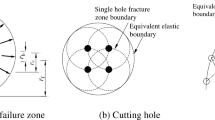
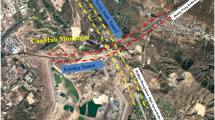
Abstract
Seismic wave induced by blasting excavation of tunnel may exert adverse effects to the surrounding rock. To study the different characteristics and attenuation of blast-induced vibration in the blasting tunnel and adjacent tunnel, field blasting tests are carried out to record velocity–time histories during blasting in Wanhua Underground Gas Storage. The characteristics and attenuation of vibration velocity and energy are presented based on the field data. And the dynamic finite-element model is established to further study the vibration attenuation law. Results demonstrate that PPV and vibration energy of the adjacent tunnel is greater than that in the blasting tunnel and attenuates more readily when monitoring points are near the blasting area. The dominant frequencies of the adjacent tunnel are higher than that in the blasting tunnel at three orthogonal directions. Adopting vibration energy as the evaluation index of seismic intensity, the fitting formula has favorable prediction accuracy, which will provide more accurate guidance for controlling the adverse effects of tunnel blasting.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PPV:
-
Peak particle velocity
- Q :
-
Maximum charge per delay, kg
- SD:
-
Scaled distance
- k and α :
-
Fitting parameters related to the transmission medium
- R :
-
Distance from the blast-face to the monitoring point
- Φ opt :
-
Optimal kernel function
- A(t;θ;τ):
-
Short-time ambiguity function
- θ :
-
Angle function in polar coordinates
- τ :
-
Time interval
- f :
-
Frequency
- E :
-
Vibration energy
- V p :
-
Peak particle velocity
- ξ :
-
Damping ratio
- ω :
-
Vibration circular frequency
- k E and α E :
-
Fitting parameters
- ρ and ρ 0 :
-
Initial and present material density
- P :
-
Pressure of detonation
- V :
-
Relative volume
- E 0 :
-
Internal energy density per unit initial volume,
- A B, R 1, R 2 :
-
Independent indicators
References
Agrawal H, Mishra AK (2019) Modified scaled distance regression analysis approach for prediction of blast-induced ground vibration in multi-hole blasting. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 11:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.07.004
Baraniuk RG, Jones DL (1993) A signal-dependent time-frequency representation: optimal kernel design. IEEE Press, Piscataway. https://doi.org/10.1109/78.212733
Bednarik RG (2019) Rock metamorphosis by kinetic energy. Emerg Sci J 3:293–302
Cardu M, Coragliotto D, Oreste P (2019) Analysis of predictor equations for determining the blast-induced vibration in rock blasting. Int J Min Sci Tech 29:905–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2019.02.009
Dai J (2013) Dynamic behaviors and blasting theory of rock , 2nd edn. Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing
Gao FQ, Hou AJ, Yang XL, Yang J (2010) Analysis of blasting vibration duration based on dimension theory. Mental Mine 41:143–145. https://doi.org/10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2010.03.001
Karadogan A, Kahriman A, Ozer U (2013) A new damage criteria norm for blast-induced ground vibrations in Turkey. Arab J Geosci 7:1617–1626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0830-8
Khandelwal M, Saadat M (2015) A dimensional analysis approach to study blast-induced ground vibration. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48:727–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0604-y
Li DL, Gao ZR, Zhu LX (1999) Analysis on several principal factors of blasting vibration hazards. Eng Blasting 3:64–67. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.1999.03.014
Li HT, Lu WB, Shu DQ, Yang XG, Yi CP (2010) Study of energy attenuation law of blast-induced seismic wave. Chin J Rock Mechan Eng 29:3364–3369
Liang QG, Li J, Li DW, Ou EF (2013) Effect of blast-induced vibration from new railway tunnel on existing adjacent railway tunnel in Xinjiang, China. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46:19–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0259-5
Lin F (2018) Construction network ventilation system for underground LPG storage cavern. Civil Eng J 4:1521–1541. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-0309192
Lin F, Luan HB, Zeng YH et al (2017) Some new correlations of Q-value with rock mechanics parameters in underground oil storage caverns. Civil Eng J 3:537–546. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2017-00000111
Peng YX, Wu L, Su Y (2016a) Study on the fitting model of underwater blasting vibration attenuation considering the effect of elevation. J Vib Shock 35:174–178. https://doi.org/10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2016.13.028
