Abstract
Land subsidence analysis using satellite imagery is a consequential subject. Earth scientists have begun utilizing satellite imagery as an alternative to in-situ measurements and conceptual models. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, moreover, utilize the reformer approach more than traditional satellite imagery with the use of high-resolution radar images. As a natural hazard, land subsidence is mostly attributed to excessive groundwater extraction, which is also the main reason for choosing the Konya Plain in Turkey as the study area for the present work. Since the Konya region is an agricultural and industrial land, groundwater extraction has been a challenging circumstance for the last few years. Change in groundwater level is also correlated with land subsidence rates through hydrogeological conceptualization. In this study, SAR images of the Sentinel 1 satellite are utilized for land subsidence rate calculation with the European Space Agency’s SNAP software. Differential SAR interferometry (DInSAR) technique was used, which makes possible to detect deformation on the ground surface of the same portion of the Earth’s surface using SAR images. The different acquisitions with DInSAR method allow to create differential interferograms that provide information ground motion with accuracy in cm. Three periods were utilized as 2016–2017, 2017–2018 and 2018–2019 the mean land subsidence rates were calculated for each period as 2.2, 1.4 and 1.7 cm/year, respectively. In the sum of the 3-year period, the maximum subsidence value went up to 16 cm.


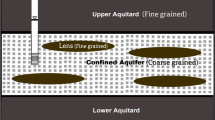
(modified from Özyurt et al. 2018)

(modified from Özyurt et al. 2018)










