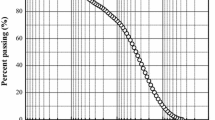
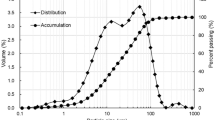
Abstract
In the long-term operation of a deep geological repository for disposal of high-level radioactive wastes, bentonite material will inevitably undergo cyclic salinization–desalinization processes, which exert significant effects on performance of the engineered barrier. In this study, cyclic salinization–desalinization tests were performed on compacted bentonite specimens at a dry density of 1.7 Mg/m3 under vertical stresses of 0.15, 0.20, 0.20–0.26, 0.34 and 0.34–0.47 MPa. Meanwhile, MIP tests were conducted on an as-compacted specimen and the specimens experienced hydrations with de-ionized water (DW) and 2.0 M NaCl solution, as well as cyclic salinization–desalinization (2.0 M NaCl–DW) processes, respectively. It was found that the specimen volume change is governed by both of the salinization–desalinization processes and the vertical stress. The accumulative strain measured over cyclic salinization–desalinization processes for specimens tested under vertical stresses trends to be zero, suggesting that there exists an equilibrium state at which the shrinkage strain induced by the salinization is equal to the swelling strain generated by the subsequent desalinization. Based on these, a swelling equilibrium line and a shrinkage equilibrium line were proposed. Meanwhile, a swelling zone and a shrinkage zone were divided with a critical separating vertical stress of 0.47 MPa. In the swelling zone (< 0.47 MPa), the specimen exhibited prevailing swelling behavior, while in the shrinkage zone (0.47–12.82 MPa), the specimen was prevailed by shrinkage behavior. Finally, these phenomena were interpreted from the microstructural point of view according to the MIP test results.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Alonso EE, Romero E, Hoffmann C, García-Escudero E (2005) Expansive bentonite-sand mixtures in cyclic controlled-suction drying and wetting. Eng Geol 81:213–226
ANDRA (2005) Synthesis—evaluation of the feasibility of a geological repository in argillaceous formation. France, ANDRA
Castellanos E, Villar MV, Romero E, Lloret A, Gens A (2008) Chemical impact on the hydro-mechanical behavior of high-density FEBEX bentonite. Phys Chem Earth 33:S516–S526
Cui YJ, Nguyen XP, Tang AM, Li XL (2013) An insight into the unloading/reloading loops on the compression curve of natural stiff clays. Appl Clay Sci 83–84:343–348
Chen YG, Zhu CM, Ye WM, Cui YJ, Wang Q (2015) Swelling pressure and hydraulic conductivity of compacted GMZ01 bentonite under salinization-desalinization cycle condition. Appl Clay Sci 114:454–460
Chen YG, Jia LY, Li Q, Ye WM, Cui YJ, Chen B (2017) Swelling deformation of compacted GMZ bentonite experiencing chemical cycles of sodium-calcium exchange and salinization-desalinization effect. Appl Clay Sci 141:55–63
Delage P, Lefebvre G (1984) Study of the structure of a sensitive Champlain clay and its evolution during consolidation. Can Geotech J 21(1):21–35
Delage P, Marcial D, Cui YJ, Ruiz X (2006) Ageing effects in a compacted bentonite: a microstructure approach. Géotechnique 56(5):291–304
Guo YH, Yang TX, Liu SF (2001) Hydrogeological characteristics of Beishan preselected area, Gansu provincefor China’s high-level radioactive waste repository. Uranium Geol 17:184–189 (in Chinese)
He Y, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Ye B, Cui YJ (2016) Influence of pore fluid concentration on water retention properties of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 129:131–141
Karnland O, Olsson S, Nilsson U (2006) Mineralogy and Sealing Properties of Various Bentonites and Smectite-Rich Clay Materials. SKB TR-06-30. Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co, Stockholm, Sweden
Lloret A, Villar MV, Sanchez M, Gens A, Pintado X, Alonso EE (2003) Mechanical behavior of heavily compacted bentonite under high suction changes. Géotechnique 53(1):27–40
Musso G, Romero E, Gens A, Castellanos E (2003) The role of structure in the chemically induced deformations of FEBEX bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 23:229–237
Musso G, Romero E, Della Vecchia G (2013) Double-structure effects on the chemo-hydro-mechanical behavior of a compacted active clay. Géotechnique 63(3):206–220
Molinero-Guerra A, Mokni N, Delage P, Cui YJ, Tang AM, Aimedieu P, Bernier F, Bornert M (2016) In-depth characterisation of a mixture composed of powder/pellets MX80 bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 135:538–546
