Abstract
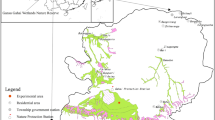
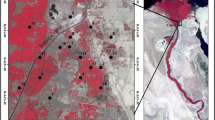
Fencing is an important method for restoring and reconstructing degraded grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. Understanding the characteristics of soil water percolation and soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) leaching and their response to long-term fencing (10 years) could provide a scientific basis for the management of soil water resources and carbon sinks in alpine grasslands. In this study, grazing plots and plots fenced for 10 years were selected in an alpine meadow, and soil bulk density, soil organic carbon (SOC) density, vegetative carbon (VC) density, soil water percolation and DOC leaching were monitored regularly in the two treatments. The results were as follows: (1) Long-term fencing reduced the soil bulk density and improved carbon sequestration in the alpine meadow. The soil bulk density at a depth of 0–20 cm in the fenced plots was significantly lower than that of the grazing plots (p < 0.05), and SOC density and VC density at a depth of 0–40 cm were higher than those of the grazing plots to a different degree. (2) During the non-frozen period (from May to September), total soil water leakage at a depth of 40 cm in the grazing plots was 9.6 mm, which accounted for 2.2% of the total rainfall in this period. After fencing for 10 years, soil water leakage was increased by 53.1%. (3) From May to September, total DOC leaching from the grazing plots was 34.6 gC m−2, and total DOC leaching from the fenced plots was increased by 55.5% compared to the grazing plots. Our results demonstrated obvious soil water percolation and DOC leaching in the alpine meadow. The DOC entered into the groundwater system with the percolation water and finally flowed into lakes and rivers, which represents an important soil carbon loss pathway in alpine meadows.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berendse F (1990) Organic matter accumulation and nitrogen mineralization during secondary succession in health land ecosystem. J Ecol 78:413–427
Berg WA, Bradford JA, Sims PL (1997) Long-term soil nitrogen and vegetation change on sandhill rangeland. J Range Manage 50:482–486
Binkley D, Singer F, Kaye M, Rochelle R (2003) Influence of elk grazing on soil properties in Rocky Mountain National Park. For Ecol Manag 185:239–247
Booth BBB, Jones CD, Collins M, Totterdell IJ, Cox PM, Sitch S, Huntingford C, Betts RA, Harris GR, Lloyd J (2012) High sensitivity of future global warming to land carbon cycle processes. Environ Res Lett 7:024002
Bu HY, Chen XL, Xu XL, Liu K, Jia P, Du GZ (2007) Seed mass and germination in an alpine meadow on the eastern Tsinghai-Tibet plateau. Plant Ecol 191:127–149
Cao GM, Tang YH, Mo WH, Wang YS, Li YN, Zhao XQ (2004) Grazing intensity alters soil respiration in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Soil Biol Biochem 36:237–243
Castellano MJ, Valone TJ (2007) Livestock, soil compaction and water infiltration rate: evaluating a potential desertification recovery mechanism. J Arid Environ 71:97–108
David CW, Jan S, Reimo K, Laura K, Klaus K, Matthew S, Martin K, Bruce AO (2011) Dissolved carbon leaching from an Irish cropland soil is increased by reduced tillage and cover cropping. Agric Ecosyst Environ 142:393–402
De JR, Bootsma A (1997) Estimates of water deficits and surpluses during the growing season in Ontario using the SWATRE model. Can J Soil Sci 77:285–294
Deng L, Zhang ZN, Shangguan ZP (2014) Long-term fencing effects on plant diversity and soil properties in China. Soil Till Res 137:7–15
Dong QM, Zhao XQ, Wu GL, Shi JJ, Ren GH (2013) A review of formation mechanism and restoration measures of “black-soil-type” degraded grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 70:2359–2370
Du YX, Wu CJ, Zhou SX, Huang L, Han SM, Xu XF, Ding Y (2011) Forest soil organic carbon density and its distribution characteristics along an altitudinal gradient in Lushan mountains of China. Chin J Appl Ecol 7:1675–1681 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Estavillo JM, Merino P, Pinto M, Yamulki S, Gebauer G, Corré W (2002) Short term effect of ploughing a permanent pasture on N2O production from nitrification and denitrification. Plant Soil 239:253–265
Fan JW, Zhong HP, Harris W, Yu GR, Wang SQ, Hu ZM, Yue YZ (2008) Carbon storage in the grasslands of China based on field measurements of above- and below-ground biomass. Clim Change 86:375–396
