review. Eng Geol 287:106090
Waseem M, Lai CG, Spacone E (2018) Seismic hazard assessment of northern Pakistan. Nat Hazards 90(2):563–600
Wells DL, Coppersmith KJ (1994) New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84(4):974–1002
Yang H, Wang D, Guo R, Xie M, Zang Y, Wang Y et al (2022) Rapid report of the 8 January 2022 MS 6.9 Menyuan earthquake, Qinghai, China. Earthq Res Adv 2(1):100113
Zheng G, Yang P, Zhou H, Zeng C, Yang X, He X et al (2019) Evaluation of the earthquake induced uplift displacement of tunnels using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Comput Geotech 113:103099
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K, I.I, Q.R., M.W., W.A.; methodology, J.K, I.I, S.T.S, S.K, Q.R., M.W., W.A.; software, J.K, W.A, M.W, S.K, S.T.S, I.I, H.T.J, G.K.; validation, J.K, Q.R., M.W., W.A., I.I, H.T.J., G.K.; formal analysis, Q.R.; investigation, Q.R., M.W., W.A., I.I, H.T.J., G.K.; resources, M.W., W.A.; data curation, Q.R., M.W., W.A.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K, W.A.; writing—review and editing, J.K, S.K, Q.R., M.W., W.A.; I.I, H.T.J., G.K.; visualization, Q.R., M.W., W.A, I.I, H.T.J, G.K.; supervision, M.W., W.A. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, J., Ahmed, W., Waseem, M. et al. Deterministic seismic hazard assessment of a long mountainous road tunnel: a case study of Lowari Tunnel, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 83, 303 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-024-11625-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-024-11625-y