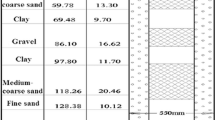
Abstract
Underground injection (UI) is an effective and efficient means of disposing of wastewater from shale gas production. However, the influence of UI on groundwater systems should be examined carefully to protect drinking groundwater sources. A regional hydrogeological model based on TOUGH2-MP/EOS7R of part of the Sichuan Basin is established to simulate pressure changes and solute transport in response to wastewater injection into deep aquifers. Wastewater is assumed to be injected through a well at a rate of 5.45 kg s−1 for 5 years and a post-injection period of 45 years. The simulation results indicate that UI will cause significant pressure buildup during the injection period, after which pressure will dissipate during the post-injection period. The mass fraction of solute increased over the entire simulation period. The draft regulation under the Safe Drinking Water Act and the level III groundwater quality standards regulated by the Chinese government is referenced as the criteria for evaluating the influence of UI on groundwater systems. It is found that maximum pressure levels caused by UI may exceed safe levels. Uncertainties with respect to permeability are analyzed from previous studies and injection test results. Lower levels of permeability incur higher degrees of pressure buildup when UI is implemented. Different injection schemes are discussed, and we verify that pressure buildup from time-variant injection schemes is less than that from constant injection schemes for the same total injection volume. Injection schemes should be carefully evaluated before implementing UI in a shale gas reservoir.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hubail J, El-Dash K (2006) Managing disposal of water produced with petroleum in Kuwait. J Environ Manag 79(1):43–50
Bayer MR, Kobelski B (2008) Underground injection control program: proposed regulations for underground injection of carbon dioxide for geologic sequestration. Groundwater Monit Remediat 28(4):42–44
Birkholzer JT, Zhou Q, Tsang C-F (2009) Large-scale impact of CO2 storage in deep saline aquifer: a sensitivity study on pressure response in stratified systems. Int J Greenh Gas Control 3(2):181–194
Cao T, Song Z, Wang S, Cao X, Li Y, Xia J (2015) Characterizing the pore structure in the Silurian and Permian shales of the Sichuan Basin, China. Mar Pet Geol 61:140–150
Chen ZQ (2009) Discussion on gas exploration of middle Permian Qixia formation, Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Geosc 03:325–334 (in Chinese)
Chen S, Zhu Y, Qin Y, Wang H, Liu H, Fang J (2014) Reservoir evaluation of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale gas in the southern Sichuan Basin of China. Mar Pet Geol 57:619–630
DHI-WASY GmbH (2013) DHI-WASY software FEFLOW 6.2: user manual. DHI-WASY, Berlin
Dillon RT, Lantz RB, Pahwa SB (1978) Risk methodology for geologic disposal of radioactive waste: The Sandia Waste Isolation Flow and Transport (SWIFT) model. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque
Dong D, Gao S, Huang J, Guan Q, Wang S, Wang Y (2015a) Discussion on the exploration and development prospect of shale gas in the Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind B 2(1):9–23
Dong D, Guan Q, Wang S, Huang J, Wang Y, Zhang C (2015b) Shale gas in China: reality and dream. Energy Explor Exploit 33(3):397–418
Ferguson G (2015) Deep injection of waste water in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. Groundwater 53(2):187–194
Guo W (2012) Sedimentary facies and reservoir characteristics of Permian Qixia formation, southwestern Sichuan Basin. Master's Thesis of Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China (in Chinese)
Horton S (2012) Disposal of hydrofracking waste fluid by injection into subsurface aquifers triggers earthquake swarm in Central Arkansas with potential for damaging earthquake. Seismol Res Lett 83(2):250–260
Li Q, Bai Y, Yin X, Li X (2007) Thermo-hydro-mechanical modeling of CO2 sequestration system around fault environment. In: Computational earthquake physics: simulations, analysis and infrastructure, Part II pp 2585–2593
Liu P, Feng Y, Zhao L, Li N, Luo Z (2015) Technical status and challenges of shale gas development in Sichuan Basin, China. Petroleum 1(1):1–7
Maliva RG, Guo W, Missimer T (2007) Vertical migration of municipal wastewater in deep injection well systems, South Florida, USA. Hydrogeol J 15(7):1387–1396
Mehl SW, Hill MC (2006) MODFLOW-2005, the US Geological Survey modular ground-water model-documentation of shared node local grid refinement (LGR) and the boundary flow and head (BFH) package. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 6-A12, USA
Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources of the People's Republic of China (1994) Quality standard for ground water (GB/T 14848-93). Standards Press of China, Beijing, China
Oldenburg CM, Pruess K (1995) EOS7R: radionuclide transport for TOUGH2 Lawrence Berkley Laboratory Report LBL-34868, Berkeley, CA, USA
Pruess K, Oldenburg C, Moridis G (1999) TOUGH2 user’s guide Version 2 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, USA
Quaranta JD, Mack B, Van Aken B, Ducatman A, Ziemkiewicz P (2014) Practical application of dilution analysis for estimating groundwater quality effects due to coal slurry injection into underground. Mine Voids Mine Water Environ 33(4):353–361
Rahm BG, Riha SJ (2012) Toward strategic management of shale gas development: regional, collective impacts on water resources. Environ Sci Policy 17:12–23
Sakamoto Y, Tanaka A, Tenma N, Komai T (2013) Numerical study on flow behavior of CO2 around injected well for risk assessment of carbon capture and storage. Energy Proc 37:4785–4793
Stephenson MH (2016) Shale gas in North America and Europe. Energy Sci Eng 4:4–13
Vengosh A, Jackson RB, Warner N, Darrah TH, Kondash A (2014) A critical review of the risks to water resources from unconventional shale gas development and hydraulic fracturing in the United States. Environ Sci Technol 48(15):8334–8348
Xia YL, Qi L, Yin XC (2015) Characteristics of acoustic emission during deformation and failure of typical reservoir rocks under triaxial compression: an example of Sinian dolomite and shale in the Sichuan Basin. Chin J Geophys Chin Edition 58:982–992
Yu B, Zhao ZJ (2011) Characteristic of the fracture cave reservoir in the Langzhong area, Sichaun Basin. West-China Explor Eng 03:59–62 (in Chinese)
Zhang X, Jiang X, Yang J, Chen M (2015) A newly developed rate analysis method for a single shale gas well. Energy Explor Exploit 33(3):309–316
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 41572220) and by the Research and Development Project on Geological Disposal of High Level Radioactive Waste managed by the State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense (Grant Number: 2012-240). We give thanks for the constructive comments for the anonymous reviewer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, W., Hu, L., Yao, L. et al. Numerical investigation of the influence of underground water injection on the groundwater system in a shale gas reservoir in southwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1092 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5889-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5889-6