Abstract
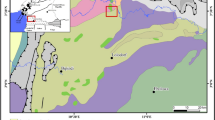
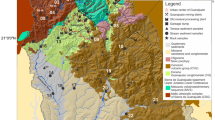
The Marahiq area represents a portion of the Pan-African belt from the Neoproterozoic age in south Egypt and includes metamorphosed ultramafic rocks, metavolcanic rocks, and granodiorite pluton. The area is characterized by the ancient abandoned Au mine and the recent active talc mines. The present paper provides a preliminary assessment of stream sediments for gold (Au) placer and environmental hazard. Steam sediments from 36 stations were analyzed using ICP-MS for determining the concentration of 53 elements. Various statistical techniques, graphical representations, a set of complementary sediment quality assessment methods, and different mapping methods have been applied. The results showed that Au and the investigated elements were influenced by long history of the ancient mining activities and weathering processes, leading to elevate Au and some heavy metal(loid)s concentrations and exhibit enrichment ratios as follows: Te > As > Au > Cu > Cd > Co > Ni > V. Whereas Cd, Co, and V were attributed to geogenic origin, As, Au, Cu, Ni, and Te were derived from anthropogenic mining activities. It is found that the anomalies of Au and the element of interest are indicative of Au placer and point out a new perspective Au-sulfide mineralization hosted along the favorable tectonic zones that were the main source of Au placer. Both As and Te are good pathfinders to explore Au placer and related mineralization. Environmentally, the excess of As, Cu, Ni, and Te could generate moderate levels of contamination and low level of ecological risk in the sediments. Although As, Cu and Ni posed medium–low potentially adverse effects and low toxicity levels, they cannot cause harmful influences on biological life. Accordingly, streambed sediments are considered as safe and acceptable as inoffensive materials for environmental management. Overall, this study is as reference values for governmental organizations for appraising future environmental pollution in the area. Also, it is fruitful for Au placer and promising with success for Au exploration along the shear zones and strike-slip faults.











Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 December 2017
The original article has been published inadvertently with some missed footnotes for Tables 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8, and missed letters in the caption of Table 7.
References
Abdel-Rahman E, Abdou NM, Fawzy KH, Eman A (1999) Geology, perology and geochemisrty of the Precambrian rocks, Marahiq area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. 1st seminar on nuclear raw materials and their technology, Cairo, Egypt. 1–3 Nov
Abrahim GMS, Parker RJ (2008) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Aukland, New Zealand. Environ Monit Assess 136:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9678-2
Adami G, Barbieri P, Reisenhofer E (2000) An improved index for monitoring metal pollutants in surface sediments. Toxicol Environ Chem 77:189–197
Adamo P, Arienzo M, Imperato M, Naimo D, Nardi G, Stanzione D (2005) Distribution and partition of heavy metals in surface and subsurface sediments of Naples city port. Chemosphere 61:800–809
Aitchison J (1986) the statistical analysis of compositional data. Chapman and Hall, London
Appleton JD, Ridgway J (1992) Regional geochemical mapping in developing countries and is application to environmental studies. Appl Geochem 2:103–110
Bea F (1996) Residence of REE, Y, Th and U in granites and crustal protoliths; implications for the chemistry of crustal melts. J Petrol 37:521–552
Bouvier A-S, Ushikubo T, Kita NT, Cavosie AJ, Kozdon R, Valley JW (2012) Li isotopes and trace elements as a petrogenetic tracer in zircon: insights from Archean TTGs and sanukitoids. Contrib Mineral Petrol 163:745–768
Broom-Fendley S, Brady AE, Wall F, Gunn G, Dawes W (2016) REE minerals at the Songwe Hill carbonatite, Malawi: HREE-enrichment in late-stage apatite. Ore Geol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.019
Cabral Pinto MMS, Ferreira da Silva EA, Silva MMVG, Dinis PA (2014) Estimated background values maps of uranium in Santiago Island topsoil and stream sediments. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 8:23–27
Campos Alvarez NO, Roser BP (2007) Geochemistry of black shales from the Lower Cretaceous Paja Formation, Eastern Cordillera, Colombia: source weathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. J S Am Earth Sci 23(2007):271–289
