Abstract
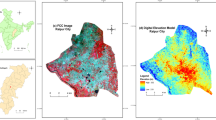
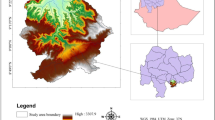
In terrestrial landscape architecture, land surface temperature (LST) is a key estimator of local climate, vegetation growth, and urban transition. It also represents the environmental factors that influence the land cover patterns using temperature variation over land use land cover (LULC) classes. In the present study, various geospatial techniques have been implemented to analyze the spatio-temporal trends in temperature among different LULC of an arid Potohar region of Pakistan using Landsat 7 (ETM+) and 8 (OLI & TIRS) and the relationship between different normalized satellite indices and LST. Results of the seasonal fluctuation in winter showed temperature range of 0–57, 0–50, 04–31 and 7–39 °C for the year 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015, respectively, while the summer exhibited the temperature range of 24–48, 27–57, 22–48, and 12–41 °C for the year 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015, respectively. The analysis established a direct correlation between LST and normalized difference vegetation index and normalized difference water index, and an indirect correlation among LST and normalized difference soil index, normalized difference built-up index and built-up index. The findings are critically important for planning and development division for sustainable use of land resources for urbanization extension projects. Future research will highlight the change in the area occupied by different land featured classes and their impacts on LST over a specified period.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan S, Mahmood R, Khan AH (2009) Water balance conditions in rainfed areas of Potohar and Balochistan plateau during 1931–08. World Appl Sci J 7:162–169
Agam N, Kustas WP, Anderson MC (2007) A vegetation index based technique for spatial sharpening of thermal imagery. Remote Sens Environ 107:545–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2006.10.006
Ahmad S, Abbas G, Ahmed M (2019) Field Crops Research Climate warming and management impact on the change of phenology of the rice-wheat cropping system in Punjab, Pakistan. Field Crops Res 230:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.10.008
Ahmed Memon R, Leung DY, Chunho L (2008) A review on the generation, determination and mitigation of Urban Heat Island. J Environ Sci 20:120–128
Amir S, Saqib Z, Khan A (2019) Land cover mapping and crop phenology of Potohar Region, Punjab, Pakistan. Pak J Agric Sci 56:187–196. https://doi.org/10.21162/PAKJAS/19.7663
Artis DA, Carnahan WH (1982) Survey of emissivity variability in thermography of urban areas. Remote Sens Environ 12:313–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(82)90043-8
Arnfield AJ (2003) Two decades of urban climate research: a review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Int J Climatol 23:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.859
Arvidson T, Goward S, Gasch J, Williams D (2006) Landsat-7 long-term acquisition plan: development and validation. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 72:1137–1146
Bala R, Prasad R, Yadav VP, Sharma J (2019) Spatial variation of urban heat island intensity in urban cities using modis satellite data. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci XLII-4/W16:147–151. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-xlii-4-w16-147-2019
Balouch S, Rais M, Hussain I, Akram A (2016) Squamate diversity in different croplands of district Chakwal, Punjab, Pakistan. J King Saud Univ Sci 28:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2016.01.003
Bowler DE, Buyung-Ali L, Knight TM, Pullin AS (2010) Urban greening to cool towns and cities: a systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc Urban Plan 97:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.05.006
Butt A, Shabbir R, Ahmad SS, Aziz N (2015) Land use change mapping and analysis using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Simly watershed, Islamabad, Pakistan. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 18:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2015.07.003
Buyadi SNA, Mohd WMNW, Misni A (2013) Green spaces growth impact on the urban microclimate. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 105:547–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.11.058
Chander G, Markham BL, Helder DL, Ali E (2009) Remote Sensing of Environment Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM +, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens Environ 113:893–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2009.01.007
Chang C-W, Laird DA, Mausbach MJ, Hurburgh CR (2001) Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy-principal components regression analyses of soil properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:480. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2001.652480x
Chang CR, Li MH, Chang SD (2007) A preliminary study on the local cool-island intensity of Taipei city parks. Landsc Urban Plan 80:386–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2006.09.005
Chastain R, Housman I, Goldstein J (2019) Remote sensing of environment empirical cross sensor comparison of sentinel-2A and 2B MSI, Landsat-8 OLI, and Landsat-7 ETM+ top of atmosphere spectral characteristics over the conterminous United States. Remote Sens Environ 221:274–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.11.012
