Abstract
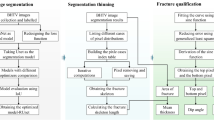
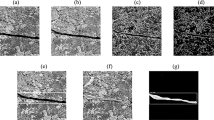
In order to realize low-cost, fast, and accurate fracture identification in lining quality inspection and underground engineering stability evaluation, we propose an intelligent fracture identification method, which can achieve depth extraction of fracture information from rock images. Firstly, the fracture identification model combined with the residual network was constructed to obtain more fracture features. Secondly, dilated convolution layers were added to improve the resolution of the fracture feature points. Meanwhile, the perceptual field is expanded to achieve the effective capture of characteristics of tiny fractures. Lastly, the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) function is introduced to realize the nonlinear transformation of the model. And the predicted results are optimized by Dice loss function to accelerate the convergence of the model. The model is applied to identify concrete fractures and rock fractures. We also conduct reliability assessment and then compare the performance of our identification model to LinkNet, U-net, CNN + ASPP models. The maximum accuracy (98.93%), recall (83.78%) values of the method far exceed that CNN + ASPP model using the same dataset. High image similarity and smaller fracture features degrade the performance of the image identification method, while the method can significantly overcome these challenges and thus greatly improve the accuracy of fracture identification. And the identification method is more accurate and robust than the comprised method. Besides the proposed method with good generalization and can be used for the rapid identification of rock mass fractures in highways, constructions, slopes, water conservancies and other projects.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Ainiwaer M, Ding J, Kasim N (2020) Deep learning-based rapid recognition of oasis-desert ecotone plant communities using UAV low-altitude remote-sensing data. Environ Earth Sci 79:216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-08965-w
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39:2481–2495. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Byun H, Kim J, Yoon D, Kang I, Song JJ (2021) A deep convolutional neural network for rock fracture image segmentation. Earth Sci Inform 14(4):1937–1951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00650-1
Cai JX, Mu TJ, Lai YK, Hu SM (2021) LinkNet: 2D–3D linked multi-modal network for online semantic segmentation of RGB-D videos. Comput Graph 98:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cag.2021.04.013
Cao T, Xiao AC, Wu L, Mao LG (2017) Automatic fracture detection based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning data: A new method and case study. Comput Geosci-Uk 106:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.04.003
Cha YJ, Choi W, Büyüköztürk O (2017) Deep learning-based crack damage detection using convolutional neural networks. Comput-Aided Civ Inf 32:361–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.12263
Chatterjee S, Askari R, Jeng JY, Abuzaied M, Miltenberger A (2020) Stochastic fracture simulation using pixel-based multiple-point geostatistics by integrating seismic radial anisotropy and well data: applications in two hydrology sites. Environ Earth Sci 79:515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09258-y
Chauhan S, Rühaak W, Khan F, Enzmann F, Mielke P, Kersten M, Sass I (2016) Processing of rock core microtomography images: Using seven different machine learning algorithms. Comput Geosci-Uk 86:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.10.013
Chaurasia A, Culurciello E (2017) LinkNet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), 20171–4. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1707.03718
Chen F, Jahanshahi MR (2018) NB-CNN: Deep Learning-Based Crack Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network and Naïve Bayes Data Fusion. Ieee T Ind Electron 65:4392–4400. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2764844
Chen N, Kemeny J, Jiang QH, Pan ZW (2017) Automatic extraction of blocks from 3D point clouds of fractured rock. Comput Geosci-Uk 109:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.08.013
Chen JY, Yang TJ, Zhang DM, Huang HW, Tian Y (2021) Deep learning-based classification of rock structure of tunnel face. Geosci Front 12:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.04.003
Deb D, Hariharan S, Rao UM, Ryu CH (2008) Automatic detection and analysis of discontinuity geometry of rock mass from digital images. Comput Geosci-Uk 34:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2007.03.007
Dong SQ, Zeng LB, Lyu WY, Xia DL, Liu GP, Wu Y, Du XY (2020) Fracture identification and evaluation using conventional logs in tight sandstones: A case study in the Ordos Basin, China. Energy Geosci 1:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engeos.2020.06.003
Dorafshan S, Thomas RJ, Maguire M (2018) SDNET2018: An annotated image dataset for non-contact concrete crack detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Data Brief 21:1664–1668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.11.015
Fan LM, Li N (2004) Intelligent interpretation method of rock fracture images based on pattern recognition technology. Natural Sci Progress 14:118–122
Gu QH (2020) Road intelligent recognition and road network modeling of open pit mine based on D-LinkNet Network. J China Coal Soc 45(S2):1100–1108. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2020.0414
Guo L, Li RZ, Jiang B, Shen X (2020) Automatic crack distress classification from concrete surface images using a novel deep-width network architecture. Neurocomputing 397:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.08.107
