Abstract
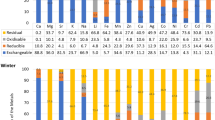
This study was carried out to elucidate the chemical fractionation pattern of selected metals (Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mg, Mn, Pb, Sr and Zn) in the soil collected from roadside, urban and suburban environment. Modified sequential extraction method was applied to assess the exchangeable, reducible, oxidisable and residual fractions of the metals in soil samples. Quantification of the metals was performed by atomic absorption spectrometry. Various statistical methods were used to evaluate the comparative distribution and mutual relationships among the metals. In addition, risk assessment employing contamination factor, enrichment factor and risk assessment code were also carried out. Among the metals, Ca, Sr, Mn, Mg, Cd, Co and Pb exhibited significant mobility and availability whereas Zn, Fe, Cu and Cr were mainly found in the residual fraction. Most of the soil samples exhibited low risk for Fe, Zn, Cu and Cr, but medium risk was associated with Co, Mn, Pb and Cd, while Ca and Sr showed high risk in most of the cases. Similarly, Zn, Co, Sr, Pb and Cd exhibited moderately severe to extremely severe enrichment of the metals in soil. Cluster analysis indicated significant anthropogenic contamination of the metals in soil.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed F, Shah MH, Shaheen N (2014) Diurnal and nocturnal variations of trace metals in urban atmospheric particulate matter from Islamabad, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 71:817–826
Borona A, Aranguiz I, Elias A (1999) Assessment of metal extraction, distribution and contamination in surface soils by a 3-step sequential extraction procedure. Chemosphere 39:1911–1922
Boughriet A, Proix N, Billon G, Recourt P, Ouddane B (2007) Environmental impacts of heavy metal discharges from a smelter in Deule-canal sediments (Northern France): concentration levels and chemical fractionation. Water Air Soil Pollut 180:83–95
Dragovic S, Mihailovi N (2009) Analysis of mosses and topsoil’s for detecting sources of heavy metal pollution: multivariate and enrichment factor analysis. Environ Monit Assess 157:383–390
Fernandez-Ondono E, Bacchetta G, Lallena AM, Navarro FB, Ortiz I, Jimenez MN (2017) Use of BCR sequential extraction procedures for soils and plant metal transfer predictions in contaminated mine tailings in Sardinia. J Geochem Explor 172:133–141
Filgueiras AV, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2002) Chemical sequential extraction for metal partitioning in environmental solid samples. J Environ Monit 4:823–857
Franco-Uria A, Lopez-Mateo C, Roca E, Fernandez-Marcos ML (2009) Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J Hazard Mater 165:1008
Gabarron M, Faz A, Martinez-Martinez S, Zornoza R, Acosta JA (2017) Assessment of metals behaviour in industrial soil using sequential extraction, multivariable analysis and a geostatistical approach. J Geochem Explor 172:174–183
Gao X, Chen CTA, Wang G, Qinzhao X, Cheng T, Shaoyong C (2010) Environmental status of Daya Bay surface sediments inferred from a sequential extraction technique. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 86:369–378
Gleyzes C, Tellier S, Astruc M (2002) Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: A review of sequential extraction procedures. Trends Anal Chem 21:451–467
Gyimah E, Akoto O, Mensah JK, Bortey-Sam N (2018) Bioaccumulation factors and multivariate analysis of heavy metals of three edible fish species from the Barekese reservoir in Kumasi. Ghana Environ Monit Assess 190:9
Hasan M, Kausar D, Akhter G, Shah MH (2018) Evaluation of the mobility and pollution index of selected essential/toxic metals in paddy soil by sequential extraction method. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:283–291
He QS, Ren Y, Mohamed I, Ali M, Hassan W, Zeng FG (2013) Assessment of trace and heavy metal distribution by four sequential extraction procedures in a contaminated soil. Soil Water Res 8:71–76
Heltai G, Gyori Z, Fekete I, Halasz G, Kovacs K, Takacs A, Boros N, Horvath M (2018) Longterm study of transformation of potentially toxic element pollution in soil/water/sediment system by means of fractionation with sequential extraction procedures. Microchem J 136:85–93
Iqbal J, Shah MH (2011) Distribution, correlation and risk assessment of selected metals in urban soils from Islamabad, Pakistan. J Hazard Mater 158:887–898
Javed MB, Shotyk W (2018) Estimating bioaccessibility of trace elements in particles suspended in the Athabasca River using sequential extraction. Environ Pollut 240:466–474
Kennou B, El Meray M, Romane A, Arjouni Y (2015) Assessment of heavy metal availability (Pb, Cu, Cr, Cd, Zn) and speciation in contaminated soils and sediment of discharge by sequential extraction. Environ Earth Sci 74:5849–5858
Kumar M, Furumai H, Kurisu F, Kasuga I (2013) Potential mobility of heavy metals through coupled application of sequential extraction and isotopic exchange: Comparison of leaching tests applied to soil and soakaway sediment. Chemosphere 90:796–804
Li X, Thornton I (2001) Chemical partitioning of trace and major elements in soil contaminated by mining and smelting activities. Appl Geochem 16:1693–1706
Liang GD (2010) Analysis and fractionation of trace element in soils. In: Hooda PS (ed) Trace Element in Soil, John Wiley and Sons, West Sussex, England
Lopez-Sanchez JF, Rubio R, Rauret G (1993) Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for trace metals partitioning in sediments. J Environ Anal Chem 51:113–121
Lu XW, Wang LJ, Li LY, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173:744–749
Nastja RS (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in paddy soils from Kočani Field (Republic of Macedonia). RMZ Mater Geoenviron 58:47–58
Nemati K, Abu Bakar NK, Sohanzadeh E, Abas MR (2009) A modification of the BCR sequential extraction procedure to investigate the potential mobility of copper and zinc in shrimp aquaculture sludge. Michrochem J 92:165–169
