Abstract
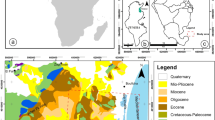
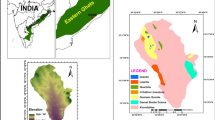
The Cretaceous Nubia sandstone aquifer is the main aquifer in East El-Oweinat area along the Egyptian–Sudanese borders and in NE Africa. East El-Oweinat project has been recently considered one of the main agricultural projects in the southwest of the Egyptian Western Desert. So, the hydrogeological assessment for the Nubia aquifer in East El-Oweinat area has been done through studying and characterising the hydraulic parameters and step-drawdown test. The well and aquifer losses coefficients (C and B, respectively), the specific capacity, and the well efficiency as well as the aquifer and aquitard thickness have been estimated and traced through a total of 46 wells that have been distributed through the study area in two sectors, southern and northern. For the purpose of further exploration, the effective porosity (∅), hydraulic conductivity (K), and transmissivity (T) have been estimated for the wells in the northern sector. In addition, an aquifer assessment quality index has been introduced to assess and to rank the studied aquifer. Therefore, it is concluded that the hydraulic and the step-draw down parameters as well as the aquifer and aquitard thicknesses are prospective for further exploration to the north and the east of the northern sector in the study area. The well efficiency is mostly affected by the studied parameters, particularly the well loss coefficient, the hydraulic parameters and the well design as well. GIS approach and ArcGIS software have been applied to delineate the spatial distribution of the well performance characteristics, in order to compare between the studied groundwater wells and to integrate the different-acquired data. A set of isocontour maps have been introduced to match the lateral variation of the studied parameters and the aquifer potential to refer to the best direction for further underground water exploration.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Temamy AMM, Barseem MSM (2010) Structural impact on the groundwater occurrence in the Nubia sandstone aquifer using geomagnetic and geoelectrical techniques, Northwest Bir Tarfawi, East El Oweinat area, Western Desert, Egyptian Geophysical Society. EGS J 8(1):47–63
Al-Dhafeeri AM, Nasr-El-Din HA (2007) Characteristics of high permeability zones using core analysis, and production logging data. J Petrol Sci Eng 55(1–2):18–36
Al-Rbeawi S, Kadhim F (2017) The impact of hydraulic flow unit & reservoir quality index on pressure profile and productivity index in multi-segments reservoirs. Petroleum 3(4):414–430
Amaefule J, Altunbay M, Tiab D, Kersey D, Keelan D (1993) Enhanced reservoir description using core and log data to identify hydraulic flow units and predict permeability in uncored intervals/wells. SPE 26436:205–220
Bakhbakhi M (2006) Nubian sandstone aquifer system. In: Non-renewable groundwater resources, a guide book on socially-sustainable management for water policy makers. In: Foster S, Loucks DP (eds) IHP-VI, series on ground water, vol 10. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris, 100p
Benzagouta MS (2015a) Reservoir characterization: evaluation for the channel deposits sequence—upper part using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and mercury injection (MICP): case of tight reservoirs (North Sea). J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 27(1):57–62
Benzagouta MS (2015b) The use of polar angle, polar arm and other physical attributes in rock characterization. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 27(2):232–237
Bierschenk WH (1963) Determining well efficiency by multiple step-drawdown tests. Intern Assoc Sci Hydrol Publ 64:493–507
Bierschenk WH, Wilson GR (1961) The exploitation and development of ground water resources in Iran. Int Assoc Sci Hydrol Publ 57:607–627
Bruin J, Hudson HE (1955) Selected methods for pumping test analysis. Ill State Water Surv Rep Investig 25:29–37