(modified from Özyurt et al. 2018)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afşin M, Mustafa, Bayari, S, Durukan, U (2012) The origin of carbon dioxide in the groundwater of Konya Closed Basin, central Anatolia, Turkey. https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.2218.7520
Aksoy R (2019) Extensional neotectonic regime in West-southwest Konya, central Anatolia, Turkey. Int Geol Rev 61:1803–1821. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2019.1581996
Bayari CS, Ozyurt NN, Kilani S (2008a) Radiocarbon age distribution of groundwater in the Konya Closed Basin, central Anatolia, Turkey. Hydrogeol J 17:347–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0358-2
Bayari CS, Pekkan E, Ozyurt NN (2008b) Obruks, as giant collapse dolines caused by hypogenic karstification in central Anatolia, Turkey: analysis of likely formation processes. Hydrogeol J 17:327–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0351-9
Canik B, Çörekçioğlu İ (1985) The formation of sinkholes (Obruk) between Karapinar and Kizoren—Konya. Karst water resources (proceedings of the Ankara—Antalya symposium), 161:193–205
Carbognin L, Teatini P, Tosi L (2004) Eustacy and land subsidence in the Venice lagoon at the beginning of the new millennium. J Mar Syst 51:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2004.05.021
Chen CW, Zebker HA (2000) Network approaches to two-dimensional phase unwrapping: intractability and two new algorithms. J Opt Soc Am A 17:401. https://doi.org/10.1364/josaa.17.000401
Chen CW, Zebker HA (2001) Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with use of statistical models for cost functions in nonlinear optimization. J Opt Soc Am A 18:338. https://doi.org/10.1364/josaa.18.000338
Chen CW, Zebker HA (2002) Phase unwrapping for large SAR interferograms: statistical segmentation and generalized network models. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 40:1709–1719. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2002.802453
Cigna F, Sowter A, Jordan CJ, Rawlins B (2014) Intermittent small baseline subset (ISBAS) monitoring of land covers unfavourable for conventional C-band InSAR: proof-of-concept for peatland environments in North Wales, UK. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1117/122067604
Crosetto M, Crippa B, Biescas E (2005) Early detection and in-depth analysis of deformation by radar interferometry. Eng Geol 79:81–91
Çomut FC, Ustun A, Lazecky M, Perissin D (2016) Capability of detecting rapid subsidence with Cosmo SkyMed and Sentinel-1 dataset over Konya city. Living planet symposium, proceedings of the conference
CORINE Land Cover. In: copernicus. https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover. Accessed 19 Mar 2020
Data products. In: ESA. https://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Sentinel-1/Data_products. Accessed 19 Mar 2020
Dirik K, Göncüoglu MC (1996) Neotectonic characteristics of central Anatolia. Int Geol Rev 38(9):807–817. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206819709465363
Doğan U, Yılmaz M (2011) Natural and induced sinkholes of the Obruk plateau and Karapınar–Hotamış plain, Turkey. J Asian Earth Sci 40:496–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.09.014
Doğdu MŞ, Toklu MM, Sağnak, C (2007) Konya kapalı havzası’nda yağış ve yeraltı suyu değerlerinin irdelenmesi. I. Türkiye İklim Değişikliği Kongresi proceedings, 394–402
Elachi C, Bicknell T, Jordan RL, Wu C (1982) Spaceborne synthetic-aperture imaging radars: applications, techniques, and technology. Proc IEEE 70(10):1174–1209. https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1982.12448
Ferretti A, Monti-Guarnieri A, Prati C, Rocca F (2007) InSAR principles: guidelines for SAR interferometry: processing and interpretation. ESA Publications, Noordwijk
Guccione P (2006) Interferometry with ENVISAT wide swath ScanSAR data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 3(3):37–382
Holzer T, Johnson A (1985) Land subsidence caused by ground water withdrawal in urban areas. GeoJournal. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00186338
Imamoglu M, Kahraman F, Cakir Z, Sanli FB (2019) Ground deformation analysis of Bolvadin (W. Turkey) by means of multi-temporal InSAR techniques and Sentinel-1 data. Remote Sens 11:1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11091069
Kocyigit A (2005) The Denizli graben-horst system and the eastern limit of western Anatolian continental extension: basin fill, structure, deformational mode, throw amount and episodic evolutionary history, SW Turkey. Geodin Acta 18:167–208. https://doi.org/10.3166/ga.18.167-208
Kontogianni V, Pytharouli S, Stiros S (2006) Ground subsidence, quaternary faults and vulnerability of utilities and transportation networks in Thessaly, Greece. Environ Geol 52:1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0548-y
Lofgren BE (1969) Land subsidence due to the application of water. In: Varnes DJ, Kiersch G (eds) Reviews in engineering geology. Geological Society of America, United States of America
Motagh M, Djamour Y, Walter TR et al (2007) Land subsidence in Mashhad valley, northeast Iran: results from InSAR, levelling and GPS. Geophys J Int 168:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246x.2006.03246.x
Okay AI, Tüysüz O (1999) Tethyan sutures of northern Turkey. Geol Soc Lond Spec Pub 156:475–515. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1999.156.01.22
Osmanoglu B, Sunar F, Wdowinski S, Cabral-Cano E (2015) Time series analysis of InSAR data: methods and trends. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.10.003
Ozdemir A (2015) Investigation of sinkholes spatial distribution using the weights of evidence method and GIS in the vicinity of Karapinar (Konya, Turkey). Geomorphology 245:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.04.034
Özyurt NN, Avcı P, Bayarı CS (2018) Using groundwater flow modelling for investigation of land subsidence in the Konya closed basin (Turkey). In: Ceryan N (ed) Handbook of research on trends and digital advances in engineering geology. United States of America, IGI Global, pp 569–590. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-2709-1.ch016
Perski Z (2003) InSAR and POLinSAR for land subsidence monitoring—user perspective. Applications of SAR polarimetry and polarimetric interferometry. France, Europe Space Agency, pp 321–326
Prats-Iraola P, Scheiber R, Marotti L et al (2012) TOPS interferometry with TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 50:3179–3188. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2011.2178247
Schubert AD, Small N, Miranda D, Geudtner D, Meier E (2015) Sentinel-1a product geolocation accuracy: commissioning phase results. Remote Sens 7(7):9431–9449
Sowter A, Bateson L, Strange P, Ambrose K, Moh FS (2013) DInSAR estimation of land motion using intermittent coherence with application to the south Derbyshire and Leicestershire coalfields. Remote Sens Lett 4(10):979–987. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2013.823673
Teatini P, Ferronato M, Gambolati G et al (2005) A century of land subsidence in Ravenna, Italy. Environ Geol 47:831–846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1215-9
Teatini P, Ferronato M, Gambolati G, Gonella M (2006) Groundwater pumping and land subsidence in Emilia-Romagna coastland, Italy: modeling the past occurrence and the future trend. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005wr004242
Jiang T-C, Li T, Liu J-N (2011) Research on deformation monitoring caused by large earthquake with WSM interferometry Proc. SPIE 8286, International symposium on lidar and radar mapping, technologies and applications, 82861N. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.912465
Potin P et al. (2015) Sentinel‐1 mission status, in 2015 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), pp 2820–2823, Milan: IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7326401
User guides—Sentinel-1 SAR—revisit and coverage—Sentinel online. In: Sentinel. https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-1-sar/revisit-and-coverage. Accessed 19 Mar 2020
Ustun A, Tusat E, Yalvac S (2010) Preliminary results of land subsidence monitoring project in Konya Closed Basin between 2006–2009 by means of GNSS observations. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 10:1151–1157. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-10-1151-2010
Üstün A, Tuşat E, Yalvaç S et al (2015) Land subsidence in Konya Closed Basin and its spatio-temporal detection by GPS and DInSAR. Environ Earth Sci 73:6691–6703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3890-5
Veci L (2015) Sentinel-1 Toolbox: TOPS interferometry tutorial; Array Systems Computing Inc
Widodo J, Herlambang A, Sulaiman A et al (2019) Land subsidence rate analysis of Jakarta metropolitan region based on D-InSAR processing of Sentinel data C-band frequency. J Phys Conf Ser 1185:012004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1185/1/012004
Xue Y-Q, Zhang Y, Ye S-J et al (2005) Land subsidence in China. Environ Geol 48:713–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-0010-6
Yague-Martinez N, Prats-Iraola P, Gonzalez FR et al (2016) Interferometric processing of Sentinel-1 TOPS data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54:2220–2234. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2015.2497902
Yilmaz M (2010) Environmental problems caused by ground water level changes around Karapinar. Ankara Üniversitesi Çevre Bilimleri Dergisi 2(2):145–163
Zan FD, Guarnieri AM (2006) TOPSAR: terrain observation by progressive scans. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 44:2352–2360. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2006.873853
Zan FD, Prats-Iraola P, Rodriguez-Cassola M (2015) On the dependence of delta-k efficiency on multilooking. Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12:1745–1749. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2015.2424272
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to General Directorate of State Hydraulic Works of Turkey for sharing the well measurement data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, HMY, CAI, BK, and MR; Methodology, HMY and CAI; Software, HMY and CAI; Validation, HMY and CAI; Formal analysis, HMY and CAI; Investigation, HMY, CAI, and BK; Resources, HMY and CAI; Data curation, HMY and CAI; Writing—original draft preparation, HMY, CAI, BK, and MR; Writing—review and editing, HMY, CAI, BK, MCC, and MR; Visualization, HMY, CAI, BK, and MR; Supervision, BK, MCC, OA, and MR; Project administration, BK, MCC, OA, and MR; Funding acquisition, BK and MR.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeşilmaden, H.M., İnan, Ç.A., Kurtuluş, B. et al. Land subsidence assessment under excessive groundwater pumping using ESA Sentinel-1 satellite data: a case study of Konya Basin, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 80, 409 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09718-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09718-z