Abstract
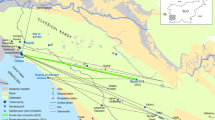
The purpose of this paper is to highlight the hydrogeological contact among aquifers in karst and fissured systems and study the different flowpaths present in said aquifers; given the complex hydrogeological and tectonics settings, detailed surveys in the Umbria-Marche limestone ridges and tracer field tests were used to achieve this goal. DNA and fluorescent tracers were injected into a sinkhole and thereafter recovered at different points, allowing both for the identification of contact among aquifers, as well as the main and secondary directions of groundwater. The tracer tests have shown that the majority of the groundwater flow is directed towards the axis of the tectonic structures, emerging in more depressed areas. In addition, they have confirmed the influence of karstification on the recharge, which allows for a more detailed characterisation of water circulation in the unsaturated zone of the Maiolica and the Calcare Massiccio limestone aquifers thus offering confirmation of the hydrogeological survey results, and providing additional information that was previously unknown. Furthermore, the DNA tracer provided good results in the field especially in the karst systems and fissured rocks, thus confirming its appropriacy for flowpath investigations and vulnerability analyses of springs. In particular, DNA is suitable for very large amounts of groundwater owing to its very low detection limit. Further investigations and studies are, however, required to assess its validity also for the evaluation of hydrogeological parameters.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquilanti L, Clementi F, Landolfo S, Nanni T, Palpacelli S, Tazioli A (2013) A DNA tracer used in column tests for hydrogeology applications. Environ Earth Sci 70(7):3143–3154. doi:10.1007/S12665-013-2379-Y
Bally AW, Burbi L, Cooper C, Ghelardoni R (1986) Balanced cross section and seismic reflection profiles across the central Apennines. Mem Soc Geol It 35:257–310
Barbieri M, Petitta M, D’Amelio L, Desiderio G, Rusi S, Marchetti A, Nanni T, Tallini M (2002) Gli isotopi ambientali (18O/2H e 87Sr/86Sr) nelle acque sorgive dell’Appennino Abruzzese: considerazioni sui circuiti sotterranei negli acquiferi carbonatici. (Environmental isotopes in the spring waters of the Abruzzo Apennines: consideration on groundwater flowpaths in the carbonate aquifers). In: Atti I (ed) Congr Naz AIGA,RENDINA ED, Chieti p 69–81
Barchi M (1991) Una sezione geologica bilanciata attraverso il settore meridionale dell’Appennino umbro-marchigiano: l’Acquasparta-Spoleto-Accumuli. (A balanced geological section across the southern sector of the Umbria-Marche Apennines: Acquasparta-Spoleto-Accumuli). Studi Geol Camerti Vol. spec. 1991/1: 347–362
Barchi MR, De Feyter AJ, Magnani MB, Minelli G, Pialli G, Sotera BM (1998) The structural style of the Umbria-Marche fold and thrust belt. Mem Soc Geol It 52:552–578
Boccaletti M, Calamita F, Deiana G, Gelati R, Massari F, Moratti G, Lucchi FR (1990) Migrating foredeep thrust belt system in the Northern Apennines and Southern Alps. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl 77:3–14. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(90)90095-O
Boni C, Bono P, Capelli G, Lombardi S, Zuppi GM (1986) Contributo all’idrogeologia dell’Italia centrale (Contribution to hydrogeology setting of central Italy). Mem Soc Geol It 35: 10
Boni C, Tarragoni C, Martarelli L, Pierdominici S (2009) Hydrogeological study of the Monti Sibillini north-western sector (central Italy): a contribution to the official hydrogeologic mapping. Ital J Eng Geol Environ 1:16. doi:10.4408/IJEGE.2009-01.O-01
Calamita F, Deiana G (1986) Evoluzione strutturale Neogenico-Quaternaria dell’Appennino Umbro-Marchigiano. (Structural Neogenic-Quaternary evolution of Umbria-Marche Apennines). Studi Geol CamertiVol spec 1986:91–98
