Abstract
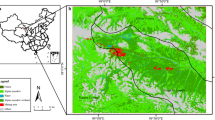
This study addresses the critical issue of land subsidence in densely populated agriculture-based country, Bangladesh, focusing on the Barapukuria coal mine area. Our research employed time-series analysis of Landsat satellite imagery from 2005 to 2020, coupled with vertical electrical sounding resistivity methods. Through the false color composite image analysis in Earth Engine and GIS-based mapping, we quantified the areal extent of subsidence, and results were validated by field visits and cross-referencing with ESRI and dynamic world land use–land cover maps. Our study revealed a concerning trend of subsidence moving from west to east, towards the two nearby residential areas. Most importantly, the rate of areal extent of subsidence was alarming (17.4 acres per year), resulting in a cumulative loss of 205 acres since 2008. Linear regression predicts that this subsided area will double to around 405 acres by 2030, indicating significant risk to nearby communities. The trajectory of subsidence extent led us to examine the subsurface condition of nearby villages using calibrated vertical electrical sounding and borehole data. This revealed a higher resistivity in the northern area, indicating a future subsidence risk compared to the southern part. This was further confirmed by subsurface lithology, composed mainly of Holocene deposits containing clay, clayey sand, and sand. These layers, with their inherent instability and higher consolidation potential, exhibited higher resistivity and more prone to land subsidence. Overall, this study provides valuable insights for predicting subsidence, assessing associated risks, and guiding policy decisions to prevent future damage and facilitate community rehabilitation.













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
The data are available on request.
Code availability
The code is available on request.
References
Abubakar S, Abir IA, Muhammad SB, Mohammed A (2020) Land subsidence studies of seberang perai Malaysia, by integrating remote sensing technique and resistivity survey method. IOSR J Appl Geol Geophys 8(1):41–47 https://doi.org/10.9790/0990-0801034147
Abubakar S, Shanmugaveloo AAL (2021) Surface deformation studies in South of Johor using the integration of InSAR and resistivity methods. Caliphate J Sci Technol 2021(2):167–172.
Alam M, Alam MM, Curray JR, Chowdhury MLR, Gani MR (2003) An overview of the sedimentary geology of the Bengal Basin in relation to the regional tectonic framework and basin-fill history. Sed Geol 155(3–4):179–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00180-X
Alam AKMB, Fujii Y, Eidee SJ, Boeut S, Rahim AB (2022) Mining-induced subsidence prediction by displacement discontinuity method: a case from Barapukuria longwall coal mine Bangladesh. Sci Rep 12(1):14800. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-19160-1
Arifeen HM, Chowdhury MS, Zhang H, Suepa T, Amin N, Techato K, Jutidamrongphan W (2021) Role of a mine in changing its surroundings—land use and land cover and impact on the natural environment in barapukuria, bangladesh. Sustainability (Switzerland) 13(24):13602. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413602
ASTM D6431 (2010) Standard guide for using the direct current resistivity method for subsurface investigation. ASTM International, West Conshohocken. https://doi.org/10.1520/D6431-99R10.2
Bagheri-gavkosh M, Mossa S, Ataie-ashtiani B, Sohani Y (2021) Land subsidence: a global challenge. Sci Total Environ 778:146193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146193
Bakr MA, Rahman QMA, Islam MM, Islam MK, et al (1996) Geology and coal deposits of Barapukuria Basin, Dinajpur District, Bangladesh. Records of Geological Survey of Bangladesh, Vol. 8 (Part 1)
Barapukuria Coal Mine (2021) Barapukuria coal mine expanding northward. The Daily Star. https://www.thedailystar.net/country/news/barapukuria-coal-mine-expanding-northward-2114077. Accessed on 20 June 2021
BBS (2021) Statistical Pocketbook 2020. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Statistics and Informatics Division, Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. https://bbs.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/bbs.portal.gov.bd/page/d6556cd1_dc6f_41f5_a766_042b69cb1687/2021-06-30-09-25-67bbe4c5c15d7773d82c86adbd26bba9.pdf. Accessed 13 Aug 2021
BCMCL (2023) Annual Report 2021–2022, Barapukuria Coal Mine Company Limited, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. https://bcmcl.org.bd/sites/default/files/files/bcmcl.portal.gov.bd/annual_reports/a351e5a3_8219_4a8a_b3f1_d0d1c5fbe7da/2023-04-06-08-17-1c35ef561d07742cb831d50219bd5ea1.pdf. Accessed on 08 March 2023
Brown CF, Brumby SP, Guzder-Williams B, Birch T et al (2022) Dynamic world, near real-time global 10 m land use land cover mapping. Sci Data 9(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01307-4
Chaaban F, El Khattabi J, Darwishe H (2022) Accuracy assessment of ESA WorldCover 2020 and ESRI 2020 land cover maps for a region in Syria. J Geovis Spat Anal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41651-022-00126-w
Choudhury I, Chakraborty M, Santra SC, Parihar JS (2012) Methodology to classify rice cultural types based on water regimes using multi-temporal RADARSAT-1 data. Int J Remote Sens 33(13):4135–4160. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2011.642018