Guo MQ, Bei WJ, Huang Y, Chen ZL, Zhao XZ (2021) Deep learning framework for geological symbol detection on geological maps. Comput Geosci-Uk 157:104943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104943
Han S, Wang G, Li MC (2018) A trace map comparison algorithm for the discrete fracture network models of rock masses. Comput Geosci-Uk 115:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2018.03.002
He XZ, Xu HD, Sabetamal H, Shen DC (2020) Machine learning aided stochastic reliability analysis of spatially variable slopes. Comput Geotech 126:103711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103711
Hou ZY, Cao DP, Ji SQ, Cui RG, Liu Q (2021) Enhancing digital rock image resolution with a GAN constrained by prior and perceptual information. Comput Geosci-Uk 157:104939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104939
Huang HW, Li QT, Zhang DM (2018) Deep learning based image recognition for crack and leakage defects of metro shield tunnel. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 77:166–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.04.002
Huynh P, Ross R, Martchenko A, Devlin J (2015) Dou-edge evaluation algorithm for automatic thin crack detection in pipelines. IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications (ICSIPA) 2015:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSIPA.2015.7412188
Ivanova VM, Sousa R, Murrihy B, Einstein HH (2014) Mathematical algorithm development and parametric studies with the GEOFRAC three-dimensional stochastic model of natural rock fracture systems. Comput Geosci-Uk 67:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.12.004
Javadi M, Sharifzadeh M, Shahriar K, Sayadi S (2016) Migration tracing and kinematic state concept embedded in discrete fracture network for modeling hydrocarbon migration around unlined rock caverns. Comput Geosci-Uk 91:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2016.02.012
Jia XH (2020) Research on Degraded Document Image Binarization Algorithm Based on Deep Learning. Hubei University of Technology in China, Master
Jia M, Zhang LH, Guo JJ (2017) Combining a connected-component labeling algorithm with FILTERSIM to simulate continuous discrete fracture networks. Environ Earth Sci 76:327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6647-0
Karimpouli S, Tahmasebi P (2019) Segmentation of digital rock images using deep convolutional autoencoder networks. Comput Geosci-Uk 126:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2019.02.003
Lemy F, Hadjigeorgiou J (2003) Discontinuity trace map construction using photographs of rock exposures. Int J Rock Mech Min 40:903–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00069-8
Leng B, Zhang Y, Yang H, Hou GP (2021) Rapid recognition of rock mass fractures in tunnel faces. J Southwest Jiaotong University 56:246–252. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190749
Liu C, Tang CS, Shi B, Suo WB (2013) Automatic quantification of crack patterns by image processing. Comput Geosci-Uk 57:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.04.008
Liu Y, Zhang ZL, Liu X, Wang L, Xia XH (2021) Deep learning-based image classification for online multi-coal and multi-class sorting. Comput Geosci-Uk 157:104922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104922
Luo ZH, Zhu ZD, Ruan HN, Shi C (2015) Extraction of microcracks in rock images based on heuristic graph searching and application. Comput Geosci-Uk 85:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.08.013
Luo W, Liang SH, Jiang X, An N, Du R (2020) Crack recognition of outcrop area based on deep learning. Comput Modern. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2020.05.010
Mandal V, Uong L, Adu-Gyamfi Y (2018). Automated Road Crack Detection Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData.2018.8622327.
Naik DL, Kiran R (2019) Identification and characterization of fracture in metals using machine learning based texture recognition algorithms. Eng Fract Mech 219:106618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106618
Nascimento L, Ruano MG (2015). Computer-aided bone fracture identification based on ultrasound images. 2015 IEEE 4th Portuguese Meeting on Bioengineering (ENBENG) https://doi.org/10.1109/ENBENG.2015.7088892
Ni F, Zhang J, Chen Z (2019) Pixel-level crack delineation in images with convolutional feature fusion. Str Control Health Monit 26:e2286. https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2286
Nurshal MEM, Sadewo MS, Hidayat A, Hamzah NW, Sapiie B, Abdurrachman M, Rudyawan A (2020) Automatic and manual fracture-lineament identification on digital surface models as methods for collecting fracture data on outcrops: case study on fractured granite outcrops. Bangka Front Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2020.560596
Oliveira, H., & Correia, P. L. (2014). CrackIT — An image processing toolbox for crack detection and characterization. Paper presented at the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2014.7025160
Patel D, Hsu W, Lee ML (2015) LinkNet: capturing temporal dependencies among spatial regions. Distrib Parallel Dat 33:165–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-014-7147-9
Rasyidi H, Khan S (2021) Historical document text binarization using atrous convolution and multi-scale feature decoder. Neural Comput Applic 33:7339–7352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05382-9
Reid TR, Harrison JP (2000) A semi-automated methodology for discontinuity trace detection in digital images of rock mass exposures. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci (Oxford, England: 1997) 37:1073–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(00)00041-1
Roubinet D, Linde N, Jougnot D, Irving J (2016) Streaming potential modeling in fractured rock: Insights into the identification of hydraulically active fractures. Geophys Res Lett 43(10):4937–4944. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL068669