Nguyen XP, Cui YJ, Tang AM, Deng YF, Li XL, Wouters L (2013) Effects of pore water chemical composition on the hydro-mechanical behavior of natural stiff clays. Eng Geol 166:52–64
Olson RE, Mesri G (1970) Mechanisms controlling compressibility of clays. Journal of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Division, Proceeding of the American Society of Civil Engineers. SM6:1863–1878
Pusch R (1983) Use of clays as buffers in radioactive repositions. KBS Report. 46–83
Rao SM, Shivananda P (2005) Role of osmotic suction in swelling of salt amended clays. Can Geotech J 42:307–315
Rao SM, Thyagaraj T (2007a) Swell-compresion behavior of compacted clays under chemical gradients. Can Geotech J 44:520–532
Rao SM, Thyagaraj T (2007b) Role of direction of salt migration on the swelling behaviour of compacted clays. Appl Clay Sci 38:113–129
Siddiqua S, Blatz J, Siemens G (2011) Evaluation of the impact of pore fluid chemistry on the hydromechanical behavior of clay-based sealing materials. Can Geotech J 48(2):199–213
Tripathy S, Schanz T (2007) Compressibility behavior of clays at large pressures. Can Geotech J 44:355–362
Thyagaraj T, Rao SM (2013) Osmotic swelling and osmotic consolidation behavior of compacted expansive clay. Geotech Geol Eng 31(2):435–445
Villar MV (2006) Infiltration tests on a granite/bentonite mixture: influence of water salinity. Appl Clay Sci 31(1–2):96–109
Wen ZJ (2006) Physical property of china’s buffer material for high-level radioactive waste repositories. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 25(4):794–800 (in Chinese)
Ye WM, Wang Q, Pan H, Chen B (2010) Thermal conductivity of compacted GMZ bentonite. Chin J Geotech Eng 32:821–826 (in Chinese)
Ye WM, Zhang F, Chen B, Chen YG, Wang Q, Cui YJ (2014a) Effects of salt solutions on the hydro-mechanical behavior of compacted GMZ01 Bentonite. Environ Earth Sci 72(7):2621–2630
Ye WM, Borrell NC, Zhu JY, Chen B, Chen YG (2014b) Advances on the investigation of the hydraulic behavior of compacted GMZ bentonite. Eng Geol 169:41–49
Ye WM, Zhang F, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2017) Influences of salt solutions and salinization-desalinization processes on the volume change of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 222:140–145
Zhang F, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2016) Influences of salt solution concentration and vertical stress during saturation on the volume change behavior of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 207:48–55
Zhang F, Ye WM, Wang Q, Chen YG, Chen B (2019) An insight into the swelling pressure of GMZ01 bentonite with consideration of salt solution effects. Eng Geol 251:190–196
Zhang F, Ye WM, Wang Q, Chen YG, Chen B (2020a) Effective stress incorporating osmotic suction and volume change behavior of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Acta Geotech 15:1925–1934
Zhang F, Cui YJ, Conil N, Talandier J (2020b) Assessment of swelling pressure determination methods with intact Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:1879–1888
Zhao NF, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2019) Investigation on swelling-shrinkage behavior of unsaturated compacted GMZ bentonite on wetting-drying cycles. Bull Eng Geo Environ 78:617–627
Zhu CM, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2013) Influence of salt solutions on the swelling pressure and hydraulic conductivity of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 166:74–80
Zhu CM, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2015) Impact of cyclically infiltration of CaCl2 solution and DW on volume change behavior of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 184:104–110
Funding
The financial supports from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (42030714), the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC1509900) and Key Laboratory of Geotechnical and Underground Engineering of Ministry of Education, Tongji University (KLE-TJGE-B2203) are greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FZ: methodology, experimental investigation, wrote original draft. W-mY: supervision, conceptualization, visualization. QW: data curation, revision and editing. Y-gC: validation. Y-jC: conceptualization, methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Ye, WM., Wang, Q. et al. Insight into volume change behavior of GMZ01 bentonite over cyclic salinization–desalinization processes. Environ Earth Sci 82, 312 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10997-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10997-x