Del Conte S, Falorni G (2019) InSAR monitoring of subsidence induced by underground mining operations. Proceedings—Rapid Excavation and Tunneling Conference, 2019-June. p 399–407. https://doi.org/10.36487/acg_rep/1815_54_falorni
Dang VK, Nguyen TD, Dao NH et al (2021) Land subsidence induced by und erground coal mining at Quang Ninh, Vietnam: persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar observation using sentinel-1 data. Int J Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2021.1875513
Ghazifard A, Akbari E, Shirani K, Safaei H (2017) Evaluating land subsidence by field survey and D-InSAR technique in Damaneh city. Iran J Arid Land 9(5):778–789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-017-0104-5
Gorelick N, Hancher M, Dixon M et al (2017) Google earth engine: planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens Environ 202:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSE.2017.06.031
Hossain MS, Khan MSH, Chowdhury KR, Abdullah R (2019) Synthesis of the tectonic and structural elements of the bengal basin and its surroundings. Springer Geology (Issue January). Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99341-6_6
Hossain MS, Xiao W et al (2020a) Geodynamic model and tectono-structural framework of the Bengal Basin and its surroundings. J Maps 16(2):445–458. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2020.1770136
Hossain MS, Khan MSH, Abdullah R, Chowdhury KR (2020) Tectonic Development of the bengal basin in relation to fold-thrust belt to the east and to the north. Springer, New York, pp 91–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40593-9_4
Howladar MF (2012) Coal mining impacts on water environs around the Barapukuria coal mining area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci. 70(1):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-012-2117-X
Howladar MF (2016) Environmental impacts of subsidence around the Barapukuria coal mining area in Bangladesh. Energy Ecol Environ 1(6):370–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-016-0031-x
Howladar MF, Hasan K (2014) A study on the development of subsidence due to the extraction of 1203 slice with its associated factors around Barapukuria underground coal mining industrial area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci 72(9):3699–3713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3419-y
Imam E (2019) Remote sensing and GIS module: colour composite images and visual image interpretation. University Grand Commission (UGC), MHRD, Government of India.
Islam MZ, Chakraborty P (2021) Importance of failure modes and effect analysis application for risk analysis in Barapukuria coal mine, Bangladesh. Int J Innov Eng Res Technol. 8:148–156. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/59G3V
Islam MR, Hayashi D (2008) Geology and coal bed methane resource potential of the Gondwana Barapukuria coal basin, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Int J Coal Geol 75(3):127–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2008.05.008
Kannaujiya S, Chattoraj SL, Jayalath D et al (2019) Integration of satellite remote sensing and geophysical techniques (electrical resistivity tomography and ground penetrating radar) for landslide characterization at Kunjethi (Kalimath), Garhwal Himalaya. India Natural Hazards 97(3):1191–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03695-0
Kaul H, Sopan I (2012) Land use land cover classification and change detection using high resolution temporal satellite data. J Environ 01(04):146–152
Khalil MI (2020) Coastal groundwater aquifer characterization from geoelectrical measurements- a case study at Kalapara, Patuakhali, Bangladesh. J Appl Geol. 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.22146/jag.55009
Lu D, Mausel P, Brondízio E, Moran E (2004) Change detection techniques. Int J Remote Sens 25(12):2365–2401. https://doi.org/10.1080/0143116031000139863
Martin LRG (1989) Accuracy assessment of Landsat-based visual change detection methods applied to the rural-urban fringe. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 55(2):209–215
Muhammad SB, Abubakar S, Abir IA, Mohammed A (2020) Land subsidence studies of Seberang Perai Malaysia, by integrating remote sensing technique and resistivity survey method. IOSR J Appl Geol Geophys 8(1):41–47. https://doi.org/10.9790/0990-0801034147
Oliver-Cabrera T, Wdowinski S, Kruse S, Robinson T (2020) InSAR detection of localized subsidence induced by sinkhole activity in suburban west-central Florida. Proc Int Assoc Hydrol Sci 382:155–159. https://doi.org/10.5194/piahs-382-155-2020
Pacheco-Martínez J, Cabral-Cano E, Wdowinski S et al (2015) Application of InSAR and gravimetry for land subsidence hazard Zoning in Aguascalientes, Mexico. Remote Sens 7(12):17035–17050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215868
Patra SK, Shekher M, Solanki SS et al (2006) A technique for generating natural colour images from false colour composite images. Int J Remote Sens 27(14):2977–2989. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160600554322
Rahman MM, Woobaidullah ASM (2020) Groundwater resources exploration in a Hillock valley at Lada refugee camp Teknaf using electrical resistivity soundings. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5056-y
Rawat JS, Kumar M (2015) Monitoring land use/cover change using remote sensing and GIS techniques: a case study of Hawalbagh block, district Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 18(1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2015.02.002