Peng YX, Wu L, Su Y, Zhu BB, Chen CH, Li B (2016b) Review of research on safety control of seismic wave and shock wave induced by underwater blasting. Geosy Eng 20:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/12269328.2016.1229639
Peng YX, Su Y, Wu L, Chen CH (2019) Study on the attenuation characteristics of seismic wave energy induced by underwater drilling and blasting. Shock Vib. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4367698
Sanchidrian JA, Segarra P, Lopez LM (2007) Energy components in rock blasting. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44:130–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.05.002
Shin JH, Moon HG, Chae SE (2011) Effect of blast-induced vibration on existing tunnels in soft rocks. Tunnel Undergr Space Tech 26:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2010.05.004
Singh PK, Roy MP (2010) Damage to surface structures due to blast vibration. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:949–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.06.010
Siren T, Kantia P, Rinne M (2015) Considerations and observations of stress-induced and construction-induced excavation damage zone in crystalline rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 73:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.11.001
Standardization Administration of China, 2014. Safety regulations for blasting. GB6722-2014
Wu C, Hao H (2005) Numerical study of characteristics of underground blast induced surface ground motion and their effect on aboveground structures. Part I. Ground motion characteristics. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 25:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2004.08.001
Wu C, Hao H, Lu Y, Zhou Y (2003) Characteristics of stress waves recorded in small-scale field blast tests on a layered rock-soil site. Geotechnique 53:587–599. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.53.6.587.37327
Xia X, Li HB, Liu YQ, Yu C (2018) A case study on the cavity effect of a water tunnel on the ground vibrations induced by excavating blasts. Tunnel Undergr Space Tech 71:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.08.026
Xie LT, Yan P, Lu WB, Chen M, Wang GH (2018) Comparison of seismic effects during deep tunnel excavation with different methods. Earthq Eng Eng Vib 17:659–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-018-0452-y
Yang JH, Lu WB, Jiang QH, Yao C, Jiang SH, Tian L (2016) A study on the vibration frequency of blasting excavation in highly stressed rock masses. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:2825–2843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0964-6
Yang JH, Lu WB, Li P, Yan P (2017) Evaluation of rock vibration generated in blasting excavation of deep-buried tunnels. KSCE J Civ Eng 22:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-0240-7
Yang JH, Cai JY, Yao C, Li P, Jiang QH, Zhou CB (2019) Comparative study of tunnel blast-induced vibration on tunnel surfaces and inside surrounding rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01875-9
Yilmaz O, Unlu T (2014) An application of the modified Holmberg-Persson approach for tunnel blasting design. Tunnel Undergr Space Technol 43:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.04.009
Zhao HB, Long Y, Li XH, Lu L (2015) Experimental and numerical investigation of the effect of blast-induced vibration from adjacent tunnel on existing tunnel. KSCE J Civ Eng 20:431–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0130-9
Zhou JR, Lu WB, Yan P, Chen M, Wang GH (2016) Frequency-dependent attenuation of blasting vibration waves. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1046-5
Zhou YC, Wu L, Li JL, Yuan Q (2018) The effect of blast-induced vibration on the stability of underground water-sealed gas storage caverns. Geosy Eng 21:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1080/12269328.2018.1452052
Zhou JR, Lu WB, Zhong DW, Leng ZD, Wu L, Yan P (2019) Prediction of frequency-dependent attenuation of blast-induced vibration in underground excavation. Eur J Environ Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2019.1620134
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 41672260), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (Grant no. 2020JJ5163; 2020JJ4300), Open Research Foundation of Hubei Key Laboratory of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation (China Three Gorges University) (Grant no. 2020KJZ06), Scientific Research Project of Hunan Education Department (Grant no. 19C0736; 20C0815).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Y., Liu, G., Wu, L. et al. Comparative study on tunnel blast-induced vibration for the underground cavern group. Environ Earth Sci 80, 68 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09362-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09362-z