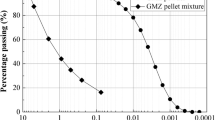
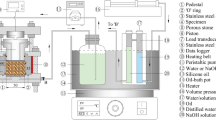
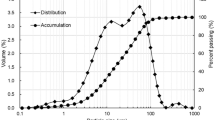
Abstract
Granular bentonite has been considered as candidate sealing material of various technological gaps in deep geological repository of high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Large inter-pellet pores inside the granular bentonite potentially work as preferential migration pathways of water, gas and radionuclides. During the long-term operation process, the inter-pellet pores will be filled by swollen pellets with the infiltration of groundwater, but it is still unclear how the inter-pellet pores evolve upon saturation and whether the mixture can reach a full homogenization. In this study, a series of constant-volume hydration tests and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) tests were performed on bentonite pellet mixture and compacted bentonite powder. Results revealed that the development curve of swelling pressure for bentonite pellet mixture exhibited a double-peak shape. The first peak value of the pellet mixture was lower than that of the compacted powder at a given dry density, but their final swelling pressures were similar. At the initial hydration stage, the water content, dry density and degree of saturation profiles along the sample height showed obvious gradients, resulting in an apparent heterogeneity of the pore structures. As hydration proceeded, the gradients in the water content and dry density profiles tended to decrease. Simultaneously, the pellet mixture gradually evolved from a trimodal porosity to a bimodal one. The pellet mixture and the compacted powder both exhibited a similar bimodal porosity at nearly saturated state. The homogenization process of the pellet mixture was quantitatively analyzed by a heterogeneity coefficient related to microstructural evolutions.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used during the study appeared in the published article.
References
Alonso EE, Romero E, Hoffmann C (2011) Hydromechanical behaviour of compacted granular expansive mixtures: experimental and constitutive study [J]. Géotechnique 61(4):329–344. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2011.61.4.329
Bernachy-Barbe F (2021) Homogenization of bentonite upon saturation: density and pressure fields[J]. Appl Clay Sci 209:106122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2021.106122
Bian X, Cui YJ, Li XZ (2019) Voids effect on the swelling behaviour of compacted bentonite[J]. Géotechnique 69(7):593–605. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.17.P.283
Chang C, Borglin S, Chou C et al (2023) Hydro-mechanical behavior of heated bentonite buffer for geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste: a bench-scale X-ray computed tomography investigation[J]. Appl Clay Sci 232:106792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106792
Chen L, Liu YM, Wang J et al (2014) Investigation of the thermal-hydro-mechanical (THM) behavior of GMZ bentonite in the China-Mock-up test [J]. Eng Geol 172:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.01.008
Darde B, Tang AM, Pereira JM et al (2018) Hydro-mechanical behaviour of high-density bentonite pellet on partial hydration[J]. Géotech Lett 8(4):330–335. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgele.18.00114
Delage P, Marcial D, Cui YJ et al (2006) Ageing effects in a compacted bentonite: a microstructure approach[J]. Géotechnique 56(5):291–304. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2006.56.5.291
Fernandez AM (2003) Caracterización y modelización del agua intersticial en materiales arcillosos. Estudio de la bentonita de Cortijo de Archidona [D]. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidad Auto´noma de Madrid, 505 pp (in Spanish)
Ferrage E, Lanson B, Sakharov BA et al (2005) Investigation of smectite hydration properties by modeling experimental X-ray diffraction patterns: Part I. Montmorillonite hydration properties[J]. Am Min 90(8–9):1358–1374. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2005.1776
Ferrari A, Bosch JA, Baryla P et al (2022) Volume change response and fabric evolution of granular MX80 bentonite along different hydro-mechanical stress paths[J]. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01481-0
Garca-Gutiérrez M, Mingarro M, Missana T et al (2004) Diffusion experiments with compacted powder/pellets clay mixtures[J]. Appl Clay Sci 26(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2003.09.014
Garcia-Sineriz JL, Villar MV, Rey M et al (2015) Engineered barrier of bentonite pellets and compacted blocks: state after reaching saturation[J]. Eng Geol 192:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.04.002
Harjupatana T, Miettinen A, Kataja M (2022) A method for measuring wetting and swelling of bentonite using X-ray imaging[J]. Appl Clay Sci 221:106485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106485
He Y, Ye WM, Chen YG et al (2016) Influence of pore fluid concentration on water retention properties of compacted GMZ01 bentonite[J]. Appl Clay Sci 129:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.05.020
Hoffmann C, Alonso EE, Romero E (2007) Hydro-mechanical behaviour of bentonite pellet mixtures[J]. Phys Chem Earth Parts ABC 32(8):832–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.04.037