CONOCO (Continental Oil Company) (1987) Stratigraphic lexicon and explanatory notes to the geologic map of Egypt 1:500,000. In: Hermina, Maurice, Eberhard, List FK (eds)
El Sharawy MS, Nabawy BS (2016a) Determination of electrofacies using wireline logs based on multivariate statistical analysis for the Kareem Formation, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 75(21):1394
El Sharawy MS, Nabawy BS (2016b) Geological and petrophysical characterization of the lower senonian matulla formation in Southern and Central Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Arab J Sci Eng 41(1):281–300
El Sharawy MS, Nabawy BS (2018) Determining the porosity exponent m and lithology factor a for sandstones and their control by overburden pressure: a case study from the Gulf of Suez,Egypt. AAPG Bull 102(9):1893–1910
GPC General Petroleum Company (1984) Hydro-agriculture study of East El-Oweinat region, Western Desert, Egypt. GPC, Ministry of Petroleum, A.R.E. 3-A:178p
Guyod H (1966) Interpretation of electric and gamma ray logs in water wells. Log Analyist 6(5):29–44
Hantush MS (1964) Hydraulics of wells. In: Chow VT (ed) Advances in hydro-science, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 281–432
Hendriks F (1988) Evolution of the depositional environments of southwestern Egypt during the Cretaceous and Lower tertiary. Belliner Geowiss Abhandlungen 75(1):49–82
Issawi B (1973) Nubia sandstone type section. Bull AAPG 57:741–745
Issawi B, Jux U (1982) Contribution to the stratigraphy of Paleozoic rocks in Egypt: geological survey of Egypt. Cairo 64:28p
Issawi B, Osman RA (1993) Tectonic-sedimentary synthesis of Paleozoic-Cretaceous clastics, SW Aswan, Egypt. J Sedimentol Soc Egypt 1:11–22
Jacob CE (1947) Drawdown test to determine effective radius of artesian well. Trans ASCE 112:1047–1070
Jacob CE (1950) Flow of ground water. Chapter 5 in Engineering hydraulics. In: Rouse H (ed) Wiley, New York, pp 321–386
Kawecki MW (1995) Meaningful Interpretation of step-drawdown tests. Ground Water 33(1):23–32
Klitzsch E (1979) Major subdivisions and Depositional Environments of Nubia Strata, Southwestern, Egypt. Egypt Bull Am Ass Petrol Geol Tulsa 63(6):967–974
Klitzsch E (1984) Northwestern Sudan and bordering areas: geological development since cambrian time. Results of the special research project Arid Areas, Berlin, pp 23–47
Kruseman GP, de Ridder NA (1994) Analysis and evaluation of pumping test data, 2nd edn. Publication 47, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 370p
Kruseman GP, de Ridder NA (2000) Analysis and evaluation of pumping test data, 2nd edn. International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement, Wageningen. The Netherlands, 377p
Levorsen AI (1967) Geology of petroleum. WH Freeman Company, San Francisco
Marotz G (1968) Techische grundlageneiner wasserspeicherung imm naturlichen untergrund habilitationsschrift. Universitat Stuttgart
Mogg JL (1969) Step-drawdown test needs critical review. Ground Water 7(1):28–34
Nabawy BS (2014) Estimating porosity and permeability using digital Image analysis (DIA) technique for highly porous sandstones. Arab J Geosci 7(3):889–898
Nabawy BS (2015) Impacts of the pore- and petro-fabrics on porosity exponent and lithology factor of Archie’s equation for carbonate rocks. J Afr Earth Sci 108:101–114
Nabawy BS, Al-Azazi NAS (2015) Reservoir zonation and discrimination using the routine core analyses data: the upper Jurassic Sab’atayn sandstones as a case study, Sab’atayn basin,Yemen. Arab J Geosci 8(8):5511–5530
Nabawy BS, Géraud Y (2016) Impacts of pore- and petro-fabrics, mineral composition and diagenetic history on the bulk thermal conductivity of sandstones. J Afr Earth Sci 115:48–62
Nabawy BS, Rochette P, Géraud Y (2009) Petrophysical and magnetic pore network anisotropy of some cretaceous sandstone from Tushka Basin, Egypt. Geophys J Int 177(1):43–61
Nabawy BS, Rochette P, Géraud Y (2010) Electric pore fabric of the Nubia sandstones in south Egypt: characterization and modelling. Geophys J Int 183:681–694
