Abstract
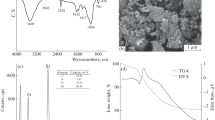
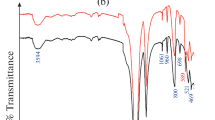
In the present study, three novel inorganic ion exchange materials based on magnesium silicates were synthesized by precipitation and hydrothermal sol–gel methods with two reagents ratio. Physico-chemical properties of samples were characterized by thermogravimetric and differential thermal analyses, low-temperature adsorption/desorption method and transmission electron microscopic studies. It was found that all sorbents were obtained in a form of amorphous layer-structure magnesium silicates with micro- and mesoporous structures. The ion exchange properties of these materials for removing Cs+, Sr2+ Cu2+, Co2+ and Cd2+ from the water solution were investigated. Data obtained showed that magnesium silicate obtained by precipitation has the higher capacity towards the heavy metal cations compared to the radionuclides regardless of the method used for synthesis. The sample synthesized with excess of metasilicate exhibited the higher efficiency of heavy metal cations sorption than the sample obtained using equimolar ratio of components. Among Langmuir, Freundlich and Dubinin–Radushkevich models, Langmuir model fitted well for experimental data received on these adsorbents.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data obtained by low temperature adsorption/desorption of nitrogen.
References
Abass MR, Diab HM, Abou-Mesalam MM (2022) New improved thermoluminescence magnesium silicate material for clinical dosimetry. SILICON 14:2555–2563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01049-9
Ahmadi SJ, Huang YD, Li W (2004) Synthetic routes, properties and future applications of polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 39:1919–1925. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000017753.90222.96
Ali IM, Kotp YH, El-Naggar IM (2010) Thermal stability, structural modifications and ion exchange properties of magnesium silicate. Desalination 259:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.03.054
Aysa-Martínez Y, Anoro-López S, Cano M, Julve D, Pérez J, Coronas J (2021) Synthesis of amorphous magnesium silicates with different SiO2:MgO molar ratios at laboratory and pilot plant scales. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 317:110946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.110946
Bhatt D, Gururani N, Srivastava A, Srivastav PCh (2021) Sorption studies of 4-NP onto goethite: effects of contact time, pH, concentration, ionic strength and temperature. Environ Earth Sci 80:273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09566-x
Bortun AI, Bortun LN, Clearfield A (1997) Hydrothermal synthesis of sodium zirconium silicates and characterization of their properties. Chem Mater 9:1854–1864. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm9701419
Brett NH, MacKenzie KJD, Sharp JH (1970) The thermal decomposition of hydrous layer silicates and their related hydroxides. Q Rev Chem Soc 24:185–207. https://doi.org/10.1039/QR9702400185
Cai Ch, Wang H, Han J (2011) Synthesis and characterization of ionic liquid-functionalized alumino-silicate MCM-41 hybrid mesoporous materials. Appl Surf Sci 257(23):9802–9808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.06.025
Chen JL, Ortiz R, Steele TWJ, Stuckey DC (2014) Toxicants inhibiting anaerobic digestion: a review. Biotechnol Adv 32(8):1523–1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.10.005
Ciesielczyk F, Krysztafkiewicz A, Jesionowski T (2007) Physicochemical studies on precipitated magnesium silicates. J Mater Sci 42:3831–3840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0464-2
Dietemann M, Baillon F, Espitalier F, Calvet R, Greenhill-Hooper M (2019) Amorphous magnesium silicate ultrasound-assisted precipitation in a mixing system: population balance modelling and crystallization rates identification. Powder Technol 356:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.08.004
Drout RJ, Robison L, Chen Zh, Islamoglu T, Farh OK (2019) Zirconium metal–organic frameworks for organic pollutant adsorption. Trends Chem 1(3):304–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trechm.2019.03.010
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Gupta S, Sireesha S, Sreedhar I, Patel ChM, Anitha KL (2020) Latest trends in heavy metal removal from wastewater by biochar based sorbents. J Water Process Eng 38:101561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101561
Hassan RS, Abass MR, Eid MA, Abdel-Galil EA (2021) Sorption of some radionuclides from liquid waste solutions using anionic clay hydrotalcite sorbent. Appl Radiat 178:109985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2021.109985
Hood C, Pensini E (2022) Alginate-bentonite clay composite porous sorbents for Cu (II) and Zn (II) removal from water. Water Air Soil Pollut 233:137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05609-6
Ihsanullah I, Sajid M, Khan S, Bilal M (2022) Aerogel-based adsorbents as emerging materials for the removal of heavy metals from water: progress, challenges, and prospects. Sep Purif Technol 291:120923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120923
Khan MU, Rai N (2022) Arsenic and selected heavy metal enrichment and its health risk assessment in groundwater of the Haridwar district, Uttarakhand. India Environ Earth Sci 81:337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10453-2
Kirillov SA, Romanova IV, Lisnycha TV, Potapenko AV (2018) High-rate electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 obtained from TiCl4 by means of a citric acid aided route. Electrochim Acta 286:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.08.034
Kumar R, Laskar MA, Hewaidy IF, Barakat MA (2019) Modified adsorbents for removal of heavy metals from aqueous environment: a Review. Earth Syst Environ 3:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-018-0085-3
Li Q, Zhang J, Lu Q, Lu J, Li J, Dong Ch, Zhu Q (2016) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of ordered mesoporous magnesium silicate-silica for dyes adsorption. Mater Lett 170:167–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.02.029
Li H, Huang Y, Liu J, Duan H (2021) Hydrothermally synthesized titanate nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals and radionuclides from water: a review. Chemosphere 282:131046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131046