Chaudhuri G, Mishra NB (2016) Spatio-temporal dynamics of land cover and land surface temperature in Ganges-Brahmaputra delta: a comparative analysis between India and Bangladesh. Appl Geogr 68:68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2016.01.002
Chen F, Yang S, Yin K, Chan P (2017) Science direct challenges to quantitative applications of Landsat observations for the urban thermal environment. J Environ Sci 59:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.02.009
Cristóbal J, Jiménez-Muñoz JC, Sobrino JA, Ninyerola M, Pons X (2009) Improvements in land surface temperature retrieval from the Landsat series thermal band using water vapor and air temperature. J Geophys Res 114:D08103. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010616
Fu B, Burgher I (2015) Riparian vegetation NDVI dynamics and its relationship with climate, surface water and groundwater. J Arid Environ 113:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2014.09.010
Ghoraba SM (2015) Hydrological modeling of the Simly Dam watershed (Pakistan) using GIS and SWAT model. Alex Eng J 54:583–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2015.05.018
Grimm NB, Grove JM, Pickett STA, Redman CL (2000) Integrated approaches to long-term studies of urban ecological systems ∗ the conceptual basis for studying urban ecological systems. Bioscience 50:571–584
Gupta N, Mathew A, Khandelwal S (2019) Analysis of cooling effect of water bodies on land surface temperature in nearby region: a case study of Ahmedabad and Chandigarh cities in India. Egypt J Rem Sens Space Sci 22:81–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2018.03.007
Handayani HH, Estoque RC, Murayama Y (2018) Estimation of built-up and green volume using geospatial techniques: a case study of Surabaya, Indonesia. Sustain Cities Soc 37:581–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.10.017
Hathway EA, Sharples S (2012) The interaction of rivers and urban form in mitigating the Urban Heat Island effect: a UK case study. Build Environ 58:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2012.06.013
He J, Zhao W, Li A, Wen F Daijun Y (2019) The impact of the terrain effect on land surface temperature variation based on Landsat-8 observations in mountainous areas. Int J Remote Sens 40:1808–1827. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1466082
Hua AK, Ping OW (2018) The influence of land-use/land-cover changes on land surface temperature: a case study of Kuala Lumpur metropolitan city. Eur J Remote Sens 51:1049–1069. https://doi.org/10.1080/22797254.2018.1542976
Inamdar AK, French A, Hook S et al (2008) Land surface temperature retrieval at high spatial and temporal resolutions over the southwestern United States. J Geophys Res Atmos 113:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009048
Jahangir M, Maria Ali S, Khalid B (2016) Annual minimum temperature variations in early 21st century in Punjab, Pakistan. J Atmos Solar-Terrestrial Phys 137:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2015.10.022
Jamei Y, Rajagopalan P, Sun Q (2019) Spatial structure of surface urban heat island and its relationship with vegetation and built-up areas in Melbourne, Australia. Sci Total Environ 659:1335–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.308
Jiménez-Muñoz JC, Sobrino JA (2009) A single-channel algorithm for land-surface temperature retrieval from ASTER data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 7:176–179. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2009.2029534
Jimenez-Munoz JC, Sobrino JA, Skokovic D et al (2014) Land surface temperature retrieval methods from landsat-8 thermal infrared sensor data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 11:1840–1843. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2014.2312032
Kothe S, Hollmann R, Pfeifroth U et al (2019) The CM SAF R Toolbox—a tool for the easy usage of satellite-based climate data in NetCDF format. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 8:109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8030109
Kustas WP, Norman JM, Anderson MC, French AN (2003) Estimating subpixel surface temperatures and energy fluxes from the vegetation index-radiometric temperature relationship. Remote Sens Environ 85:429–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00036-1
Latif ZA, Kamsan MES (2017) Assessing the relationship of land use land cover on surface temperature in city of Shah Alam, Malaysia using landsat-8 oli. J Fundam Appl Sci 9:514. https://doi.org/10.4314/jfas.v9i5s.36
Li J, Song C, Cao L et al (2011) Impacts of landscape structure on surface urban heat islands: a case study of Shanghai, China. Remote Sens Environ 115:3249–3263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.07.008
Li W, Saphores JDM, Gillespie TW (2015) A comparison of the economic benefits of urban green spaces estimated with NDVI and with high-resolution land cover data. Landsc Urban Plan 133:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.09.013
Mallick J, Kant Y, Bharath BD (2008) Estimation of land surface temperature over Delhi using Landsat-7 ETM+. J Ind Geophys Union 12:131–140