Calamita F, Cello G, Centamore E, Deiana G, Micarelli A, Paltrinieri W, Ridolfi M (1991a) Stile deformativo e cronologia della deformazione lungo tre sezioni bilanciate dell’Appennino umbro-marchigiano della costa adriatica. (Deformative style and cronology of deformation along three balancede sections of Umbria-Marche Apennines in the adriatic shore). Studi Geol Camerti 1991/1: 295–314
Calamita F, Deiana G, Invernizzi C, Pizzi A (1991b) Tettonica (Tectonics). In: Marche Region (ed) L’ambiente fisico delle Marche. Geologia, Geomorfologia, Idrogeologia. SELCA:67–80
Calamita F, Centamore E, Deiana G, Ridolfi M (1995) Caratterizzazione geologico-strutturale dell’area marchigiano-abruzzese (Appennino centrale). (Geostructural characterisation of the Marche-Abruzzo area (central Apennines). Studi Geol Camerti vol spec 1995/1: 171–182
Calamita F, Coltorti M, Pieruccini P, Pizzi A (1999) Evoluzione strutturale e morfogenesi plio-quaternaria dell’Appennino umbro-marchigiano tra il pedappennino umbro e la costa adriatica. (Structural evolution and Plio-Quaternary morphogenesys of Umbria-Marche Apennines included between the Umbria hills and the adriatic coast). Boll Soc Geol It 118:125–139
Centamore E, Micarelli A (1991) Stratigrafia. (Stratigraphy). In: Marche R (ed) L’ambiente fisico delle Marche. Geologia, Geomorfologia, Idrogeologia. SELCA:1–66
Centamore E, Chiocchini M, Deiana G, Micarelli A, Pieruccini U (1971) Contributo alla conoscenza del Giurassico dell’Appennino umbro-marchigiano. (Contribution to the knowledge of the Jurassic in Umbria-Marche Apennines). Studi Geol Camerti 1:7–89
Davis SN, Thompson GM, Bentley HW, Stiles G (1980) Ground-water tracers–a short review. Groundwater 18:14–23. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.1980.tb03366.x
De Feyter A, Koopman A, Molenaar N, Van Den Ende C (1987) Detachment tectonics and sedimentation, Umbro-Marchean Apennines, Italy. Boll Soc Geol It 105:65–85
EPA US (2002) The Qtracer2 Program for tracer-breakthrough curve analysis for tracer tests in Karstic Aquifers and other hydrologic systems. USEPA
Field MS (2003) A review of some tracer-test design equations for tracer-mass estimation and sample-collection frequency. Environ Geol 43:867–881
Field MS, Nash SG (1997) Risk assessment methodology for karst aquifers: (1) Estimating karst conduit-flow parameters. Environ Monit Assess 47:1–21. doi:10.1023/A:1005753919403
Foppen JW, Orup C, Adell R, Poulalion V, Uhlenbrook S (2011) Using multiple artificial DNA tracers in hydrology. Hydrol Process 25:3101–3106
Foppen JW, Seopa J, Bakobie N, Bogaard T (2013) Development of a methodology for the application of synthetic DNA in stream tracer injection experiments. Water Resour Res 49(9):5369–5380
Galdenzi S, Paggi S, Pistolesi E, Cotechini G (2008) Le grotte di Sefro: guida al carsismo del territorio di Sefro. (The Sefro caves: guide to karst of the Sefro area). Jesi, p 24
Goldscheider N, Meiman J, Pronk M, Smart C (2008) Tracer tests in karst hydrogeology and speleology. Int J Speleol 37(1):27–40
Hadi S, Leibundgut C, Friedrich K, Maloszewski P (1997) New fluorescent tracers. In: Kranic A (ed) Tracer Hydrology 97. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 55–62
Maloszewski P, Zuber A (1992) On the calibration and validation of mathematical models fort he interpretation of tracer experiments in groundwater. Adv Water Resour 15:47–62
Mirabella F, Barchi MR, Lupattelli A (2008) Seismic reflection data in the Umbria Marche Region: limits and capabilities to unravel the subsurface structure in a seismically active area. Ann Geophys-Italy 51:383–396
Nanni T, Vivalda PM (1999) Le acque solfuree della regione marchigiana. (The sulphur groundwater of the Marche Region). Boll Soc Geol It 118:585–599
Nanni T, Vivalda PM (2005) The aquifers of the Umbria-Marche adriatic region: relationships between structural setting and groundwaters chemistry. Boll Soc Geol It 124:24–37
Nanni T, Vivalda PM, Marcellini M, Palpacelli S (2006) Spring monitoring and analysis of groundwater circulation in the Sibillini mountains aquifers (adriatic side of central Apennines, Italy). In: Goldscheider N, Mudry J, Savoy L, Zwahlen F (eds) 8th conference on limestone hydrogeology Presses universitaires de Franche-Comté, Université de Franche-Comté, Neuchatel:197–200