Feng ZZ, Wang XK, Feng ZW (2005) Soil N and salinity leaching after the autumn irrigation and its impact on groundwater in Hetao irrigation district, China. Agric Water Manage 71:131–143
Forrester DI, Pares A, O’Hara C (2013) Soil organic carbon is increased in mixed-species plantations of Eucalyptus and nitrogen-fixing Acacia. Ecosystems 16:123–132
Guo DL, Yang MX, Wang HJ (2011) Sensible and latent heat flux response to diurnal variation in soil surface temperature and moisture under different freeze/thaw soil conditions in the seasonal frozen soil region of the central Tibetan Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 63:97–107
Han DR, Cao GM, Guo XW, Zhang FW, Li YK, Lin L, Li J, Tang YH, Gu S (2011) The potential of carbon sink in alpine meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecol Sin 31:7408–7417 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hannu N, Jukka A, Kristiina L, Jouko S, Pertti JM (1995) Emissions of CH4, N2O and CO2 from a Virgin Fen and a Fen Drained for Grassland in Finland. J Biogeogr 22:351–357
Heng LK, White RE, Helyar KR, Chen D (2001) Seasonal differences in the soil water balance under perennial and annual pastures on an acid Sodosol in southeastern Australia. Eur J Soil Sci 52:227–236
Hiernaux P, Bielders CL, Valentin C, Bationo A, Fernández-Rivera S (1999) Effects of livestock grazing on physical and chemical properties of sandy soils in Sahelian rangelands. J Arid Environ 41:231–245
Holt JA (1997) Grazing pressure and soil carbon, microbial biomass and enzyme actives in semi-arid northeastern Australia. Appl Soil Ecol 5:143–149
Jette BC, Dorthe LJ, Thomas HC (1996) Effect of dissolved organic carbon on the mobility of cadmium, nickel and zinc in leachate polluted groundwater. Water Res 30:3037–3049
Ji JJ, Huang M, Li KR (2008) Prediction research on the carbon exchange between atmosphere and terrestrial ecosystem in China during 21st century. Sci China Earth Sci 38:211–223 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li XJ, Zhang XZ, Wu JS, Shen ZX, Zhang YJ, Xu XL, Fan YZ, Zhao YP, Yan W (2011) Root biomass distribution in alpine ecosystems of the northern Tibetan Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 64:1911–1919
Li YY, Dong SK, Wen L, Wang XX, Wu Y (2013) The effects of fencing on carbon stocks in the degraded alpine grass lands of the Qinghai-Tibet an Plateau. J Environ Manage 128:393–399
Li EH, Mu XM, Zhao GJ (2014) Temporal changes in annual runoff and influential factors in the upper and middle reaches of Yellow River from 1919 to 2010. Adv Water Sci 25:155–163 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mack UD, Feger KH, Gong Y, Stahr K (2005) Soil water balance and nitrate leaching in winter wheat summer maize double cropping systems with different irrigation and N fertilization in the North China Plain. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 168:454–460
Marios S (2002) Interactions between groundwater and surface water: the state of the science. Hydrogeol J 10:52–67
Naeth MA, Rothwell RL, Chanasyk DS, Bailey AW (1990) Grazing impacts on infiltration in mixed prairie and fescue grassland ecosystems of Alberat. Can J Soil Sci 70:593–605
Ni J (2002) Carbon storage in grasslands of China. J Arid Environ 50:205–218
Reeder JD, Schuman GE (2002) Influence of livestock grazing on sequestration in semi-arid mixed-grass and short-grass rangelands. Environ Pollut 116:457–463
Reeder JD, Schuman GE, Morgen JA, LeCain DR (2004) Response of organic and inorganic carbon and nitrogen to long-term grazing of the short grass steppe. Environ Manage 33:485–495
Reimo K, Jan S, Klaus K, David CW, Christian B, Nina B, Pierre C, Werner E, Gerd G, Thomas G, Alexander H, Anderas I, Stephanie KJ, Mike J, Katja K, Wener K, Klaus SL, Simon L, Benjamin L, Rebecca M, Eddy M, Bruce O, Kim P, Corinna R, Matthew S, Michael WIS, Marion S, Janine S, Ute S, Jean-francois S, Mark AS, Cindy T, Bernhard V, Matthias JZ, Martin K (2011) Dissolved carbon leaching from soil is a crucial component of the net ecosystem carbon balance. Glob Change Biol 17:1167–1185
Risser PG, Birney EC, Blocker HD (1981) The true prairie ecosystem. Hutchinson Ross Pub. Co, New York
Robert GQ, Bruce LH (1990) Geochemistry of dissolved organic nutrients in water percolating through a forest ecosystem. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:1112–1123