Nabawy BS, Sediek KN, Nafee SA (2015) Pore fabric assignment using electrical conductivity of some Albian-Cenomanian sequences in north Eastern Desert, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 8(8):5601–5615
Nabawy BS, Basal AMK, Sarhan MA, Safa MG (2018a) Reservoir zonation, rock typing and compartmentalization of the Tortonian-Serravallian sequence, Temsah Gas Field, offshore Nile Delta, Egypt. Mar Pet Geol 92:609–631
Nabawy BS, Rashed MA, Mansour AS, Afify WSM (2018b) Petrophysical and microfacies analysis as a tool for reservoir rock typing and modeling: Rudeis Formation, off-shore October Oil Field, Sinai. Mar Pet Geol 97:260–276
Nabway BS, Kassab MA (2014) Porosity-reducing and porosity-enhancing diagenetic factors for some carbonate microfacies: a guide for petrophysical facies discrimination. Arab J Geosci 7(11):4523–4539
Nabawy BS, Barakat MK (2017) Formation evaluation using conventional and special core analyses: belayim Formation as a case study, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 10(2)
Nour SE (1979) Preliminary investigations of groundwater and soil resources in East Oweinat area, Western Desert, Egypt. The General Petroleum Company (GPC). Report, Cairo University, 64p
Nour S (1996) Groundwater potential for irrigation in the East Oweinat area, western desert, Egypt. Environmental Geology 27(3):143–154
Poehls DJ, Gregory JS (2009) Encyclopedic dictionary of hydrogeology. Academic Press, Boca Raton, p 517
Riazi Z (2018) Application of integrated rock typing and flow units identification methods for an Iranian carbonate reservoir. J Pet Sci Eng 160:483–497
RIGW (2008) Research institute for ground water. Internal report about the potentiality of groundwater in East El-Oweinat area. Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation, Water Resources Research Institute, Egypt. Interior unpublished report, 18p
Sabet SS, Zeid AM (2003) Contributions to the hydrogeology of Nubian sandstone aquifer in East El-Oweinat area, South Western Desert,Egypt. Isot Rad Res 33:11–177
Said R (1962) Geology of Egypt. Elsevier, Amsterdam, New York, pp 218–287
Salem O, Pallas P (2001) The Nubian sandstone aquifer system (NSAS). In: International shared (transboundary) aquifer resources management—their significance and sustainable management. In: Puri S (ed) IHP-VI, IHP non serial publications in hydrology. UNESCO, Paris, pp 41–44
Soto RS, Arteaga D, Hidalgo CM, Rodriguez F (2010) Pore-type determination from core data using a new polar-transformation function from hydraulic flow units. SPE 136805
Thabit GK (1994) Sedimentology of the Nubia group in the area southwest of Aswan, Abu Simbil area. Master’s thesis, Assuit University, Egypt, 164 p
Thorweihe U, Heinl M (1993) Groundwater resources and management in SW Egypt: catena supplement, Biomineralization processes of Iron and Manganese. Berliner geowissenschaftliche Abhandlungen 26:99–121
Tiab D, Donaldson EC (1996) Petrophysics, theory and practice of measuring reservoir rock and fluid transport properties. Gulf Publ. Co., Houston, Texas, pp 205–220
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, p 535p
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to the General Company for Research and Groundwater “REGWA” for releasing some of the data. The authors would like also to express their deepest gratitude to Geologist Awsy Khalil Swailam, Chairman of REGWA and Dr. Amal Hosny Esmail, Head of Executive Sector, Director of Training Department for their helpful spirit in providing the necessary information. Special thanks are due to the great efforts of the Editor-in-Chief Prof Dr James LaMoreaux and the anonymous reviewers whose constructive comments greatly contributed to and enhanced the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabawy, B.S., Abdelhalim, A. & El-Meselhy, A. Step-drawdown test as a tool for the assessment of the Nubia sandstone aquifer in East El-Oweinat Area, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 78, 375 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8375-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8375-0