Abstract
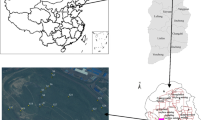
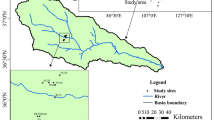
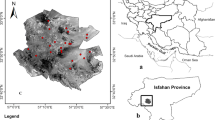
Conducting research about the relationships between soil chemical properties and vegetation coverage at different slope aspects is especially important in reconstructed ecosystems of vulnerable ecological regions. This study was conducted in the first reclaimed dump within the Pingshuo mining area of Shanxi Province, China, to analyze patterns of soil chemical properties (soil organic matter (SOM), soil total nitrogen (STN), soil available phosphorus (SAP) and soil available potassium (SAp) and vegetation coverage (NDVI) and their correlations at different slope aspects. In the reclaimed dump, 26 quadrats were established along four slope aspects (i.e., shady, semi-shady, sunny and semi-sunny slopes). There was no significant difference in SOM or STN among different slope aspects, while SAP differed between shady slopes compared to semi-shady, sunny and semi-sunny slopes; SAP differed significantly between semi-shady and semi-sunny slopes. The NDVI of semi-sunny slopes differed significantly from that of the other three aspects. There was variation in the relationships between NDVI and soil chemical properties, depending on the slope aspects. The logarithm of SOM and NDVI was related linearly on shady and semi-shady slopes, while NDVI was inversely related to the natural logarithm of the logarithm of SOM on sunny and semi-sunny slopes. STN and NDVI had a first-order function relationship on shady and semi-shady slopes, yet a quadratic function relationship on sunny and semi-sunny slopes. The relationships between SAP and NDVI were inverse on all types of slopes. On shady and semi-shady slopes, NDVI had a quadratic relationship with the logarithm of SAp, but it was well fitted by using a cubic function on sunny and semi-sunny slopes. The sensitivity coefficients of soil chemical properties and NDVI were different, and soil chemical properties changed differently depending on changes in NDVI at different slope aspects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-hashim M, Elsayed M, Belal A (2016) Effect of land-use changes and site variables on surface soil organic carbon pool at Mediterranean Region. J Afri Earth Sci 114:78–84
Adugna A, Abegaz A, Cerdà A (2015) Soil erosion assessment and control in Northeast Wollega, Ethiopia. Solid Earth Discuss 7:3511–3540
Ajami M, Heidari A, Khormali F, Gorji M, Ayoubi S (2016) Environmental factors controlling soil organic carbon storage in loess soils of a subhumid region, northern Iran. Geoderma 281:1–10
Austin AT, Vivanco L (2006) Plant litter decomposition in a semi-arid ecosystem controlled by photodegradation. Nature 442:555–558
Bao SD (2000) Analyses of soil agriculture chemistry. Chinese Agriculture Publish, Beijing
Bao G, Bao YH, Qin ZH, Zhou Y, Huang MX, Zhang HB (2013) Hyper-spectral remote sensing estimation for the vegetation cover. J Nat Res 28:1243–1254
Başnou C, Pino J, Šmilauer P (2009) Effect of grazing on grasslands in the Western Romanian Carpathians depends on the bedrock type. Preslia 81:91–104
Beaudette DE, O’Geen AT (2009) Quantifying the aspect effect: an application of solar radiation modeling for soil survey. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:1345–1352
Bronick CJ, Lal R (2005) Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma 124:3–22
Cammeraat LH, Imeson AC (1999) The evolution and significance of soil-vegetation patterns following land abandonment and fire in Spain. CATENA 37:107–127
Cao YG, Wang JM, Bai ZK, Zhou W, Zhao ZQ, Ding X, Li YN (2015) Differentiation and mechanisms on physical properties of reconstructed soils on open-cast mine dump of loess area. Environ Earth Sci 74:6367–6380
