Abstract
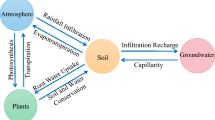
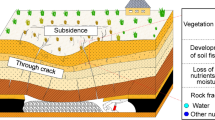
The erosion gully is serious in black soil area of Northeast China and the study of gully restoration is less. In this paper, based on the reconstructed soil, coal gangue was used to filling and cover topsoil on coal gangue to conserve soil and water. To explore the reconstructed soil structural change on properties, the hydraulic and physicochemical parameters of 36 combined treatments with coal gangue and topsoil of different sizes and thicknesses were carried out in the soil column for the experiment. The variations of infiltration, soil water storage capacity (SWSC), and physical and chemical properties under the treatments were discussed. The results showed that coal gangue thickness of reconstructed soil had influence the infiltration rate and cumulative infiltration. The Kostiakov model is most suitably applied to reconstructed soil infiltration. The SWSCs indicated that soil thickness determined the SWSCs, and the interaction between large-sized coal gangue and topsoil thickness had a significant effect on MRWSC. The soil layer was positively correlated with soil nutrients, and coal gangue layer has contributed to reduce the fertility loss. Coal gangue had a significant effect on TP, soil shrinkage and DIR, which is beneficial to reconstructed soil stability and surface water–groundwater conversion. The coal gangue reconstructed soil structure contributed to gully restoration which the large-sized coal gangue of 50 cm thickness, small-sized coal gangue of 50–60 cm thickness and topsoil of 50–70 cm thickness should be used to fill and repaired erosion gullies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeli A, McLaughlin MR, Brooks JP, Read JJ, Willers JL, Lang DJ, Mcgrew R (2013) Age chronosequence effects on restoration quality of reclaimed coal mine soils in Mississippi agroecosystems. Soil Sci 178:335–343. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0b013e3182a79e37
Bao SD (2008) Agricultural Soil analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, pp 30–38
Bian Z, Miao X, Lei S, Chen S-E, Wang W, Struthers S (2012) The challenges of reusing mining and mineral-processing wastes. Science 337:702–703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224757
Borrelli P, Robinson DA, Fleischer LR, Lugato E, Ballabio C, Alewell C, Meusburger K, Modugno S, Schütt B, Ferro V (2017) An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat Commun 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02142-7
Chen X, Zhang L, Chen M, Xing Y, Hu Z, Liu B (2018) Aggregate distribution and organic carbon mineralization of reconstructed soils filled with coal gangue in a Huainan coal mining area, China. Fresenius Environ Bull 2712A:8882–8891. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA08002J
Cheng W, Bian Z-F, Dong J-H, Lei S-G (2014) Soil properties in reclaimed farmland by filling subsidence basin due to underground coal mining with mineral wastes in China. T Nonferr Metal Soc 24:2627–2635. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-63261463392-6
Cheng Y, Hongqiang M, Hongyu C, Jiaxin W, Jing S, Zonghui L, Mingkai Y (2018) Preparation and characterization of coal gangue geopolymers. Constr Build Mater 187:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.220
Feng Y, Wang J, Bai Z, Reading L (2019) Effects of surface coal mining and land reclamation on soil properties: a review. Earth Sci Rev 191:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.02.015
He H, Hong F-F, Tao X-X, Huang G-H, Leng Y-W, Shao J-F, Zhao Y-D (2016) A study on soil basic characteristics, main microbial flora and typical metal fraction surrounding coal gangue dump in Xiangtan Hunan Province, south of China. Environ Earth Sci 75:488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5340-z
Horton RE (1941) An approach toward a physical interpretation of infiltration-capacity. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 5C:399–417. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1941.036159950005000C0075x
Hu Z (1997) Principle and method of soil profile reconstruction for coal mine land reclamation. J China Coal Soc 6:59–64. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.1997.06.012
Huang J, Wang P, Xu C, Zhu Z (2018a) Fly ash modified coalmine solid wastes for stabilization of trace metals in mining damaged land reclamation: a case study in xuzhou coalmine area. Int J Environ Res Public Health 1510:2317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102317
Huang Y, Kuang X, Cao Y, Bai Z (2018b) The soil chemical properties of reclaimed land in an arid grassland dump in an opencast mining area in China. RSC Adv 8:41499–41508. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08002j
Jiang X, Lu WX, Zhao HQ, Yang QC, Yang ZP (2014) Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy-metal pollution around coal gangue dump. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 14:1599. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-14-1599-2014
Kostiakov AN (1932) On the dynamics of the coefficient of water percolation in soils and the necessity of studying it from the dynamic point of view for the purposes of amelioration. Trans Sixth Comm Int Soc Soil Sci 1:7–21
