Abstract
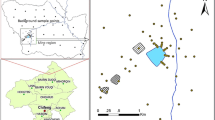
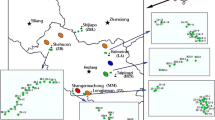
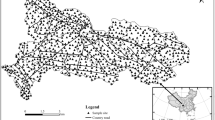
To explore the impact of metal smelting activities on surrounding environment in the water source area of the Mid–route of South–to–North Water Transfer Project of China, soil samples of farmland around a zinc smelter in this area were collected and the pollution, risk, and source of heavy metal(loid)s (As, Cu, Cr, Pb, Mn, Ni, V, and Zn) in soil samples were determined in this study. The heavy metal(loid)s contents were measured by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and their pollution levels and ecological risks were assessed by geoaccumulation index, Nemerow synthetic pollution index,and potential ecological risk index. The possible sources of the heavy metals(loid)s were identified by multivariate statistical analysis methods. The results show that the mean contents of all analyzed heavy metal(loid)s in the farmland soil were above the local soil background values except Mn; the contents of As, Cu, Pb, Zn, and Ni in the downwind direction soil decreased with the distance increasing between the sampling site and the zinc smelter; the investigated soils were moderately to seriously polluted by heavy metal(loid)s and the heavy metal(loid)s presented moderately ecological risk as a whole; As, Cu, Pb, and Zn mainly originated from zinc–smelting activities; Cr, Mn, and V primarily derived from natural source; Ni mainly came from zinc–smelting activities, partly from natural source. The zinc–smelting activity influenced the heavy metal(loid)s content, particularly Zn and Pb, in the surrounding farmland soil. The local government should strengthen the cooperative monitoring of heavy metal(loid)s in farmland and agricultural products, as well as pollutant emission monitoring and control.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akopyan K, Petrosyan V, Grigoryan R, Melkomian DM (2018) Assessment of residential soil contamination with arsenic and lead in mining and smelting towns of Northern Armenia. J Geochem Explor 184:97–109
Baltas H, Sirin M, Gökbayrak E, Ozcelik AE (2020) A case study on pollution and a human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around Sinop province, Turkey. Chemosphere 241:125015
Bhatti SS, Kumar V, Sambyal V, Singh J, Nagpal AK (2018) Comparative analysis of tissue compartmentalized heavy metal uptake by common forage crop: a field experiment. CATENA 60:185–193
Chakraborty S, Man T, Paulette L, Deb S, Li B, Weindorf DC, Frazier M (2017) Rapid assessment of smelter/mining soil contamination via portable X–ray fluorescence spectrometry and indicator kriging. Geoderma 306:108–119
Chen X, Lu X, Li LY, Yang G (2013) Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an second ringroad, NW China. Environ Earth Sci 68:1979–1988
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Centre) (1990) The background values of elements in Chinese soils. Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Csavina J, Field J, Taylor MP, Gao S, Landázuri A, Betterton EA, Sáez AE (2012) A review on the importance of metals and metalloids in atmospheric dust and aerosol from mining operations. Sci Total Environ 433:58–73
Dong B, Zhang R, Gan Y, Cai L, Freidenreich A, Wang K, Guo T, Wang H (2019) Multiple methods for the identification of heavy metal sources in cropland soils from a resource–based region. Sci Total Environ 651:3127–3138
Duodu GO, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2016) Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ Pollut 219:1077–1091
Ettler V (2016) Soil contamination near non–ferrous metal smelters: a review. Appl Geochem 64:56–74
Fan X, Lu X, Yu B, Zuo L, Fan P, Yang Y, Zhuang S, Liu H, Qin Q (2021) Risk and sources of heavy metals and metalloids in dust from university campuses: a case study of, Xi’an China. Environ Res 202:111703
Félix OI, Csavina J, Field J, Rine KP, Sáez AE, Betterton EA (2015) Use of lead isotopes to identify sources of metal and metalloid contaminants in atmospheric aerosol from mining operations. Chemosphere 122:219–226
Ghayoraneh M, Qishlaqi A (2017) Concentration, distribution and speciation of toxic metals in soils along a transect around a Zn/Pb smelter in the northwest of Iran. J Geochem Explor 180:1–14
Hakånson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control–a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Jiang Y, Guo X (2019) Multivariate and geostatistical analysis of heavy metal pollution from different sources among farmlands in the Poyang Lake region, China. J Soils Sediments 19:2472–2484
