Abstract
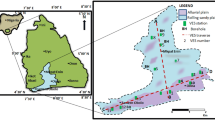
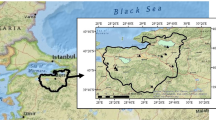
This research revises and improves previous studies conducted in the Adamawa region regarding aquifer characterisation. Linear regression technique is used to predict hydrogeological parameters from electrical data, where different empirical relationships are established on the basis of geological settings. Hence, for each parameter to be predicted, there are two relationships, the equal number of geological groups encountered in the study area, namely metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. For this, electrical data were interpreted using conjointly curve-matching method and inverse slope method to improve the previous results, taking into account geological inhomogeneities of the region. Hydraulic conductivity and transmissivity values are determined from pumping tests conducted on 13 VESs out of a total of 50. From those experimental values, strong relationships are established between these hydrogeological parameters and electrical data, with regard to the two main geological settings existing within the region. Aquifer parameters are consequently improved. Hydraulic conductivity, transmissivity, resistivity, thickness and transverse resistance changed in their mean values, respectively, as follows: 2.74–0.3 m/day, 31.15–31 m2/day, 225–30.8 Ω m, and 31–4.9 m. Same change trends are also noted in the extremum values. Major changes are observed in aquifer resistivity and thickness. In addition to those changes, “Pan-African” syntax does no more fit to design this aquifers system because it refers to a regional stratigraphic and plate tectonic setting which does not have strong impact on the major aquifer parameters.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Major data are included in the manuscript. However, any further data would be provided if required.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aretouyap Z, Njandjock Nouck P, Bisso D, Nouayou R, Lengué B, Lepatio Tchieg A (2014a) Climate variability and its possible interactions with water resources in Central Africa. J Appl Sci 14:2219–2233. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2014.2219.2233
Aretouyap Z, Njandjock Nouck P, Ekoro Nkoungou H, Meli’i JL, Lepatio Tchieg A (2014b) Investigation of groundwater quality control in Adamawa-Cameroon region. J Appl Sci 14:2309–2319. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2014.2309.2319
Aretouyap Z, Nouayou R, Njandjock Nouck P, Asfahani J (2015) Aquifers productivity in the Pan-African context. J Earth Syst Sci 124:527–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0561-1
Aretouyap Z, Njandjock Nouck P, Nouayou R, Teikeu Assatse W, Asfahani J (2017) Aquifer porosity in the Pan-African context. Environ Earth Sci 76:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6440-0
Aretouyap Z, Bisso D, Njandjock Nouck P, Amougou Menkpa LE, Asfahani J (2018) Hydrogeophysical characteristics of Pan-African aquifer specified through an alternative approach based on the interpretation of vertical electrical sounding data in the Adamawa Region, Central Africa. Nat Resour Res 28:63–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-018-9373-8
Aretouyap Z, Bisso D, Méli’i JL, Njandjock Nouck P, Njoya A, Asfahani J (2019a) Hydraulic parameters evaluation of the Pan-African aquifer by applying an alternative geoelectrical approach based on vertical electrical soundings. Geofis Int 58:113–126. https://doi.org/10.22201/igeof.00167169p.2018.58.2.1964
Aretouyap Z, Bisso D, Njandjock Nouck P, Asfahani J (2019b) A coupled hydrogeophysical approach to enhance groundwater resources management in developing countries. In: Chaminé H, Barbieri M, Kisi O, Chen M, Merkel B (eds) Advances in sustainable and environmental hydrology, hydrogeology, hydrochemistry and water resources. Advances in science, technology and innovation (IEREK Interdisciplinary Series for Sustainable Development). Springer, Cham, pp 363–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01572-5_85
Aretouyap Z, Billa L, Jones M, Richter G (2020) Geospatial and statistical interpretation of lineaments: salinity intrusion in the Kribi-Campo coastland of Cameroon. Adv Space Res 66:844–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2020.05.002