Kuang X, Cao Y, Luo G, Huang Y (2019) Responses of melilotus officinalis growth to the composition of different topsoil substitute materials in the reclamation of open-pit mining grassland area in inner mongolia. Mater Basel Switzerland 1223:3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233888
Li MS (2006) Ecological restoration of mineland with particular reference to the metalliferous mine wasteland in China: a review of research and practice. Sci Total Environ 357:38–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.05.003
Li S, Liber K (2018) Influence of different revegetation choices on plant community and soil development nine years after initial planting on a reclaimed coal gob pile in the Shanxi mining area, China. Sci Total Environ 618:1314–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.252
Li J, Wang J (2019) Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: a review. J Clean Prod 239:117946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117946
Li F, Li X, Hou L, Shao A (2020) A long-term study on the soil reconstruction process of reclaimed land by coal gangue filling. CATENA 195:104874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104874
Liu H, Liu Z (2010) Recycling utilization patterns of coal mining waste in China. Resour Conserv Recy 54:1331–1340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.05.005
Motesharezadeh B, Ahmadiyan E, Alikhani HA, Azarnivand H (2017) The use of coal gangue as a cultivation bed conditioner in forage maize inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 48:1266–1279. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2017.1322602
Novák V, Kňava K, Šimůnek J (2011) Determining the influence of stones on hydraulic conductivity of saturated soils using numerical method. Geoderma 161:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.12.016
Page KL, Dang YP, Dalal RC, Reeves S, Thomas G, Wang W, Thompson JP (2019) Changes in soil water storage with no-tillage and crop residue retention on a Vertisol: impact on productivity and profitability over a 50 year period. Soil till Res 194:104319. https://doi.org/10.1015/j.still.2019.104319
Peng D, Wang Y, Liu X, Tang B, Zhang N (2019) Preparation, characterization, and application of an eco-friendly sand-fixing material largely utilizing coal-based solid waste. J Hazard Mater 373:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.092
Philip JR (1957) The theory of infiltration: 1. the infiltration equation and its solution. Soil Sci 835:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200606001-00009
Querol X, Zhuang X, Font O, Izquierdo M, Alastuey A, Castro I, Van Drooge BL, Moreno T, Grimalt JO, Elvira J (2011) Influence of soil cover on reducing the environmental impact of spontaneous coal combustion in coal waste gobs: a review and new experimental data. Int J Coal Geol 85:2–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2010.09.002
Shrestha RK, Lal R (2011) Changes in physical and chemical properties of soil after surface mining and reclamation. Geoderma 161:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.12.015
Thierfelder C, Wall PC (2009) Effects of conservation agriculture techniques on infiltration and soil water content in Zambia and Zimbabwe. Soil till Res 105:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.07.007
Thompson JP, Chen M, Chen X, Huang H, Liu B, Hu Z (2018) Effects of fly ash, silty clay loam and loamy sand on the hydraulic conductivity and air permeability of coal gangue. Fresen Environ Bull 27:2035–2042
Tong W, Ying W, Jun W (2008) Research on potential fertilization of coal gangue in the Weibei Coalfield, China. Acta Geol Sin Engl 82:717–721. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.2008.tb00623.x
Ussiri DAN, Lal R (2013) Land management effects on carbon sequestration and soil properties in reclaimed farmland of Eastern Ohio, USA. Open J Soil Sci 3:1–46. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojss.2013.31006
Wang J, Zhang M, Bai Z, Yang R, Guo L (2014) Multi-fractal characteristics of reconstructed soil particle in opencast coal mine dump in loess area. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 304:230–238
Wang J, Meng Z, Zhongke B, Lingli G (2015a) Multi-fractal characteristics of the particle distribution of reconstructed soils and the relationship between soil properties and multi-fractal parameters in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3761-0
Wang J, Zhang M, Bai Z, Guo L (2015b) Multi-fractal characteristics of the particle distribution of reconstructed soils and the relationship between soil properties and multi-fractal parameters in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Environ Earth Sci 73:4749–4762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3761-0
Wang J, Li X, Bai Z, Huang L (2017a) The effects of coal gangue and fly ash on the hydraulic properties and water content distribution in reconstructed soil profiles of coal-mined land with a high groundwater table. Hydrol Process 31:687–697. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11065