Carranza EJM, Hale M (1997) A catchment basin approach to the analysis of reconnaissance geochemical-geological data from Albay Province, Philippines. J Geochem Explor 60:157–171
Cevik F, Goksu MZL, Derici OB, Findik O (2009) An assessment of metal pollution in surface sediments of seyhan dam by using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index and statistical analyses. Environ Monit Assess 152:309–317
Chapman D (1996) Water quality assessments. A guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. Chapman & Hall, London
Chapman PM, Wang F, Janssen C, Persoone G, Allen HE (1998) Ecotoxicology of metals in aquatic sediments: binding and release, bioavailability, risk assessment, and remediation. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 5:2221–2243
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135154
Edwards R, Lepp NW, Jones KC (1999) Weniger häufig vorkommende Element emit potentieller Bedeutung für die Umwelt. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Schwermetalle in Böden. Springer, Berlin, pp 332–337
Egyptian Geological Survey and Mining Authority (EGSMA) (1996) Geologic map of Wadi Jabjabah quadrangle, Egypt. Geol. Surv, Cairo
El Kazzaz YAHA (1995) ‘Tectonics and mineralization of Wadi Allaqi, south Eastern Desert, Egypt’, Ph.D. thesis. University of Luton
El Shimy KM (1996) Geology, structure and exploration of gold mineralization in Wadi Allaqi area SW, Eastern Desert Egypt. Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Egypt, Ph.D. thesis, 327 p
El Shimy KM (2006) Application of remote sensing in mineral exploration at Wadi Allaqi district, SW Eastern Desert of Egypt. Ann Geo Surv Egypt Cairo 28:205–223
El-Alfy Z, Azer HW, Mohamed AS, Aly A, Omar MA, Mohamed TR (2000) Geochemical exploration for copper and gold mineralization in the area north and south Wadi Allaqi. Sout Eastern Desert Egypt. Geo. Surv. Egypt. Intern. Report 054-2000
El-Boghdady AA, Stamatakis MG, Dawood M (2004) Mineralogy, chemistry and origin of talc deposits at Wadi Marahiq, South Eastern Desert Egypt. In: 7th international conference Geol. Arab World, Agenda & Abstr. Cairo Univ. Egypt. Feb. 2004. p 55
El-Sabagh MEI (2001) Geological, petrographical and geochemical studies of the Pan-African rocks between Wadi Neqiet and Wadi Marahiq, Allaqi area, South Eastern Desert Egypt. Faculty of Science, Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. M. Sc. thesis, 213 p
Ezz-El-Din NAM (2002) Mineralogical and geochemical studies on the sulphides and gold mineraliztion at Wadi Umm Rilan El Atshan, Sout Eastern Desert Egypt. M.Sc. Fac. Sci. Al Azhar Uni., Cairo, Egypt. 178 p
Fawzy KH, Abdou NM, Abdel-Rahman E, Emam A (1999) Ore mineralogy and geochemistry of Marahiq gold mineralization, South-Eastern Desert, Egypt. 1st seminar on nuclear raw materials and their technology, Cairo, Egypt, 1–3 Nov
Fawzy KH, Abdel-Rahman E, Abdou N (2002) Geochemical studies on placer gold deposit at Marahiq gold mine, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. J Sedimentol Soc Cairo Egypt 10:259–271
Fedo CM, Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1995) Unrevealing the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 23:921–924
Fedo CM, Young GM, Nest HW, Hanchar JM (1997) Potassic and sodic metasomatism in the Southern Province of the Canadian Shield: evidence from the Paleoproterozoic Serpent Formation, Huronian Supergroup, Canada. Precambr Res 84:17–36
Ferguson C, Kasamas H (1999) Risk assessment for contaminated sites in Europe. Policy Framework, vol 2. LQM Press, Nottingham NG7 2RD. UK
Fu B, Page FZ, Cavosie AJ, Fournelle J, Kita NT, Lackey JS, Wilde SA, Valley JW (2008) Ti-in-zircon thermometry: applications and limitations. Contrib Mineral Petrol 156:197–215
Graham GE, Taylor RD, Lee GK, Tripp RB (2015) Targeting Cu–Au and Mo resources using multi-media exploration geochemistry: an example from Tyonek Quadrangle, Alaska Range, Alaska. J Geochem Explor 157:52–65
Grunsky EC (2010) The interpretation of geochemical survey data. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 10:27–74
Grunsky EC, Drew LJ, Sutphin DM (2009) Process recognition in multi-element soil and stream-sediment geochemical data. Appl Geochem 24:1602–1616
Guillén MT, Delgado J, Albanese S, Nieto JM, Lima A, De Vivo B (2011) Environmental geochemical mapping of Huelva municipality soils (SW Spain) as a tool to determine background and baseline values. J Geochem Explor 109:59–69