Cao YG, Zhou W, Bai ZK, Wang JM, Zhang XR (2016) Differentiations in nutrients of reconstruction soils on opencast mine dump of loess area. Fresen Environ Bull 25:2331–2342
Caravaca F, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B (2002) Land use in relation to soil chemical and biochemical properties in a semiarid Mediterranean environment. Soil and Tillage Research 68(1):23–30
Chen YC, Yang CX, Li CL, Tang L (2012) Variations of phosphorus in rubber forest soil. Chin J Soil Sci 43:1201–1206
Chen QC, Xu FL, Wang WL, Cheng ZW (2014) Seasonal dynamics of available K in soil for different ages of Larix principis-rupprechtii in the northern foot of the Qinling. J Plant Nutr Fertil 20:1243–1249
Chu HY, Xiang XJ, Yang J, Jonathan MADAMS, Zhang KP, Li YT, Shi Y (2016) Effects of slope aspects on soil bacterial and arbuscular fungal communities in a boreal forest in China. Pedosphere 26(2):226–234
Critchley CNR, Chambers BJ, Fowbert JA, Bhogal A, Rose SC, Sanderson RA (2002) Plant species richness, functional type and soil properties of grasslands and allied vegetation in english environmentally sensitive areas. Grass Forage Sci 57:82–92
Dai QH, Liu GB, Jiang J, Xue C, Zhai S (2008) Effect of soil enzyme activities under different vegetation restoration in eroded hilly loess plateau. Chin Agric Sci Bull 24:429–434
Deering DW (1978) Rangeland reflectance characteristics measured by aircraft and spacecraft sensors. Ph. D. thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station
Deng OP, Zhou X, Huang PP, Deng LJ (2013) Correlations between spatial variability of soil nutrients and topographic factors in the purple hilly region of Sichuan. Res Sci 35:2434–2443
Detsch F, Otte I, Appelhans T, Hemp A, Nauss T (2016) Seasonal and long-term vegetation dynamics from 1-km GIMMS-based NDVI time series at Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Remote Sens Environ 178:70–83
Do T, Bigot S, Galle S (2014) Vegetation activity in the upper Oueme Basin (Benin, Africa): studied from SPOTVGT (2002–2012) according to Land Cover. Int J Remote Sens 4:121–133
Dorji T, Odeh IOA, Field DJ (2014) Vertical distribution of soil organic carbon density in relation to land use/cover, altitude and slope aspect in the eastern Himalayas. Land 3:1232–1250
Dou XL, Li M, Wang WB, Zhang QF (2012) Cheng XL (2012) Changes in soil nutrients in different eroded soils in pinus massoniana forest ecosystems in Fujian Province, China. J Wuhan Bot Res 30:161–168
El-Ghani MMA, Amer WM (2003) Soil-vegetation relationships in a coastal desert plain of southern Sinai, Egypt. J Arid Environ 55:607–628
Fan FJ, Song TQ, Huang GQ, Zeng FP, Peng WX, Du H, Lu SY, Shi WW, Tan QJ (2014) Characteristics of spatial variation of soil nutrients in sloping field in a gorge karst region, southwest China. Chin J Appl Ecol 25:92–98
Fang H, Guo M (2015) Aspect-induced differences in soil erosion intensity in a gullied hilly region on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 74:5677–5685
Fenn ME, Poth MA, Aber JD, Baron JS, Bormann BT, Johnson DW, Lemly AD, McNulty SG, Ryan DE, Stottlemyer R (1998) Nitrogen excess in North American ecosystems: predisposing factors, ecosystem responses, and management strategies. Ecol Appl 8:706–733
Fisk MC, Schmidt SK, Seastedt TR (1998) Topographic patterns of above- and belowground production and nitrogen cycling in alpine tundra. Ecology 79:2253–2266
Ganuza A, Almendros G (2003) Organic carbon storage in soils of the Basque Country (Spain): the effect of climate, vegetation type and edaphic variables. Biol Fert Soils 37:154–162
Gao YF, Liu QQ, Wang W, Wang WJ (2017) The discussing of normal distribution and log value in geochemical exploration. Comput Tech Geophys Geochem Explor 39:404–410