Lothenbach B, Nied D, L’Hôpital E, Achiedo G, Dauzères A (2015) Magnesium and calcium silicate hydrates. Cem Concr Res 77:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2015.06.007
Maciaszek K, Brown DM, Ston V (2022) An in vitro assessment of the toxicity of two-dimensional synthetic and natural layered silicates. Toxicol in Vitro 78:105273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105273
Maslova M, Mudruk N, Ivanets A, Shashkova I, Kitikova N (2020) A novel sorbent based on Ti-Ca-Mg phosphates: synthesis, characterization, and sorption properties. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:3933–3949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06949-3
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajjadi M, Iravani S, Varmac RS (2021) Carbon-based sustainable nanomaterials for water treatment: state-of-art and future perspectives. Chemosphere 263:128005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128005
Nikolov A, Nugteren H, Rostovsky I (2020) Optimization of geopolymers based on natural zeolite clinoptilolite by calcination and use of aluminate activators. Constr Build Mater 243:118257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118257
Persson I (2010) Hydrated metal ions in aqueous solution: how regular are their structures? Pure Appl Chem 82(10):1901–1917. https://doi.org/10.1351/PAC-CON-09-10-22/html
Qi G, Lei X, Li L, Yuan Ch, Sun Y, Chen J, Chen J, Wang Y, Hao J (2015) Preparation and evaluation of a mesoporous calcium-silicate material (MCSM) from coal fly ash for removal of Co(II) from wastewater. Chem Eng J 279:777–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.077
Qu J, Tian X, Jiang Zh, Cao B, Akindolie MS, Hu Q, Feng Ch, Feng Y, Meng X, Zhang Y (2020) Multi-component adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) onto microwave-functionalized cellulose: kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, mechanisms and application for electroplating wastewater purification. J Hazard Mater 387:121718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121718
Rena X, Chena Ch, Nagatsu M, Wang X (2011) Carbon nanotubes as adsorbents in environmental pollution management: a review. Chem Eng J 170:395–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.045
Romanova IV, Kirillov SA (2018) Preparation of Cu, Ni and Co oxides by a citric acid-aided route. J Therm Anal Calorim 132:503–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6880-5
Safari S, Lottermoser BG, Alessi DS (2020) Metal oxide sorbents for the sustainable recovery of lithium from unconventional resources. Appl Mater Today 19:100638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100638
Shende P, Devlekar NP (2021) Adsorption potential of nanocomposites for the removal of toxins in healthcare. Curr Nanosci 17(6):819–828. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573413716999201209105819
Spinthaki A, Petratos G, Matheis J, Hater W (2018) The precipitation of “magnesium silicate” under geothermal stresses. Formation and characterization. Geothermics 74:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.03.001
Sun Zh, Srinivasakannan C, Liang J, Duan X (2019) Preparation of hierarchical magnesium silicate with excellent adsorption capacity. Ceram Int 45(4):4590–4595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.146
Tarnovsky DV, Tsyba MM, Kuznetsova LS, Khodakovska TA, Romanova IV (2021) Physico-chemical properties of cerium and ferric doped titanium hydroxides synthesized by two methods. J Chem Technol 29(2):192–199. https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v29i2.232199
Temuujin J, Okada K, MacKenzie KJD (1998) Formation of layered magnesium silicate during the aging of magnesium hydroxide–silica mixtures. J Am Ceram Soc 81(3):754–756. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1998.tb02405.x
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing SWK (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Tobilko VYu, Spasonova LM, Kovalchuk IA, Kornilovych BYu, Kholodko Yu (2019) Adsorption of uranium (VI) from aqueous solutions by amino-functionalized clay minerals. Colloids Interfaces 3(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010041
Vassileva P, Tzvetkova P, Lakov L, Peshev O (2008) Thiouracil modified activated carbon as a sorbent for some precious and heavy metal ions. J Porous Mater 15:593–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-007-9138-y
Zhao Zh, Zhang X, Zhou H, Liu G, Kong M, Wang G (2017) Microwave-assisted synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4-mesoporous magnesium silicate core-shell composites for the removal of heavy metal ions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 242:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.01.006
Zhuravlev IZ, Kovtun MF, Botsman AV (2021) Zirconium phosphates deposited on the granulated silica gel as adsorbents for the extraction of cesium, strontium radioisotope ions. Sep Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2021.1934024
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this study has been provided by National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine within the framework of the target research program “Synthesis and physicochemical studies of composite materials for environmental purposes based on natural and synthetic silicates”, 2022-2024. The authors thank N. I. Danilenko and O. I. V'yunov for their help in carrying out TEM and XRD measurements, and M. M. Tsyba for supporting the porous investigations of the materials.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MVK – Junior Researcher, synthesized all samples, took part in the investigation of physico-chemical properties of materials and in discussion of rezults, prepared Figures 2-4. TAK – Lead engeneer, prepared all solutions for synthesis and adsorption experiments, analysed solutions by complexonometric titration. MFK – Researcher, measured concentrations of cesium, strontium, copper, cobalt and cadmium in initial and equilibrium solutions of chlorides and nitrates by atomic adsorption analyzer. IVR – idea of investigation, fitted the experimantal data by theoretical models, analysed results of physico-chemical investigation, wrote the main manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kravchenko, M.V., Khodakovska, T.A., Kovtun, M.F. et al. Inorganic sorbents based on magnesium silicates obtained by two synthetic routes. Environ Earth Sci 81, 549 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10664-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10664-7