Kang M-J, Kwon YK, Yu S, Lee P-K, Park H-S, Song N (2019) Assessment of Zn pollution sources and apportionment in agricultural soils impacted by a Zn smelter in South Korea. J Hazard Mater 364:475–487
Kang M-J, Yu S, Jeon SW, Jung MC, Kwon YK, Lee P-K, Chae G (2021) Mobility of metal(loid)s in roof dusts and agricultural soils surrounding a Zn smelter: focused on the impacts of smelter–derived fugitive dusts. Sci Total Environ 757:143884
Karim Z, Qureshi BA, Mumtaz M, Qureshi S (2014) Heavy metal content in urban soils as an indicator of anthropogenic and natural influences on landscape of Karachi: a multivariate spatio–temporal analysis. Ecol Indic 42:20–31
Ke X, Gui S, Huang H, Zhang H, Wang C, Guo W (2017) Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 175:473–481
Kříbek B, Nyambe I, Majer V, Knésl I, Mihaljevič M, Ettler V, Vaněk A, Penížek V, Sracek O (2019) Soil contamination near the Kabwe Pb–Zn smelter in Zambia: environmental impacts and remediation measures proposal. J Geochem Explor 197:159–173
Kumar V, Sharma A, Kaur P, Sidhu GPS, Bali AS, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK, Cerda A (2019) Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: a state–of–the–art. Chemosphere 216:449–462
Lee P-K, Kang M-J, Jeong Y-J, Kwon YK, Yu S (2020) Lead isotopes combined with geochemical and mineralogical analyses for source identification of arsenic in agricultural soils surrounding a zinc smelter. J Hazard Mater 382:121044
Li Z, Feng X, Li G, Bi X, Sun G, Zhu J, Qin H, Wang J (2011) Mercury and other metal and metalloid soil contamination near a Pb/Zn smelter in east Hunan province, China. Appl Geochem 26:160–166
Li Y, Shen F, Li X, Zhang Z, Wang J (2015) Theoretical research and immobilization practice of heavy metal polluted soil in a closed lead–zinc smelter and surrounding farmland in Tongguan, Shaanxi. J Agro-Environ Sci 34(7):1269–1276 (in Chinese)
Li Y, Wang S, Daniel P, Xu S, Nan Z, Zang F, Zhang Q (2017) Accumulation and interaction of fluoride and cadmium in the soil–wheat plant system from the wastewater irrigated soil of an oasis region in Northwest China. Sci Total Environ 595:344–351
Li X, Li Z, Lin C, Bi X, Liu L, Feng X, Zhang H, Chen J, Wu T (2018) Health risks of heavy metal exposure through vegetable consumption near a large–scale Pb/Zn smelter in central China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:99–110
Li Y, Wang S, Nan Z, Zang F, Sun H, Zhang Q, Huang W, Bao L (2019) Accumulation, fractionation and health risk assessment of fluoride and heavy metals in soil–crop systems in Northwest China. Sci Total Environ 663:307–314
Liu B, Ai S, Zhang W, Huang D, Zhang Y (2017) Assessment of the bioavailability, bioaccessibility and transfer of heavy metals in the soil–grain–human systems near a mining and smelting area in NW China. Sci Total Environ 609:822–829
Lu X, Li LY, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y (2009) Contamination assessment of mercury and arsenic in roadway dust from Baoji, China. Atmos Environ 43:2489–2496
Lu X, Zhang X, Li LY, Chen H (2014a) Assessment of metals pollution and health risk in dust from nursery schools in Xi’an, China. Environ Res 128:27–34
Lu X, Wu X, Wang Y, Chen H, Gao P, Fu Y (2014b) Risk assessment of toxic metals in street dust from a medium–sized industrial city of China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:154–163
MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment) (2018) Soil environmental quality–Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (GB 15618–2018). Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Müller G (1969) Index of geo accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J 2(3):108–118
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2017) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi’an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361–1369
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2020) Contamination identification of trace metals in roadway dust of a typical mountains county in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China, and its relationships with socio–economic factors. Sustainability 12:5624
Peng H, Chen Y, Weng L, Ma J, Ma Y, Li Y, Islam MS (2019) Comparisons of heavy metal input inventory in agricultural soils in North and South China: a review. Sci Total Environ 660:776–786
Phil-Eze PO (2010) Variability of soil properties related to vegetation cover in a tropical rainforest landscape. J Geogr Reg Plan 3:177–184