Sadighi M, Motamedvaziri B, Ahmadi H, Moeini A (2020) Assessing landslide susceptibility using machine learning models: a comparison between ANN, ANFIS, and ANFIS-ICA. Environ Earth Sci 79:536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09294-8
Saha S, Sarkar R, Thapa G, Roy T (2021) Modeling gully erosion susceptibility in Phuentsholing, Bhutan using deep learning and basic machine learning algorithms. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09599-2
Selvam S, Magesh NS, Chidambaram S, Rajamanickam M, Sashikkumar MC (2015) A GIS based identification of groundwater recharge potential zones using RS and IF technique: a case study in Ottapidaram taluk, Tuticorin district, Tamil Nadu. Environ Earth Sci 73:3785–3799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3664-0
Shafiabadi M, Kamkar-Rouhani A, Riabi S, Kahoo AR, Tokhmechi B (2021) Identification of reservoir fractures on FMI image logs using Canny and Sobel edge detection algorithms. Oil Gas Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.2516/ogst/2020086
Shin H, Santamarina JC (2021) Numerical study of fractured rock masses: Transverse isotropy vs. implicit joint-continuum models. Comput Geotech 138:104317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104317
Shu L, Mcisaac K, Osinski GR, Francis R (2017) Unsupervised feature learning for autonomous rock image classification. Comput Geosci-Uk 106:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.05.010
Sidorenko M, Orlov D, Ebadi M, Koroteev D (2021) Deep learning in denoising of micro-computed tomography images of rock samples. Comput Geosci-Uk 151:104716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104716
Sun ZH, Wang LQ, Zhou JQ, Wang CS (2020) A new method for determining the hydraulic aperture of rough rock fractures using the support vector regression. Eng Geol 271:105618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105618
Tian M, Li Bt Xu, Hm YDZ, Gao YN, Lang XZ (2021) Deep learning assisted well log inversion for fracture identification. Geophys Prospect 69:419–433. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2478.13054
Tschandl P, Sinz C, Kittler H (2019) Domain-specific classification-pretrained fully convolutional network encoders for skin lesion segmentation. Comput Biol Med 104:111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.11.010
Tut Haklidir FS, Haklidir M (2020) Prediction of geothermal originated boron contamination by deep learning approach: at Western Anatolia Geothermal Systems in Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 79:180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-08907-6
Wu M, Zhang C, Liu JM, Zhou LC (2019) Towards accurate high resolution satellite image semantic segmentation. Ieee Access 7:55609–55619. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913442
Wulamu A, Shi ZX, Zhang DZ, He ZY (2019) Multiscale road extraction in remote sensing images. Comput Intel Neurosc 2019:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2373798
Xu HY, Su X, Wang Y, Cai HY (2019) Automatic bridge crack detection using a convolutional neural network. Appl Sci 9:2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9142867
Xu Z, Shi H, Lin P, Liu TH (2021a) Integrated lithology identification based on images and elemental data from rocks. J Petrol Sci Eng 205:108853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108853
Xu ZH, Ma W, Lin P, Shi H, Pan DD, Liu TH (2021b) Deep learning of rock images for intelligent lithology identification. Comput Geosci-Uk 154:104799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104799
Xue DJ, Tang QC, Wang A, Zhang L, Zhou HW (2019) FCN-based intelligent identification of crack geometry in rock or concrete. Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 38:3393–3403. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0010
Yang BX (2019) Road and Small Building Extraction Methods Based on Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing Image. Master, Huazhong University of Science & Technology
Yu X, Han J, Shi LQ, Wang Y, Zhao YP (2017) Application of a BP neural network in predicting destroyed floor depth caused by underground pressure. Environ Earth Sci 76:535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6878-0
Zhang LH, Wang H, Xue BW, He LM, Lu Y (2021) Road extraction of high-resolution remote sensing image based on improved D-LinkNet model. Comput Eng 47(09):288–296. https://doi.org/10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0058977
Zhou L, Zhang C, Wu M (2018) D-LinkNet: LinkNet with Pretrained Encoder and Dilated Convolution for High Resolution Satellite Imagery Road Extraction. Paper Presented at the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2018.00034
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. s: 52022053, 52109129), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. s: ZR2021QE163) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No.: BK20210114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D. D. Pan contributed in the developed of idea, wrote the manuscript, supervised the work and the correction of manuscript. Y.H. Li: obtained the input data, developed and tested the code and analyzed the results. C.J. Lin contributed in the developed of idea and critically revised the manuscript. X.T. Wang: obtained the input data and contributed in the code. Z.H. Xu: analysed the results and contributed revising critically the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relation-ships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, D.D., Li, Y.H., Lin, C.J. et al. Intelligent rock fracture identification based on image semantic segmentation: methodology and application. Environ Earth Sci 82, 71 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10705-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10705-1