Sala OE, Oesterheld M, Leόn RJC, Soriano A (1986) Grazing effects upon plant community structure in subhumid grasslands of Argentina. Vegetatio 67:27–32
Scholes B (1999) Will the terrestrial carbon sink saturate soon? IGBP Glob Change Newsl 37:2–3
Song MH, Jiang J, Cao GM, Xu XL (2010) Effects of temperature, glucose and inorganic nitrogen inputs on carbon mineralization in a Tibetan alpine meadow soil. Eur J Soil Biol 46:375–380
Tao Z, Sheng CD, Gao QZ, Sun YM, Yi WX, Li YN (2007) Soil organic carbon storage and CO2 flux in alpine meadow. Sci China Earth Sci 37:553–563 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang GX, Qian J, Cheng GD, Lai YM (2002) Soil organic carbon pool of grassland soils on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its global implication. Sci Total Environ 291:207–217
Wang GX, Cheng GD, Shen YP, Qian J (2003) Influence of land cover changes on the physical and chemical properties of alpine meadow soil. Chin Sci Bull 48:118–124
Wang CT, Long RJ, Wang QJ (2007) Effects of altitude on plant-species diversity and productivity in an alpine meadow, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Aust J Bot 55:110–117
Wang WJ, Qiu L, Zu YG, Su DX, An J, Wang HY, Zheng GY, Sun W, Chen XQ (2011) Changes in soil organic carbon, nitrogen, pH and bulk density with the development of larch (Larixgmelinii) plantations in China. Global Change Biol 17:2657–2676
Wang GX, Liu GS, Li CJ (2012) Effects of changes in alpine grassland vegetation cover on hillslope hydrological processes in a permafrost watershed. J Hydrol 444–445:22–33
Wu HB, Guo ZT, Peng CH (2003) Distribution and storage of soil organic carbon in China. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 17:1–11
Wu GL, Du GZ, Liu ZH, Simon T (2009) Effect of fencing and grazing on a Kobresia-dominated meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 319:115–126
Wu GL, Liu ZH, Zhang L, Chen JM, Hu TM (2010) Long-term fencing improved soil properties and soil organic carbon storage in an alpine swamp meadow of western China. Plant Soil 332:331–337
Xiong DP, Shi PL, Sun YL, Wu JS, Zhang XZ (2014a) Effects of grazing exclusion on plant productivity and soil carbon, nitrogen storage in alpine meadows in northern Tibet, China. Chin Geogr 24:488–498
Xiong DP, Shi PL, Sun YL, Wu JS, Zhang XZ (2014b) Effects of grazing exclusion on plant productivity and soil carbon, nitrogen storage in alpine meadows in northern Tibet, China. Chin Geogr 24:488–498
Yang YH, Fang JY, Ji CJ, Han WX (2009) Above- and below ground biomass allocation in Tibetan grasslands. J Veg Sci 20:177–184
Yang WB, Tang JN, Liang HR, Dang HZ, Li W (2014) Deep soil water infiltration and its dynamic variation in the shifting sandy land of typical deserts in China. Sci China Earth Sci 57:1816–1824
Yi XS, Li GS, Yin YY (2012) The impacts of grassland vegetation degradation on soil hydrological and ecological effects in the source region of the Yellow River—a case study in Junmuchang region of Maqin country. Proced Environ Sci 13:967–981
Zeng CX, Wu JS, Zhang XZ (2015) Effects of grazing on above- vs. below-ground biomass allocation of alpine grasslands on the northern Tibetan Plateau. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135173
Zhang JX, Cao GM, Zhou DW, Hu QW, Zhao XQ (2003) The carbon storage and carbon cycle among the atmosphere, soil, vegetation and animal in the Kobresia humilis alpine meadow ecosystem. Acta Ecol Sin 23:627–634 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zou JR, Zhao L, Xu S, Xu XL, Chen DD, Li Q (2013) Livestock exclosure with consequent vegetation changes alters photo-assimilated carbon cycling in a Kobresia meadow. Biogeosci Discuss 10:17633–17661
Acknowledgements
We sincerely appreciate the invaluable comments of two anonymous reviewers. This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDB03030502) the Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai Province (No. 2014-ZJ-901, 2016-ZJ-943Q) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31300385, 31270523).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Li, H., Zhang, L. et al. Characteristics of soil water percolation and dissolved organic carbon leaching and their response to long-term fencing in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6178-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6178-0