Imbert C, Villar MV (2006) Hydro-mechanical response of a bentonite pellets/powder mixture upon infiltration[J]. Appl Clay Sci 32(3–4):197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2006.01.005
Liu ZR, Cui YJ, Ye WM et al (2020) Investigation on vibration induced segregation behaviour of crushed GMZ bentonite pellet mixtures[J]. Constr Build Mater 241:117949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117949
Liu ZR, Ye WM, Cui YJ et al (2022) Temperature effects on water retention behaviour and structural evolution of GMZ bentonite pellet mixtures[J]. Appl Clay Sci 222:106492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106492
Lloret A, Villar MV (2007) Advances on the knowledge of the thermo-hydro-mechanical behaviour of heavily compacted FEBEX bentonite[J]. Phys Chem Earth Parts a/b/c 32(8–14):701–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.03.002
Luo SM, Zhou B, Peng J et al (2023) Unit weight of water in clayey soil[J]. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 149(3):04022134. https://doi.org/10.1061/JGGEFK.GTENG-10844
Mašín D, Khalili N (2015) Swelling phenomena and effective stress in compacted expansive clays[J]. Can Geotech J 53(1):134–147. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0479
Massat L, Cuisinier O, Bihannic I et al (2016) Swelling pressure development and inter-aggregate porosity evolution upon hydration of a compacted swelling clay[J]. Appl Clay Sci 124:197–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.01.002
Molinero-Guerra A, Mokni N, Cui YJ et al (2019) Impact of initial structural heterogeneity on long-term swelling behavior of MX80 bentonite pellet/powder mixtures[J]. Can Geotech J 57(9):1404–1416. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2018-0301
Molinero-Guerra A, Delage P, Cui YJ et al (2020) Water-retention properties and microstructure changes of a bentonite pellet upon wetting/drying; application to radioactive waste disposal[J]. Géotechnique 70(3):199–209. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.17.P.291
Saiyouri N, Tessier D, Hicher PY (2004) Experimental study of swelling in unsaturated compacted clays[J]. Clay Miner 39(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1180/0009855043940148
Seiphoori A, Ferrari A, Laloui L (2004) Water retention behaviour and microstructural evolution of MX-80 bentonite during wetting and drying cycles[J]. Géotechnique 64(9):721–734. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.14.p.017
Van Geet M, Volckaert G, Roels S (2005) The use of microfocus X-ray computed tomography in characterising the hydration of a clay pellet/powder mixture[J]. Appl Clay Sci 29(2):73–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2004.12.007
Villar MV, Iglesias RJ, Gutiérrez-Álvarez C et al (2021) Pellets/block bentonite barriers: laboratory study of their evolution upon hydration[J]. Eng Geol 292:106272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106272
Wang Q, Tang AM, Cui YJ et al (2013) The effects of technological voids on the hydro-mechanical behaviour of compacted bentonite–sand mixture[J]. Soils Found 53(2):232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2013.02.004
Wen Z (2006) Physical property of China’s buffer material for high-level radioactive waste repositories[J]. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 25(4):794–800 (in Chinese)
Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B et al (2010) Advances on the knowledge of the buffer/backfill properties of heavily-compacted GMZ bentonite[J]. Eng Geol 116(1–2):12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.06.002
Zhang Z, Ye WM, Liu ZR et al (2018) Influences of PSD curve and vibration on the packing dry density of crushed bentonite pellet mixtures[J]. Constr Build Mater 185:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.096
Zhang Z, Ye WM, Liu ZR et al (2020) Mechanical behavior of GMZ bentonite pellet mixtures over a wide suction range[J]. Eng Geol 264:105383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105383
Zhang Z, Ye WM, Wang Q et al (2022a) Investigation on healing behavior of unsaturated GMZ bentonite pellet mixture based on compressibility[J]. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01494-9
Zhang Z, Cui YJ, Yang JW et al (2022b) Investigation into hydro-mechanical behaviour and microstructural evolution of MX80 bentonite pellet upon wetting/drying [J]. Constr Build Mater 345:128319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128319
Funding
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42207227 & 52208379) and the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (Project 2021RC2004). Besides, this work was also funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Project 2022JJ40586) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M713509).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZ: investigation, writing —original draft, methodology. XN: supervision, methodology, writing—review and editing. YH: supervision. HW: formal analysis, investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Ni, Xq., Wang, H. et al. Homogenization of a granular bentonite material upon saturation: an analysis based on pore structure evolutions. Environ Earth Sci 83, 16 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11305-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11305-3