Wang J, Wang P, Qin Q, Wang H (2017b) The effects of land subsidence and rehabilitation on soil hydraulic properties in a mining area in the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 159:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.08.001
Wang J, Qin Q, Bai Z (2018a) Characterizing the effects of opencast coal-mining and land reclamation on soil macropore distribution characteristics using 3D CT scanning. CATENA 171:212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.07.022
Wang J, Qin Q, Guo L, Feng Y (2018b) Multi-fractal characteristics of three-dimensional distribution of reconstructed soil pores at opencast coal-mine dump based on high-precision CT scanning. Soil till Res 182:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.05.013
Wang F, Wang J, Wang Y (2019) Using multi-fractal and joint multi-fractal methods to characterize spatial variability of reconstructed soil properties in an opencast coal-mine dump in the Loess area of China. CATENA 182:104111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104111
Wang L, Wang F, Wang S, Huang Y, Zhang Z, Bai Z, Cao Y (2021) Analysis of differences in chemical properties of reconstructed soil under different proportions of topsoil substitute materials. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-021-12803-2
Xu LJ, Yan JP (2010) Analysis of different thickness topsoil quality of reclamation land in Huainan coal mining area. Conf Environ Sci Inf Appl Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESIAT.2010.5567342
Xu L, Huang C, Li Q, Zhu X, Liu SG (2016) Study on the physicalchemical properties of reconstructed soil in filling area affected by the substrate made of coal gangue with different particle size distribution and the crop effect. Ecol Environ Sci 251:141–148. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2016.01.021
Xu H, Song W, Cao W, Shao G, Lu H, Yang D, Chen D, Zhang R (2017) Utilization of coal gangue for the production of brick. J Mater Cycles Waste 19:1270–1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0521-0
Zhang J, Lei T, Qu L, Chen P, Gao X, Chen C, Yuan L, Zhang M, Su G (2017) Method to measure soil matrix infiltration in forest soil. J Hydrol 552:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.032
Zhang K, Xu LJ, Huang GD, Meng XY, Yao JX, Jiang BX (2020) Coupled variations of soil temperature and moisture in reclaimed fields filled with coal gangue of different grain size distributions. J Soils Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02579-2
Zhen Q, Zheng J, Zhang X, Shao M (2019) Changes of solute transport characteristics in soil profile after mining at an opencast coal mine site on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci Total Environ 665:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.035
Zhou BB, Ming’an S, Mingxia W, Quanjiu W, Horton R (2010) Effects of coal gangue content on water movement and solute transport in a China Loess Plateau soil. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 3811:1031–1038. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000056
Zhou C, Liu G, Cheng S, Fang T, Lam PKS (2014) The environmental geochemistry of trace elements and naturally radionuclides in a coal gangue brick-making plant. Sci Rep Uk 4:6221. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06221
Zhou BB, Li Y, Wang QJ, Jiang YL, Li S(2019) Preferential water and solute transport through sandy soil containing artificial macropores. Environ Earth Sci, 2013 70(5):2371-2379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2339-6
Zhu P, Zheng M, Zhao S, Wu J, Xu H (2016) A novel environmental route to ambient pressure dried thermal insulating silica aerogel via recycled coal gangue. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9831515
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge that this research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0504200).
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0504200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Among the authors in the list, DL mainly takes charge of the writing and researching, and he finished the main experiment, he also finish the manuscript submission, ZW plays a guiding role in the research, he is the research funding leader, he provides the experiment help, BW provides the some suggestions in the experiments and he joins in the research funding, he also help us to make the experiment perfect and provides us better method to improve the experiment, JZ is as the teamworker in the experiment and he provides a great help to implementation of the experiment, also he helps to improve the manuscript’s quality, TH helps to corrected the manuscript langue.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare to have no conflicts of interest or competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or used during the study are available in a repository or online.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Wang, Z., Wang, B. et al. Experimental study on reconstructed soil properties based on numerical analysis. Environ Earth Sci 80, 767 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09976-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09976-x