Asfahani J (2016) Hydraulic parameters estimation by using an approach based on vertical electrical soundings (VES) in the semi-arid Khanasser valley region, Syria. J Afr Earth Sci 117:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.01.018
Bisso D, Arétouyap Z, Nshagali Biringanin G, Njandjock Nouck P, Asfahani J (2019) Variation of Subsurface Resistivity in the Pan-African Belt of Central Africa. In: Rossetti F et al (eds) The structural geology contribution to the Africa-Eurasia geology: basement and reservoir structure, ore mineralisation and tectonic modelling. Advances in science, technology & innovation (IEREK Interdisciplinary Series for Sustainable Development). Springer, Cham, pp 25–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01455-1_6
Chandra S, Ahmed S, Ram A, Dewandel B (2008) Estimation of hard rock aquifers hydraulic conductivity from geoelectrical measurements: a theoretical development with field application. J Hydrol 357:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.05.023
Chen J, Hubbard S, Rubin Y (2001) Estimating the hydraulic conductivity at the South Oyster Site from geophysical tomographic data using Bayesian techniques based on the normal linear regression model. Water Resour Res 37(6):1603–1613. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000WR900392
De Almeida A, Marciel DF, Sousa KF, Nascimento CTC, Koide D (2021) Vertical electrical sounding (VES) for estimation of hydraulic parameters in the porous aquifer. Water 13:170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020170
Frohlich RK, Fisher JJ, Summerly E (1996) Electric-hydraulic conductivity correlation in fractured crystalline bedrock: Central Landfill, Rhode Island, USA. J Appl Geophys 35:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-9851(96)00028-6
Hubbard S, Rubin Y (2000) A review of selected estimation techniques using geophysical data. J Contam Hydrol 45:3–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(00)00117-0
Huntley D (1986) Relation between permeability and electrical resistivity in a granular aquifer. Groundwater 24:466–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1986.tb01025.x
Kelly WE (1977) Geoelectric sounding for estimating hydraulic conductivity. Groundwater 15:420–425. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1977.tb03189.x
Khalil MA, Santos FAM (2009) Influence of degree of saturation in the electric resistivity-hydraulic conductivity relationship. Surv Geophys 30:601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-009-9072-4
Kirkby A, Heinson G (2015) Linking electrical and hydraulic conductivity through models of random resistor networks. ASEG Extended Abstr 1:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1071/ASEG2015ab017
Lesmes DP, Friedman SP (2005) Relationships between the electrical and hydrogeological properties of rocks and soils. In: Rubin Y, Hubbard SS (eds) Hydrogeophysics. Water Science and Technology Library. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 87–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3102-5_4
Maréchal A (1976) Géologie et géochimie des ressources thermominérales du Cameroun. Doc ORSTOM 59:169–176
Massoud U, Santos F, El Qady G, Atya M, Soliman M (2010) Identification of the shallow subsurface succession and investigation of the seawater invasion to the Quaternary aquifer at the northern part of El Qaa plain, Southern Sinai, Egypt by transient electromagnetic data. Geophys Prospect 58:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2478.2009.00804.x
Mawer C, Knight R, Kitanidis PK (2015) Relating relative hydraulic and electrical conductivity in the unsaturated zone. Water Resour Res 51:599–618. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014WR015658
Mazac O, Kelly WE, Linda I (1985) A hydrogeophysical model for relations between electrical and hydraulic properties of aquifers. J Hydrol 79:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(85)90178-7
Niwas S, Celik M (2012) Equation estimation of porosity and hydraulic conductivity of Ruhrtal aquifer in Germany using near surface geophysics. J Appl Geophys 84:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2012.06.001
Niwas S, De Lima OAL (2003) Aquifer parameter estimation from surface resistivity data. Ground Water 41:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2003.tb02572.x
Niwas S, Singhal DC (1981) Estimation of aquifer transmissivity from Dar-Zarrouk parameters in porous media. J Hydrol 50:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(81)90082-2