Gebrelibanos T, Assen M (2014) Effects of slope aspect and vegetation types on selected soil properties in a dryland Hirmi watershed and adjacent agro-ecosystem, northern highlands of Ethiopia. Afr J Ecol 52:292–299
Ghosh BN, Sharma NK, Alam NM, Singh RJ, Juyal GP (2014) Elevation, slope aspect and integrated nutrient management effects on crop productivity and soil quality in North-west Himalayas, India. J Mt Sci 11:1208–1217
Gong X, Brueck H, Giese KM, Zhang L, Sattelmacher B, Lin S (2008) Slope aspect has effects on productivity and species composition of hilly grassland in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. J Arid Environ 72:483–493
Guo SL, Liu WZ, Shi ZY, Hou XL, Li FM (2003) Soil nutrients distribution and its relation to landform and vegetation at small watershed in semiarid area. Agric Res Arid Areas 21:40–43
He QH, He YH, Bao WK (2004) Dynamics of soil water contents on south-facing slope of dry valley area in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River. Chin J Appl Envi Bio Environ Biol 10:68–74
Holwerda F, Bruijnzeel LA, Munoz-Villers LE, Equihua M, Asbjornsen H (2010) Rainfall and cloud water interception in mature and secondary lower montane cloud forests of central Veracruz, Mexico. J Hydrol 384:84–96
Huang Z, Ouyang Z, Li F, Zheng H, Wang X (2010) Response of runoff and soil loss to reforestation and rainfall type in red soil region of southern China. J Environ Sci 22(11):1765–1773
Huang YM, Liu D, An SS (2015) Effects of slope aspect on soil nitrogen and microbial properties in the Chinese Loess region. CATENA 125:135–145
Janssens F, Peters A, Tallowin JRB, Bakker JP, Bekker RM, Fillat F, Oomes MJM (1998) Relationship between soil chemical factors and grassland diversity. Plant Soil 202:69–78
Jeong G, Oeverdieck H, Park SJ, Huwe B, Ließ M (2017) Spatial soil nutrients prediction using three supervised learning methods for assessment of land potentials in complex terrain. CATENA 154:73–84
Kalamees R, Puessa K, Zobel K, Zobel M (2012) Restoration potential of the persistent soil seed bank in successional calcareous (alvar) grasslands in Estonia. Appl Veg Sci 15:208–218
Khormali F, Ayoubi S, Foomani FK, Fatemi A, Hemmati K (2007) Tea yield and soil properties as affected by slope position and aspect in Lahijan area, Iran. Int J Plant Prod 1:95–111
Kutiel P (1992) Slope aspect effect on soil and vegetation in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Isr J Bot 41:243–250
Kutiel P, Lavee H (1999) Effect of slope aspect on soil and vegetation properties along an aridity transect. Isr J Plant Sci 47:169–178
Lian G, Guo XD, Fu BJ, Hu CX (2008) Spatial variability and prediction of soil nutrients on a county scale on the loess plateau-a case study of Hengshan County, Shaanxi Province. Acta Pedol Sin 45:577–584
Liu ZK, Wang SP, Zhong CZ, Wang YF, Han JG (2006) Properties of soil nutrients and plant community after rest grazing in Inner Mongolia steppe, China. Acta Ecol Sin 26:2048–2056
Liu R, Zhang WG, Jiang XL, Zhang J (2010) Study on the characteristics of degradation succession of Elymus nutans community and its correlation to soil properties. Pratacultural Sci 27:96–103
Liu XY, Zhou W, Bai ZK (2016) Vegetation coverage change and stability in large open-pit coal mine dumps in China during 1990-2015. Ecol Eng 95:447–451
Liu X, Bai Z, Zhou W, Cao Y, Zhang G (2017) Changes in soil properties in the soil profile after mining and reclamation in an opencast coal mine on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol Eng 98:228–239
Lozano-Garcia B, Parras-Alcantara L, Brevik EC (2016) Impact of topographic aspect and vegetation (native and reforested areas) on soil organic carbon and nitrogen budgets in Mediterranean natural areas. Sci Total Environ 544:963–970