Sidhu N, Pebesma E, Câmara G (2018) Using google earth engine to detect land cover change: Singapore as a use case. Eur J Remote Sens. 51(1):486–500. https://doi.org/10.1080/22797254.2018.1451782
Singh PK, Kumar S, Singh UC (2011) Evaluation de la ressource en eaux souterraines dans la zone de Gwalior, Inde, au moyen de données satellitaires: Une approche géomorphologique et géophysique intégrée. Hydrogeol J 19(7):1421–1429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-011-0758-6
Sunny S (2018) Barapukuria: are people really as content as the government would have us believe? The Daily Star. https://www.thedailystar.net/star-weekend/environment/barapukuria-1587976. Accessed 10 July 2020
Thabit JM, Al-zubedi AS (2015) Aquifers delineation using vertical electrical sounding in south and southwest of Samawa city, Southern Iraq. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 11(1):133–141
Tiwari MK, Saxena A (2011) Change detection of land use/landcover pattern in an around mandideep and obedullaganj area, using remote sensing and GIS. Int J Technol Eng Syst. 2(3):342–350
Ulfah S, Marzuki M, Susilo A (2021) Analysis vulnerability disaster of landslide in Lantan village using geoelectric data and sentinel image. J Penelit Pendidik IPA. 7(4):794–801. https://doi.org/10.29303/jppipa.v7i4.915
Wenner F (1916) A method of measuring earth resistivity. Bull Bur Stand 12(4):469. https://doi.org/10.6028/bulletin.282
Widada S, Saputra S, Hariadi, (2018) Determination of soft lithology causes the land subsidence in coastal Semarang city by resistivity methods. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/116/1/012092
Widada S, Zainuri M, Yulianto G, Saputra S, Rochaddi B (2019) Distributian of depth and clay-silt to sand ratio of land subsidence in coastal Semarang city by resistivity methods. J Kel Trop. 22(1):63. https://doi.org/10.14710/jkt.v22i1.4463
Widada S, Zainuri M, Yulianto G, Satriadi A, Wijaya YJ (2020) Estimation of land subsidence using sentinel image analysis and its relation to subsurface lithology based on resistivity data in the coastal area of Semarang city Indonesia. J Ecol Eng. 21(8):47–56. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/127394
Woobaidullah A, Rahman MM, Uddin MZ (2016) Evaluation of hydrogeological conditions through vertical electrical soundings survey at Mankiganj pourashava, Manikganj, central part of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Sci Res 27(2):109–120. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjsr.v27i2.26229
Woobaidullah ASM, Islam MA, Hossain MZ, Islam MS (2020) Geo-electrical resistivity survey for fresh groundwater investigation in Mirsharai economic zone, Chittagong in the south-eastern coastal areas of Bangladesh. J Nepal Geol Soc 60:181–194. https://doi.org/10.3126/jngs.v60i0.31262
Xiong J, Thenkabail PS, Tilton JC et al (2017) Nominal 30-m cropland extent map of continental Africa by integrating pixel-based and object-based algorithms using Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 data on google earth engine. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS9101065
Xu H, Chen Y (2012) A technique for simulating pseudo natural color images based on spectral similarity scales. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 9(1):70–74. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2011.2160710
Yan W, Chen J, Tan Y et al (2021) Theoretical analysis of mining induced overburden subsidence boundary with the horizontal coal seam mining. Adv Civil Eng 2021:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6657738
Zhu Z (2017) Change detection using landsat time series: a review of frequencies, preprocessing, algorithms, and applications. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 130:370–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.06.013
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the authority of the Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (BCSIR) for approving the Research and Development Project for the fiscal years 2020–2021 having Reference No. 39.02.0000.011.14.128.2020/636, Serial-65, Unit Code-IMMM-01. The authors also express their gratitude to anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments to improve the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was received from Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (BCSIR), Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh, for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MISH: conceptualization, field investigation, formal analysis, statistical analysis, original manuscript writing, project administration, methodology, data curation, visualization, software. MSA: field visit and calibration of data. PKB: supervision, project administration. MSR: review of the original draft of manuscript and editing, map preparation, manuscript formatting. MSS: valuable feedback during field work. MNZ: fund manage, project administration. MAS: conceptualization, manuscript reviewing and editing, MJR: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision. ASMW: fund manage, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding publishing of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, M.I.S., Alam, M.S., Biswas, P.K. et al. Integrated satellite imagery and electrical resistivity analysis of underground mine-induced subsidence and associated risk assessment of Barapukuria coal mine, Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci 82, 537 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11215-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11215-4