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hassan MM (2006) Gold deposits in Egypt a renewing resource for national income. In: 9th Arab. Conf. Mineral resour., Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, vol 3, pp 1–45
Hassan MM, El-Sheshtawy YA, Ramadan TM, El-Sayed AA (1997) Geology, petrology and geochemistry and economic aspects of Marahiq Talc deposits, Southern Eastern Desert, Egypt. In: 3rd conference on geochem. Alex. Egypt. V.1 (Geochem. Igneous rocks and geochem. exploration) pp 333–344
Hirst DM (1962) The geochemistry of modern sediments from the Gulf of Paria—II The location and distribution of trace elements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 26(11):1147–1187
Hoskin PWO, Schaltegger U (2003) The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. In: Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO (eds), Zircon. Rev. Mineral. Geochem, vol 53, pp 27–62
Hu Z, Gao S (2008) Upper crustal abundances of trace elements: a revision and update. Chem Geol 253(3):205–221
Hume WF (1937) Geology of Egypt, vol. II, Part III. Geol. Surv. Egypt
Ionov DA, Dupuy C, O’Reilly SY, Kopylova MG, Genshaft YS (1993) Carbonated peridotite xenoliths from Spitsbergen: implications for trace element signature of mantle carbonate metasomatism. Earth Planet Sci Lett 119(3):283–297
Jamshidi-Zanjani A, Saeedi M (2013) Metal pollution assessment and multivariate analysis in sediment of Anzali international wetland. Environ Earth Sci 2013(70):1791–1808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2267-5
Jiao S, Guo J, Harley SL, Peng P (2013) Geochronology and trace element geochemistry of zircon, monaziteand garnet from the garnetite and/or associated other high-graderocks: implications for Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal evolution ofthe Khondalite Belt, North China Craton. Precambr Res 237:78–100
Jimoh MT, Bolarinwa AT, Kolawole T (2015) Geochemical stream reconnaissance survey of the schist belt around Igbo-Ora, Southwestern Nigeria. J Geol Min Res 7(7):65–73
Jordan C, Zhang C, Higgins A (2007) Using GIS and statistics to study influences of geology on probability features of surface soil geochemistry in Northern Ireland. J Geochem Explor 93:135–152
Kitajima K, Ushikubo T, Kita NT, Maruyama S, Valley JW (2012) Relative retention of trace element and oxygen isotope ratios in zircon from Archean rhyolite, Panorama Formation, North Pole Dome, Pilbara Craton,Western Australia. Chem Geol 332–333(2012):102–115
Klemm R, Klemm D (2013) Gold and gold mining in ancient Egypt and Nubia. Springer, Berlin, p 649
Kochin GG, Bassyouni FA (1968) Mineral resource of the UAR. (Part I Metallic minerals) Geological Survey Egypt, Internal Report 1968/013, 493 p
Kusky TM, Ramadan TM (2002) Structural controls on Neoproterozoic mineralization in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt: an integrated field, Landsat TM, and SIR-C/X SAR approach. J Afr Earth Sc 35:107–121
Lapworth DJ, Knights KV, Key RM, Johnson CC, Ayoade E, Adekanmi MA, Arisekola TM, Okunlola OA, Backman B, Eklund M, Everett PA, Lister RT, Ridgway J, Watts MJ, Kemp SJ, Pitfield PEJ (2012) Geochemical mapping using stream sediments in west-central Nigeria: implications for environmental studies and mineral exploration in West Africa. Appl Geochem 27:1035–1052
Levinson AA (1974) Introduction to exploration geochemistry. Applied Publishing Limited, Calgary, p 611
Liu WX, Li XD, Shen ZG, Wang DC, Wai OWH, Li YS (2003) Multivariate statistical study of heavy metal enrichment in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Environ Pollut 121:377–388
Long ER, MacDonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manag 19:81–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472006
Long ER, Field LJ, MacDonald DD (1998) Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:714–727
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieria M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily),Italy. Sci Total Environ 300:229–243
Marques R (2007) Geoquimica e mineralogia de argilas do Cretacico de Taveiro e Aveiro, Portugal. M.Sc. in Geosciences, University of Aveiro, 109p
Marques R, Prudencio MI, Dias MI, Rocha F (2011) Patterns of rare earth and other trace elements in different size fractions of clays of Campanian-Maastrichtian deposits from the Portuguese western margin (Aveiro and Taveiro Formations). Chem Erde 71(2011):337–347