Lu YH, Liao YL, Huang TP, Xia HA, Luo ZC, Nie JK (2011) Fertilizer effect of early rice and abundance and deficiency indices of soil available K in different regions of Hu’nan Province. Hunan Agric Sci 2:63–66
Magagi RD, Kerr YH (2001) Estimating surface soil moisture and soil roughness over semiarid areas from the use of the copolarization ration. Remote Sens Environ 75:432–445
Måren IE, Karki S, Prajapati C, Yadav RK, Shrestha BB (2015) Facing north or south: does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley? J Arid Environ 121:112–123
Marini L, Scotton M, Klimek S, Isselstein J, Pecile A (2007) Effects of local factors on plant species richness and composition of Alpine meadows. Agric Ecosyst Environm 119:281–288
Marque MA, Mora E (1992) The influence of aspect on runoff and soil loss in a Mediterranean burnt forest (Spain). CATENA 19:333–344
Marrs RH (1993) Soil fertility and nature conservation in Europe: theoretical considerations and practical management solutions. Advances Ecol Res 24:241–300
Martinez-Fernandez J, Lopez-Bermudez F, Martinez-Fernandez J, Romero-Diaz A (1995) Land use and soil-vegetation relationships in a Mediterranean ecosystem: el Ardal, Murcia, Spain. CATENA 25:153–167
Mendez MO, Maier RM (2008) Phytostabilization of mine tailings in arid and semiarid environments: an emerging remediation technology. Environ Health Perspect 116:278–283
Mokhtari AR, Roshani Rodsari P, Cohen DR, Emami A, Dehghanzadeh Bafghi AA, Khodaian Ghegeni Z (2015) Metal speciation in agricultural soils adjacent to the Irankuh Pb-Zn mining area, central Iran. J Afr Earth Sci 101:186–193
Nadal-Romero E, Petrlic K, Verachtert E, Bochet E, Poesen J (2014) Effects of slope angle and aspect on plant cover and species richness in a humid Mediterranean badland. Earth Surf Proc Land 39:1705–1716
Nyssen J, Vermeersch D (2010) Slope aspect affects geomorphic dynamics of coal mining spoil heaps in Belgium. Geomorphology 123:109–121
Peng H, Zhang XC, Shao MA (2004) Study on soil potassium loss in Loess Area. J Soil Water Conserv 18:70–73
Piao S, Friedlingstein P, Ciais P, Viovy N, Demarty J (2007) Growing season extension and its impact on terrestrial carbon cycle in the Northern Hemisphere over the past 2 decades. Global Biogeochem Cy 21(3):GB3018
Press I (2006) Ecosystems and human well-being: synthesis. Future Surv 34:534
Puigdefabregas J (2005) The role of vegetation patterns in structuring runoff and sediment fluxes in drylands. Earth Surf Proc Land 30:133–147
Qi J, Marsett RC, Moran MS, Goodrich DC, Heilman P, Kerr YH, Dedieu G, Chehbouni A, Zhang XX (2000) Spatial and temporal dynamics of vegetation in the San Pedro River basin area. Agric For Meteorol 105:55–68
Qin S, Fan Y, Liu HB, Wang ZY (2008) Study on the relations between topographical factors and the spatial distributions of soil nutrients. Res Soil Water Conserv 15:46–49
Raiesi F (2017) A minimum data set and soil quality index to quantify the effect of land use conversion on soil quality and degradation in native rangelands of upland arid and semiarid regions. Ecol Indic 75:307–320
Ruiz-Colmenero M, Bienes R, Eldridge DJ, Marques MJ (2013) Vegetation cover reduces erosion and enhances soil organic carbon in a vineyard in the central Spain. CATENA 104:153–160
Sariyildiz T, Anderson JM, Kucuk M (2005) Effects of tree species and topography on soil chemistry, litter quality, and decomposition in Northeast Turkey. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1695–1706
Sharma CM, Baduni NP, Gairola S, Ghildiyal SK, Suyal S (2010) Effects of slope aspects on forest compositions, community structures and soil properties in natural temperate forests of Garhwal Himalaya. J For Res 21:331–337