Niwas S, Singhal DC (1985) Aquifer transmissivity of porous media from resistivity data. J Hydrol 82:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(85)90050-2
Niwas S, Tezkan B, Israil M (2011) Aquifer hydraulic conductivity estimation from surface geoelectrical measurements for Krauthausen test site, Germany. Hydrogeol J 19(2):307–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-010-0689-7
Njonfang E, Ngako V, Moreau C, Affaton P, Diot H (2008) Restraining bends in high temperature shear zones: “The Central Cameroon Shear Zone”, Central Africa. J Afr Earth Sci 52:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2008.03.002
Orellana E, Mooney HM (1966) Master tables and curves for vertical electrical soundings over layered structures. Interciencia, Madrid. https://lib.ugent.be/catalog/rug01:001374284
Sikandar P, Christen E (2012) Geoelectrical sounding for the estimation of hydraulic conductivity of alluvial aquifers. Water Resour Manag 26(5):1201–1215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9954-3
Singh VP, Frevert DK (2005) Watershed models. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420037432
Singh S, Singh VS (2016) Estimation of hydraulic characteristics from electrical resistivity data in coastal aquifers of southern India. J Geol Soc India 88:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-016-0460-3
Soupios PM, Kouli M, Vallianatos F, Vafidis A, Stavroulakis G (2007) Estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters from surficial geophysical methods: a case study of Keritis Basin in Chania (Crete–Greece). J Hydrol 338(1–2):122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.02.028
Stelmach RD, Clasen T (2015) Household water quantity and health: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:5954–5974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120605954
Tchameni R, Mezger R, Nsifa NE, Pouclet A (2001) Crustal origin of early proterozoïc syenites in the Congo (Ntem Complex), South Cameroon. Lithos 57:23–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00072-4
Tijani MN, Oluchukwu IN, Oladunjoye MA (2018) Estimation of hydraulic properties from resistivity sounding data: a case study of basement aquifer in Ibadan, SW-Nigeria. J Min Geol 54(1):59–74
Toteu SF, Ngako V, Affaton P, Nnange JM, Njanko TH (2000) Pan-African tectonic evolution in Central and Southern Cameroon: tranpression and transtension during sinistral shear movements. J Afr Earth Sci 36:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-5362(03)00023-X
Toteu SF, Van Schmus WR, Michard A (2001) New U-Pb and Sm-Nd data from North-Central Cameroun and its bearing on the pre-pan African history of Central Africa. Precambr Res 180:45–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00149-2
Youssef MAS (2020) Geoelectrical analysis for evaluating the aquifer hydraulic characteristics in Ain El-Soukhana area, West Gulf of Suez, Egypt. NRIAG J Astron Geophys 9(1):85–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/20909977.2020.1713583
Zohdy AAR (1989) A new method for the automatic interpretation of Schlumberger and Wenner sounding curves. Geophysics 54:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1442648
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to thank Prof. I. Othman, General Director of the Syrian Atomic Energy Commission for allowing Prof. J. Asfahani to join the research team that conducted this investigation. We are very grateful to the four anonymous reviewers who help us improve the quality of this article, and to the Editor-in-Chief, Prof. James LaMoreaux.
Funding
This study was supported by authors’ income sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DB emitted the idea of revising the hydro-parameters within the region of Adamawa. ZA conducted the literature search and drafted the outlines of the initial manuscript. WT, JD and FK analysed it under the supervision of JA. RN, PN as well as DB revised and criticized the final version. Their comments and criticisms have been addressed by ZA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aretouyap, Z., Bisso, D., Assatse, W.T. et al. A detailed analysis of hydro-parameters of the Adamawa Plateau watershed derived from the application of geoelectrical technique. Environ Earth Sci 80, 774 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10080-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10080-3