Martínez J, Llamas J, de Miguel E, Rey J, Hidalgo MC (2007) Determination of the geochemical background in a metal mining site: example of the mining district of Linares (South Spain). J Geochem Explor 94:19–29
Moreno T, Querol X, Castillo S, Alastuey A, Cuevas E, Herrmann L, Mounkaila M, Elvira J, Gibbons W (2006) Geochemical variations in Aeolian mineral particles from the Sahara-Sahel Dust Corridor. Chemosphere 65(2):261–270
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Müller G (1981) Die Schwermetallbelastung der Sedimente des Neckars und seiner Nebenflusse: eine Bestandsaufnahme. Chem Zeitung 105:157–164
Nasr BB, Masoud MS (1999) Geology and genesis of Wadi Allaqi talc deposit. South Eastern Desert Egypt. Ann Geo Surv Egypt Cairo 22:309–317
Navas A, Machĭn J (2002) Spatial distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in soils of Arago´ n (northeast Spain): controlling factors and environmental implications. Appl Geochem 17:961–973
Nesbitt HW, Markovics G, Price RC (1980) Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 44:1659–1666
Nude PM, Arhin E (2009) Overbank sediments as appropriate geochemical sample media in regional stream sediment surveys for gold exploration in the savannah regions of northern Ghana. J Geochem Explor 103:50–56
Nykairu GWA, Koeberl C (2001) Mineralogical and chemical composition and distribution of rare earth elements in clay-rich sediments from central Uganda. Geochem J 35:13–28
Ohta A, Imai N, Terashima S, Tachibana Y (2005) Application ofmulti-element statistical analysis for regional geochemical mapping in Central Japan. Appl Geochem 20:1017–1037
Ohta A, Imai N, Terashima S, Tachibana Y, Ikehara K, Okai T, Ujiie-Mikoshiba M, Nriagu JO, Kubota R (2007) Elemental distribution of coastal sea and stream sediments in the island-arc region of Japan and mass transfer processes from terrestrial to marine environments. Appl Geochem 22:2872–2891
Papadopoulou-Vrynioti K, Alexakis D, Bathrellos GD, Skilodimou HD, Vryniotis D, Vassiliades E, Gamvroula D (2013) Distribution of trace elements in stream sediments of Arta plain (western Hellas): the influence of geomorphological parameters. J Geochem Explor 134:17–26
Plant JA, Smith D, Smith B, Williams L (2001) Environmental geochemistry at the global scale. Appl Geochem 16:1291–1308
Purves D (1966) Contamination of urban garden soils with copper and boron. Nature 210:1077–1078
Purves D, Mackenzie EJ (1969) Trace element contamination of parklands in urban areas. J Soil Sci 20:288–290
Qiu H (2010) Studies on the potential ecological risk and homology correlation of heavy metal in the surface soil. J Agric Sci 2(2):194
Rantitsch G (2004) Geochemical exploration in a mountainous area by statistical modeling of polypopulational data distributions. J Geochem Explor 82:79–95
Reimann C, De Caritat P (2005) Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Sci Total Environ 337:91–107
Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Garrett RG, Dutter R (2008) Statistical data analysis explained. Wiley, Chichester
Rose A, Hawkes HE, Webb JS (1979) Geochemistry in mineral exploration, vol 2. Academic Press Inc (Ltd), London
Roychoudhury AN, Starke MF (2006) Partitioning and mobility of trace metals in the Blesbokspruit: impact assessment of dewatering of mine waters in the East Rand. Appl Geochem 21(6):1044–1063
Ruiz F (2001) Trace metals in estuarine sediments from the southwestern Spanish Coast. Mar Poll Bull 42:482–490
Šajn R, Aliu M, Stafilov T, Alijagić J (2013) Heavy metal contamination of topsoil around a lead and zinc smelter in Kosovska Mitrovica/Mitrovicë, Kosovo/Kosovë. J Geochem Explor 134:1–16
Salem IA, Ali SM, Scott P, El-Sharkawy MF (1997) Mineralogy, geochemistry and condition of formation Marahique Talc deposits, South Eastern Desert Egypt. In: 3rd conference on geochem. Alex. Egypt. V.1 (Geochem. Igneous rocks and geochem. exploration) pp 265–285
Serage AASM (1996) studies on some talc carbonates and serpentinite rocks and their refractory aspects. Faculty of Science, Al Azhar University, Egypt, M. Sc. thesis, 105 p
Shin PKS, Lam WKC (2001) Development of a marine sediment pollution index. Environ Pollut 113:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00192-5
Smith SL, MacDonald DD, Keenleyside KA, Ingersoll CG, Field LJ (1996) A preliminary evaluation of sediment quality assessment values for freshwater ecosystems. J Great Lakes Res 22:624–638