Shelford VE (1911) Ecological succession: stream fishes and the method of physiographic analysis. Biol Bull 21:9–34
Sheoran V, Sheoran AS, Poonia P (2010) Soil reclamation of abandoned mine land by revegetation: a review. Int J Soil Sedim Water 3:1–20
Sidari M, Ronzello G, Vecchio G, Muscolo A (2008) Influence of slope aspect on soil chemical and biochemical properties in a Pinuslaricio forest ecosystem of Aspromonte (Southern Italy). Eur J Soil Biol 44:364–372
Splittstoesser WE (1990) Vegetable growing handbook: organic and traditional methods, 3rd edn. Van Nostrand Reinhold, NewYork
Sternberg M, Shoshany M (2001) Influence of slope aspect on Mediterranean woody formations: comparison of a semiarid and an arid site in Israel. Ecol Res 16:335–345
Su YZ, Chang XX, He ZB, Wang F (2008) Changes in vegetative patches and characteristics in soil properties in the valleys of Qilian Mountains. Acta Ecol Sin 28:212–219
Wang GL, Wang XL, Li DF, Bai ZK (2001) Correlation between nutrients of reclaimed soil in Antaibao open cast mine. Coal Mine Environ Prot 15:25–27
Wang ZT, Bao Y, Li Y (2012) Community characteristics and soil nutrient dynamics in the beginning two years after artificial vegetation on rock slope. Acta Prataculturae Sin 21:34–42
Wang G, Wu B, Zhang L, Jiang H, Xu Z (2014) Role of soil erodibility in affecting available nitrogen and phosphorus losses under simulated rainfall. J Hydrol 514:180–191
Xie YZ, Qiu KY, Xu DM, Shi XF, Qi TY, Pott R (2015) Spatial heterogeneity of soil and vegetation characteristics and soil-vegetation relationships along an ecotone in Southern Mu Us Sandy Land. China J Soils Sedim 15:1584–1601
Yang JH, Chang HL, Wei Q (2014) Spatial characteristics of soil nutrients in the Loess Plateau watershed and its correlation with terrain factors. J Northwest A&F Univ (Nat Sci Edit) 42:85–90
Yuan ZQ, Epstein H, Li FM (2015) Factors affecting the recovery of abandoned semi-arid fields after legume introduction on the Loess Plateau. Ecol Eng 79:86–93
Zewdie W, Csaplovics E, Inostroza L (2017) Monitoring ecosystem dynamics in northwestern Ethiopia using NDVI and climate variables to assess long term trends in dryland vegetation variability. Appl Geogr 79:167–178
Zhang Q, Xiao FJ, Niu HS, Dong WJ (2005) Analysis of vegetation index sensitivity to soil moisture in Northern China. Chin J Ecol 24:715–718
Zhang GH, Liu GB, Wang GL (2010) Effects of Caragana Korshinskii Kom. cover on runoff, sediment yield and nitrogen loss. Int J Sedim Res 25:245–257
Zhang XR, Cao YG, Bai ZK, Wang JM, Zhou W, Ding X (2016) Relationships between vegetation coverage and soil properties on the reclaimed dump of opencast coal mine in loess plateau, China. Fresenius Environ Bull 25:4767–4776
Zhao W, Zhang R, Huang C, Wang B, Cao H, Koopal LK, Tan W (2016) Effect of different vegetation cover on the vertical distribution of soil organic and inorganic carbon in the Zhifanggou Watershed on the loess plateau. CATENA 139:191–198
Zheng SS, Wu PF, Ma XQ (2014) Research progress in nutrient spatial heterogeneity in forest soil. World For Res 27:13–17
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41701607, 41571508) and the Basic Scientific Research Foundation for Excellent Supervisors (2-9-2015-173, 2-9-2017-103). Yingui Cao would like to thank China Scholarship Council (201606405024) for the financial support and thank Xiang Ding, Yuanqing Lu, Zhili Yu, Hongdan Wang, Qian Qin, Wenwen Gao for the soil sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Cao, Y., Bai, Z. et al. Evaluating relationships between soil chemical properties and vegetation cover at different slope aspects in a reclaimed dump. Environ Earth Sci 76, 805 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7157-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7157-9