Nanni T, Tazioli A, Vivalda PM (2013) Problems in the application of environmental isotopes to the hydrogeology of high mountain aquifers. AquaMUNDI 4:55–66. doi:10.4409/Am-055-13-0052
Palpacelli S (2013) Techniques and Methodologies for the hydrodynamic characterization of fissured aquifers. PhD Thesis, Università Politecnica delle Marche
Pierantoni PP, Deiana G, Romano A, Paltrinieri W, Borraccini F, Mazzoli S (2005) Geometrie strutturali lungo la thrust zone del fronte montuoso umbro-marchigiano-sabino. (Structural geometries along the thrust zone of Umbria-Marche-Sabina ridge). Boll Soc Geol It 124:395–411
Ptak T, Piepenbrink M, Martac E (2004) Tracer tests for the investigation of heterogeneous porous media and stochastic modelling of flow and transport-a review of some recent developments. J Hydrol 294:122–163. doi:10.1016/J.Jhydrol.01.020
Sabir I H, Haldorsen S, Torgersen J, Aleström P, Gaut S, Colleuille H, Pedersen T S (2000) Synthetic DNA tracers: examples of their application in water related studies. In: A D (ed) Tracers and Modelling in Hydrogeology. TraM’2000 Conference Belgium, 2000. IAHS International Association of Hydrological Sciences:159–165
Sabir IH, Torgersen J, Haldorsen S, Aleström P (1999) DNA tracers with information capacity and high detection sensitivity tested ingroundwater studies. Hydrogeol J 7(3):264–272
Sabir IH, Aleström P, Haldorsen S (2001) Use of synthetic DNA as new tracers for tracing groundwater flow and multiple contaminants. Pak J Appl Sci 1(3):233–238
Scisciani V (2009) Styles of positive inversion tectonics in the Central Apennines and in the Adriatic foreland: Implications for the evolution of the Apennine chain (Italy). J Struct Geol 31:1276–1294
Sharma AN, Luo D, Walter MT (2012) Hydrological tracers using nanobiotechnology: proof of concept. Environ Sci Technol 46(16):8928–8936
Tarragoni C (2005) Definizione dell’assetto idrogeologico dei Monti Sibillini e sua verifica col contributo della simulazione numerica delle condizioni di flusso e dell’idrologia isotopica. (Definition of the hydrogeological setting of Mt Sibillini and verify with the contribution of numerical simulation of flow conditions and of isotope hydrology). PhD Thesys, Università degli Studi di Roma “La Sapienza”
Tarragoni C (2006) Determinazione della “quota isotopica” del bacino di alimentazione delle principali sorgenti dell’alta Valnerina. (Evaluation of the isotopic altitude of the recharge areas of main springs in high Valnerina). Geol Romana 39: 8
Tazioli A (2011) Experimental methods for river discharge measurements: comparison among tracers and current meter. Hydrol Sci J 56:1314–1324. doi:10.1080/02626667.2011.607822
Tazioli A, Palpacelli S (2013) Scelta del tracciante ideale per indagini idrogeologiche: risultati preliminari da test in laboratorio. Acque Sotter Ital J Groundw 2:7–12. doi:10.7343/AS-021-13-0000
Tazioli A, Mosca M, Tazioli GS (2007) Location of recharge area of Gorgovivo Spring, Central Italy. A contribution from Isotope Hydrology. In: Iaea (ed) Advances in isotope hydrology and its role in sustainable water resources management iaea, Wien. 27–34
Tazioli A, Conversini P, Peccerillo A (2012) Hydrogeological and geochemical characterisation of the rock of Orvieto. Environ Earth Sci 66:55–65. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1206-6
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr Mirco Marcellini for the excellent support during tracer tests and laboratory analyses. A special thank to the company financing part of the field operations (A.S.SE.M. SpA of S. Severino Marche, MC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aquilanti, L., Clementi, F., Nanni, T. et al. DNA and fluorescein tracer tests to study the recharge, groundwater flowpath and hydraulic contact of aquifers in the Umbria-Marche limestone ridge (central Apennines, Italy). Environ Earth Sci 75, 626 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5436-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5436-5