Spearman CE (1904) “General intelligence” objectively determined and measured. Am J Psychol 15:201–293
Stein M, Goldstein SL (1996) From plume head to continental lithosphere in the Arabian-Nubian Shield. Nature 382:773–778
Stern RJ (1994) Arc assembly and continental collision in the Neoproterozoic East African Orogen: implications for the consolidation of Gondwanaland. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 22:319–351
Stern RJ, Hedge CE (1985) Geochronological and isotopic constraints on late Precambrian crustal evolution in the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Am J Sci 285:97–127
Suda A, Makino T (2016) Functional effects of manganese and iron oxides on the dynamics of trace elements in soils with a special focus on arsenic and cadmium: a review. Geoderma 270(2016):68–75
Swartz RC (1999) Consensus sediment quality guidelines for PAH mixtures. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:780–787
Tayae AEA (1999) Ore microscopy, geochemistry of host rock and concentration pattern of gold and associated elements, Marahiq gold mine, south Eastern Desert, Egypt. M.Sc. Thesis, Aswan Fcacult of Science, South Valley University, Egypt
Tayae AEA (2005) Mineralogy and geochemical studies on some gold deposits and host rocks, Wadi Allaqi, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Aswan Facult of Science, South Valley University, Egypt
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell Scientific, Boston, p 312
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1995) The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev Geophys 33:241–265
Tijani MN, Onodera S (2009) Hydro geochemical Assessment of metals contamination in an urban drainage system: a case study of Osogbo township, SW-Nigeria. J Water Res Protect 3:164–173
Tukey JW (1997) Exploratory data analysis. Addison-Wesley Publishing 7 Company, Massachusett
Van der Oever F (2000) Aruba—a geochemical baseline study, Geologie en Mijnbouw/Netherlands. J Geosci 79(4):467–477
van Helvoort PJ, Filzmoser P, van Gaans PFM (2005) Sequential factor analysis as a new approach to multivariate analysis of heterogeneous geochemical datasets: an application to a bulk chemical characterization of fluvial deposits (Rhine–Meuse delta, The Netherlands). Appl Geochem 20:2233–2251
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang B, Xia DS, Yu Y, Jia J, Xu SJ (2013) Magnetic properties of river sediments and their relationship with heavy metals and organic matter in the urban area in Lanzhou, China. Environ Earth Sci 70:605–614
Wedepohl H (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1217–1239
Whitfield A, Elliott M (2002) Fishes as indicators of environmental and ecological changes within estuaries: a review of progress and some suggestions for the future. J Fish Biol 61:229–250. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2002.tb01773.x
Wilde AR, Bierlein FP, Pawlitschek M (2004) Lithogeochemistry of orogenic gold deposits in Victoria, SE Australia: a preliminary assessment for undercover exploration. J Geochem Explor 84:35–50
Williams TM, Dunkley PN, Cruz E, Acitimbay V, Gaibor A, Lopez E, Baez N, Aspden JA (2000) Regional geochemical reconnaissance of the Cordillera Occidental of Ecuador: economic and environmental applications. Appl Geochem 15:531–550
Wronkiewicz DJ, Condie KC (1990) Geochemistry and mineralogy of sediments from the Ventersdorp and Transvaal Supergroups, South Africa: cratonic evolution during the early Proterozoic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:343–354
Xu ZQ, Ni SJ, Tuo XG, Zhang CJ (2008) Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ Sci Technol 31:112–115
Yisa J, Jacob JO, Onoyima CC (2012) Assessment of toxic levels of some heavy metals in road deposited sediments in Suleja, Nigeria. Am J Chem 2(2):34–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The original article has been published inadvertently with some missed footnotes for Tables 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8, and missed letters in the caption of Table 7.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7173-9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Darwish, M.A.G. Reconnaissance geochemical survey in the Marahiq area, Wadi Allaqi region, south Egypt: a preliminary assessment of stream sediments for gold placer and environmental hazard. Environ Earth Sci 76, 804 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7152-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7152-1