Abstract
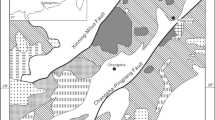
Concentrations of biotite flakes were distributed at multiple locations during the site investigation for the Tianchi Pumped Storage Power Station project in Henan Province, China. Rock mass was highly weathered on both sides of a prominent fault, and a large number of white and gray, locally yellow–brown, argillaceous agglomerations were observed. The local core at the end of the ZK44 hole presented a gray and white sandstone structure. Petrochemical tests, which included sheet identification, scanning electron microscopy, electron probe analysis, and X-ray diffraction, showed that the main alteration types were mica-rich-type altered rocks and clay-type altered rocks, which were accompanied by chlorite, epidote, actinolite, and other alteration minerals. According to the mechanical test results, the smallest antidisintegration index was 84 %, disintegration was easily accomplished, the maximum axial free expansion rate was 0.00204 %, the maximum free expansion rate in the radial direction was 0.0178 %, and maximum lateral constrained expansion rate was 0.0194 %. The swelling pressure of all the specimens did not exceed 10 kPa, and the clay-type altered rocks exhibited three large expansion parameters. Uniaxial and triaxial compression tests showed that the strength of granite, as reflected by its deformation and elastic moduli, decreased to values even lower than those of highly weathered rocks because of alteration. The poor characteristics of the altered rock presented great challenges for support or lining during the construction and operation stages. After excavation, the expanded altered rocks should be cleaned up immediately, the support or lining should be in place immediately, and water should be drained in time.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bozkurtoğlu Erkan, Vardar Mahir, Suner Fikret, Zambak Caner (2006) A new numerical approach to weathering and alteration in rock using a pilot area in the Tuzla geothermal area, Turkey. Eng Geol 87:33–47
Huang ZQ, Hou HM, Wang Z (2011) Alteration and engineering characteristics of altered-rock in Tianchi Pumped-storage Power Station. J North China Univ Water Conserv Electr Power 32:1–5 (in Chinese)
Jiang XZ (2001) Some main technical problems of investigation and design of pumped storage hydroelectric. J Zhejiang Water Conserv Hydropower 13:13–15 (in Chinese)
Krauskopf KR (1979) Introduction to geochemistry. McGraw-Hill College, New York 617
North China University of Water Conservancy and Electric Power, HydroChina Zhongnan Engineering Corporation (2010) Research report on engineering geologic characteristics study of altered rocks of Henan Tianchi pumped storage power station (in Chinese)
Shao ZP (1986) Engineering geology study on soft rock of Ertan hydropower station dam site flash petrochemical basalt fiber. Des Hydropower Stat 1:28–32 (in Chinese)
Tu XB, Jian B, Wang SJ, Bian HY, Wang J, Li SG (2005) Swelling behavior induced by alteration in granite and its implications on underground excavation. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 20:378–389
Yang GL (2007) Altered rock characteristics and its engineering responses studying-exemplified by Xiaowan hydropower station Lancang river. Phd thesis, Chengdu University of technology (in Chinese)
Zang JL (1981) Engineering geological characteristics of granite body corrosion variant. Water Resour Hydropower Technol 10:33–39 (in Chinese)
Zhang FG, Tu XX (1994) Engineering geologic characteristics of clay altered granite. Guangdong Geol 3:48–50 (in Chinese)
Zhang YS, Qu YX, Liu JR, Guo CB (2007) Engineering geological research on altered rocks in the area of NW Yunnan along Yunnan-Tibet Railway line. J Chin Geotech Eng 29:531–536 (in Chinese)
Zhang GB, Gong HL, Zhang HL (2008) Engineering geologic characteristics study of altered rocks in underground powerhouse rock caverns of langyashan pumped storage power station. In: Proceedings of the first academic meeting, the fourth professional Committee of geology and exploration, Society of China hydropower
Acknowledgments
This study obtained the support and help of Central-South Design & Research Institute for Hydroelectric Projects, China Hydropower Engineering Consulting Group Corporation, and the Geomechanics and Structural Engineering Key Laboratory of Henan Province in China. This research was financed by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51004049), Foundation for Plan For Scientific Innovation Talent of Henan Province, the Key Science and Technique Foundation of Henan Province, University Key Teacher of Henan Province (2010GGJS-129), and the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Geomechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Z013010). Professors Liu Handong and Dai Fuchu gave special instruction to the study; Southwest Mineral Resource of National Territory Resources Department, Chengdu University of Science and Technology and Henan Province geological investigation courtyard in China had tested the related project; Song Lijuan, Wang Zhen et al. took part in the study. We express our sincere gratitude is given to them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Am., Li, Xg., Huang, Zq. et al. Laboratory study on engineering geological characteristics and formation mechanism of altered rocks of Henan Tianchi pumped storage power station, China. Environ Earth Sci 74, 5063–5075 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4520-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4520-6