Abstract
In the present paper, the impact of the main environmental factors on slope stability is analyzed by deriving a model for slope safety factor as a nonlinear function of geomechanical soil properties (bulk density γ, cohesion c, angle of internal friction φ and pore water pressure coefficient r u ) and terrain geometry (slope height H, bedrock depth d and slope angle β). The suggested model is derived using the response surface method, based on Spencer’s stability analyses of homogeneous slopes with circular slip surface. The analyzed parameter ranges were chosen according to the commonly determined values for unstable slopes in Neogene clay–marl deposits in Belgrade. The statistical reliability of the suggested model was confirmed by analyzing the stability of slopes with random geomechanical soil properties and terrain geometry. The obtained results indicate that all the examined environmental factors have statistically significant impact on the slope stability with prevailing linear effect, while geometrical factors and cohesion also show substantial quadratic effect. The existence of two-factor interactions imply that the impact of slope height on its stability is strongly dependent on slope angle, cohesion and bedrock depth, while the latter two also significantly affect the impact of slope angle on F s .





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop AW, Morgenstern NR (1960) Stability coefficients for earth slopes. Geotechnique 10:129–150
Boutrup E, Lovell CW (1980) Searching techniques in slope stability analysis. Eng Geol 16:51–61
Cousins BF (1978) Stability charts for simple earth slopes. J Geotech Eng ASCE 104:267–279
Das SK, Biswal RK, Sivakugan N, Das B (2011) Classification of slopes and prediction of factor of safety using differential evolution neural networks. Environ Earth Sci 64:201–210
Deming SN, Morgan SL (1996) Experimental design: a chemometric approach. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Duncan JM, Wright SG (2005) Soil strength and slope stability. Wiley, New York
Erzin Y, Cetin T (2013) The prediction of the critical factor of safety of homogeneous finite slopes using neural networks and multiple regressions. Comp Geotech 51:305–313
Fisher RA (1935) The design of experiments. Haffner Press, New York
Janjić M (1962) Engineering-geological properties of Serbia. Institute for geological and geophysical research, Special publications 12 (in Serbian)
Janjić I (1996) Origin and properties of landslides in Neogene sediments of southern edge of Panonian basin. Magister Paper, University of Belgrade Faculty of Mining and Geology (in Serbian)
Jevremović D (1999) Influence of weathering decomposition of clays and marls on the geotechnical properties, with special implications to the area of Belgrade. University of Belgrade Faculty of Mining and Geology, monograph series (in Serbian)
Kostić S, Vasović N, Sunarić D (2015a) Slope stability analysis based on experimental design. Int J Geomech. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000551
Kostić S, Vasović N, Sunarić D (2015b) A new approach to grid search method in slope stability analysis using Box–Behnken statistical design. Appl Math Comp 256:425–437
Lazić M (1991) Geological conditions of the occurrence and development of landsliding in Serbia (without the autonomous provices). Magister Paper, University of Belgrade Faculty of Mining and Geology (in Serbian)
Li YC, Chen YM, Zhan TLT, Ling DS, Cleall PJ (2010) An efficient approach for locating the critical slip surface in slope stability analyses using a realcoded genetic algorithm. Can Geotech J 47:806–820
Pavlov AP (1968) Landslide general classifications. In: Engineering geology reference book. Nedra Publishers, Moscow, p 181 (in Russian)
Rocscience Inc. (2002) Slide version 5.0—2D limit equilibrium slope stability analysis, Toronto, ON, Canada. www.rocscience.com
Savarensky FP (1981) Landslides, landslides classification. In: Engineering geology reference book. Nedra Publishers, Moscow, pp 87–88 (in Russian)
Sun J, Zhao Z (2013) Stability charts for homogeneous soil slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron 139:2212–2218
Taylor DW (1937) The stability of earth slopes. J Boston Soc Civ Eng 24:337–386
Varnes DJ (1978) Slope movement types and processes. In: Schuster RL, Krizek RJ (eds) Landslides—analysis and control: National Research Council, Special Report 176. Transportation Research Board, Washington, DC, pp 11–33
Acknowledgments
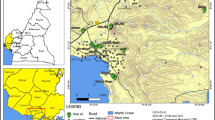
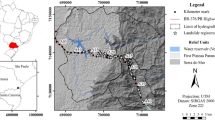
This research was partly supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Contract No. 176016). Special thanks go to prof. Dr. Marinko Toljić from the University of Belgrade Faculty of Mining and Geology regarding the quality of Fig. 1 and useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostić, S., Vasović, N. & Jevremović, D. Stability of earth slopes under the effect of main environmental properties of weathered clay–marl deposits in Belgrade (Serbia). Environ Earth Sci 75, 492 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5339-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5339-5