Nemati K, Abu Bakar NK, Abas MR, Sobhanzadeh E (2011) Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J Hazard Mater 192:402–410
Parat C, Leveque J, Doousset S, Chaussod R, Andreaux F (2003) Comparison of three sequential extraction procedures used to study trace metal distribution in an acidic sandy soil. Anal Bioanal Chem 376:243–247
Perin G, Craboledda L, Lucchese M, Cirillo R, Dotta L, Zanetta ML, Oro AA (1985) Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of northern Adriatic Sea: A new approach for environmental toxicity determination. In: Lakkas TD (ed) Heavy Metals in the Environment, Vol 2, CEP Consultants, Edinburg
Prechthai T, Parkpian P, Visvanathan C (2008) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and its mobilization from municipal solid waste open dumping. J Hazard Mater 156:86–94
Quevauviller P, Rauret G, Griepink B (1993) Conclusion of the workshop-single and sequential extraction in sediments and soils. Int J Environ Anal Chem 51:231–235
Radojevic M, Bashkin VM (1999) Practical Environmental Analysis. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Rauret G (1998) Extraction procedures for the determination of heavy metals in contaminated soil and sediment. Talanta 46:449–455
Relic D, Heberger K, Sakan S, Skrbic B, Popovic A, Dordevic D (2018) Ranking and similarity of conventional, microwave and ultrasound element sequential extraction methods. Chemosphere 198:103–110
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Shah MH (2016) Spatio-temporal variability and pollution assessment of selected metals in freshwater sediments, Pakistan. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 44:402–410
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Akhter G, Shah MH (2018) Fractionation, bioavailability, contamination and environmental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. J Geochem Explor 184:199–208
Shah MH, Shaheen N (2008) Annual and seasonal variations of trace metals in atmospheric suspended particulate matter in Islamabad, Pakistan. Water Air Soil Pollut 190:13–25
Skipperud L, Salbu B (2015) Sequential extraction as a tool for mobility studies of radionuclides and metals in soils and sediments. Radiochim Acta 103:187–197
StatSoft (1999) STATISTICA for windows. Computer Programme Manual, Tulsa
Sundaray SK, Nayak BB, Lin S, Bhatta D (2011) Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediment-A case study: Mahanadi basin, India. J Hazard Mater 186:1837–1846
Sungur A, Soylak M, Yilmaz E, Yilmaz S, Ozcan H (2015) Characterization of heavy metal fractions in agricultural soils by sequential extraction procedure: the relationship between soil properties and heavy metal fractions. Soil Sediment Contam 24:1–15
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed-sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu. Hawaii Environ Geol 39:611–627
Sutherland RA, Tack FMG, Tolosa CA, Verloo MG (2001) Metal extraction from road sediment using different strength reagents: Impact on anthropogenic contaminant signals. Environ Monit Assess 71:221–242
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Tokalioglu S, Yilmaz V, Kartal S (2010) An assessment of metal sources by multivariate analysis and speciation of metals in soil samples using the BCR sequential extraction procedure. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 38:713–718
Tume P, Gonzalez E, King RW, Monsalve V, Roca N, Bech J (2018) Spatial distribution of potentially harmful elements in urban soils, city of Talcahuano, Chile. J Geochem Explor 184:333–344
Vega FA, Covelo EF, Cerqueira B, Andrade ML (2009) Enrichment of marsh soils with heavy metals by effect of anthropic pollution. J Hazard Mater 170:1056–1063
Xiao L, Guan DS, Peart MR, Chen YJ, Li QQ (2017) The respective effects of soil heavy metal fractions by sequential extraction procedure and soil properties on the accumulation of heavy metals in rice grains and brassicas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2558–2571
Yang K, Zhang T, Shao YQ, Tian C, Cattle SR, Zhu Y, Song JJ (2018) Fractionation, bioaccessibility, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of an urban recreational area amended with composted sewage sludge. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:4
Zemberyova M, Bartekova J, Hagarova I (2006) The utilization of modified three-step sequential extraction procedure for the fractionation of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in soil reference materials of different origins. Talanta 70:973
Zemberyova M, Hagarová I, Zimová J, Barteková J, Kuss HM (2010) Determination of molybdenum in extracts of soil and sewage sludge CRMs after fractionation by means of BCR modified sequential extraction procedure. Talanta 82:582–586
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Makino T, Wu LH, Nanzyo M (2013) The heavy metal partition in size-fractions of the fine particles in agricultural soils contaminated by wastewater and smelter dust. J Hazard Mater 248:303–312
Zhang Y, Yin CB, Cao SZ, Cheng LL, Wu GS, Guo JB (2018) Heavy metal accumulation and health risk assessment in soil-wheat system under different nitrogen levels. Sci Total Environ 622:1499–1508
Zimmerman AJ, Weindrof DC (2010) Heavy metal and trace metal analysis in soil by sequential extraction: A review of procedures. Int J Anal Chem 2010:1–7
Funding
Financial and technical help provided by Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan to carry out this project is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parveen, R., Khan, Y.K., Toqeer, M. et al. Study of fractionation, mobility and risk assessment of selected metals in suburban, urban and roadside soil from Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 80, 584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09898-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09898-8