Shen F, Liao R, Ali A, Mahar A, Guo D, Li R, Sun X, Awasthi MK, Wang Q, Zhang Z (2017) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a Pb/Zn smelter in Feng County, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:254–262
Shiel AE, Weis D, Orians KJ (2010) Evaluation of zinc, cadmium and lead isotope fractionation during smelting and refining. Sci Total Environ 408:2357–2368
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamy V, Venkatachalapathy R (2012) Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:117–124
Tembo BD, Sichilongo K, Cernak J (2006) Distribution of copper, lead, cadmium and zinc concentrations in soils around Kabwe town in Zambia. Chemosphere 63:497–501
Wang X, He M, Xie J, Xi J, Lu X (2010) Heavy metal pollution of the world largest antimony mine–affected agricultural soils in Hunan province (China). J Soils Sediments 10:827–837
Wang L, Lu X, Jing Q, Ren C, Chen C, Li X, Luo D (2012) Heavy metals pollution in soil around the lead–zinc smelting plant in Changqing town of Baojing City, China. J Agro-Environ Sci 32(2):325–330 (in Chinese)
Wang J, Su J, Li Z, Liu B, Cheng G, Jiang Y, Li Y, Zhou S, Yuan W (2019a) Source apportionment of heavy metal and their health risks in soil–dustfall–plant system nearby a typical non–ferrous metal mining area of Tongling, Eastern China. Environ Pollut 254:113089
Wang Y-Y, Li F-F, Wang X-Y, Yang Z-H, Han K, Ruan X-L (2019b) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface farmland soil around a lead and zinc smelter. Environ Sci 40(1):438–444 (in Chinese)
Wen H, Zhang Y, Cloquet C, Zhu C, Fan H, Luo C (2015) Tracing sources of pollution in soils from the Jinding Pb–Zn mining district in China using cadmium and lead isotopes. Appl Geochem 52:147–154
Wu J, Margenot AJ, Wei X, Fan M, Zhang H, Best JL, Wu P, Chen F, Gao C (2020) Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in fluvial islands, Anhui section of the lower Yangtze River: comparison of APCS–MLR and PMF. J Soils Sediments 20:3380–3393
Yang Y, Chang AC, Wang ME, Chen WP, Peng C (2018) Assessing cadmium exposure risks of vegetables with plant uptake factor and soil property. Environ Pollut 238:263–269
Yuan G-L, Sun T-H, Han P, Li J, Lang X-X (2014) Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. J Geochem Explor 136:40–47
Zhang J, Wang Y, Liu J, Liu Q, Zhou Q (2016) Multivariate and geostatistical analysis of the sources and spatial distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Gongzhuling, Northeast China. J Soils Sediments 16:634–644
Zhang Z, Zhang N, Li H, Lu Y, Wang Q, Yang Z (2019) Risk assessment, spatial distribution, and source identification of heavy metal(loid)s in paddy soils along the Zijiang River basin, in Hunan Province, China. J Soils Sediments 19:4042–4051
Zhao X, He B, Wu H, Zheng G, Ma X, Liang J, Li P, Fan Q (2020) A comprehensive investigation of hazardous elements contamination in mining and smelting–impacted soils and sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 192:110320
Zhou J, Du B, Liu H, Cui H, Zhang W, Fan X, Cui J, Zhou J (2020) The bioavailability and contribution of the newly deposited heavy metals(copper and lead) from atmosphere to rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Hazard Mater 384:121285
Zhuang S, Lu X (2020) Environmental risk evaluation and source identification of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soil of Shangdan valley, Northwest China. Sustainability 12:5806
Zhuang S, Lu X, Yu B, Fan X, Yang Y (2021) Ascertaining the pollution, ecological risk and source of metal(loid)s in the upstream sediment of Danjing River, China. Ecol Indic 125:107502
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41271510), the Research and Development Key Project of Shaanxi Province (2020SF–433), Shaanxi Province Natural Science Foundation Research Project (Youth Talent Project) (2014JM2–4040) and Science and Technology Research Project of Shangluo University (SK2014–01–24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ: field sampling, methodology, statistical analysis, writing—original draft. XL: funding acquisition, conceptualization, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest with respect to the publication and authorship of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, S., Lu, X. Determining environmental risk and source of heavy metal(loid)s in the surrounding farmland soil of a zinc smelter in water source area, Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 81, 67 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10203-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10203-4