Meng X, Cheng J, Liang S (2017) Estimating land surface temperature from Feng Yun-3C/MERSI data using a new land surface emissivity scheme. Remote Sens 9:9–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121247
Owojori A, Hongjie X (2015) Landsat image-based lulc changes of san antonio, texas using advanced atmospheric correction and object-oriented image analysis approaches. Remote sensing image processing and analysis (ES 6973)
Pal S, Ziaul S (2017) Detection of land use and land cover change and land surface temperature in English Bazar urban centre. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 20:125–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2016.11.003
Peng J, Pan Y, Liu Y et al (2018) Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape. Habitat Int 71:110–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.010
Rashid K, Rasul G (2007) Rainfall variability and maize production over the potohar plateau of Pakistan. Pak J Meteorol 8:63–74
Rehman Z, Kazmi SJH, Khanum F, Samoon ZA (2015) Analysis of land surface temperature and ndvi using geo-spatial technique: a case study of Keti Bunder, Sindh, Pakistan. J BasicAppl Sci 11:514–527. https://doi.org/10.6000/1927-5129.2015.11.69
Rong-bo X, Zhi-yun O, Hua Z et al (2007) Spatial pattern of impervious surfaces and their impacts on land surface temperature in Beijing, China. J Environ Sci 19:250–256
Rosas J, Houborg R, McCabe MF (2017) Sensitivity of Landsat 8 surface temperature estimates to atmospheric profile data: a study using MODTRAN in dryland irrigated systems. Remote Sens 9:1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9100988
Sayão VM, Demattê JAM, Bedin LG et al (2018) Satellite land surface temperature and reflectance related with soil attributes. Geoderma 325:125–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.03.026
Smakhtin VU, Hughes DA (2007) Automated estimation and analyses of meteorological drought characteristics from monthly rainfall data. Environ Model Softw 22:880–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2006.05.013
Sobrino JA, Oltra-carrió R, Sòria G et al (2012) Remote Sensing of Environment Impact of spatial resolution and satellite overpass time on evaluation of the surface urban heat island effects. Remote Sens Environ 117:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.04.042
Srivanit M, Hokao K, Phonekeo V (2012) Assessing the Impact of urbanization on urban thermal environment: a case study of Bangkok metropolitan. Int J Appl Sci Technol 2:243–256
Suresh S, Ajay SV, Mani K (2016) Mountain landscape of Devikulam Taluk using Landsat 8 data. Int J Res Eng Technol 5:92–96
Voogt JA, Oke TR (2003) Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sens Environ 86:370–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00079-8
Weng Q (2004) Thermal infrared remote sensing for urban climate and environmental studies: methods, applications, and trends. J Photogramm Remote Sens 64:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2009.03.007
Weng Q, Yang S (2004) Managing the adverse thermal effects of urban development in a densely populated Chinese city. J Environ Manag 70:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2003.11.006
Weng Q, Lu D, Schubring J (2004) Estimation of land surface temperature—vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens Environ 89:467–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.11.005
Xiong Y, Huang S, Chen F et al (2012) The impacts of rapid urbanization on the thermal environment: a remote sensing study of Guangzhou, South China. Remote Sens 4:2033–2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs4072033
Xu W, Gu S, Zhao XQ et al (2011) High positive correlation between soil temperature and NDVI from 1982 to 2006 in alpine meadow of the Three-River Source Region on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 13:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2011.02.001
Xu LY, Xie XD, Li S (2013) Correlation analysis of the urban heat island effect and the spatial and temporal distribution of atmospheric particulates using TM images in Beijing. Environ Pollut 178:102–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.03.006
Yang B, Meng F, Ke X, Ma C (2015) The impact analysis of water body landscape pattern on urban heat island: a case study of Wuhan City. Adv Meteorol 2015:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/416728
Zhu X, Liu D, Chen J (2012) Remote Sensing of Environment A new geostatistical approach for filling gaps in Landsat ETM+ SLC-off images. Remote Sens Environ 124:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.04.019
Acknowledgments
Authors highly acknowledge Prof. Dr. David Crowley (Rtd.), Department of Environmental Sciences, University of California Riverside, USA, for taking a keen interest in proofreading and improving the quality of the manuscript. We dedicate this humble effort in honor of his services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tariq, A., Riaz, I., Ahmad, Z. et al. Land surface temperature relation with normalized satellite indices for the estimation of spatio-temporal trends in temperature among various land use land cover classes of an arid Potohar region using Landsat data. Environ Earth Sci 79, 40 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8766-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8766-2