Abstract
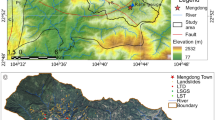
Topographic analysis is an important component of research on geomorphologic and surface process. The threshold value method was used to obtain the topographic relief of the study area based on 1:100,000 digital elevation model (DEM). Through mean change-point analysis method, the optimal statistical unit of topographic relief was determined as 0.15 km2. The swath profile method was used to analyze topographic and geomorphological characteristics of the Three Gorges Area. Combined with geosciences research method, the spatial analysis technique was applied to quantitatively analyze the relationship between topographic relief and settlements as well as settlement density (SD) in the Three Gorges Area. The results show that: (1) The Three Gorges Area is mainly covered by hilly regions, accounting for 58.93 % of the study area. The cascade structure of planation surface is very significant. Northeast undulating mountains have greater topographic relief. The peaks are generally located at the elevation from 1500 to 2000 m, i.e., high planation surface; southwest low mountain valley regions have greater topographic relief. The summit level is generally located at the elevation from 500 to 1500 m, i.e., low planation surface with an elevation from 1200 to 1500 m, pediment with an elevation from 500 to 1200 m; the general elevation gradually decreases from east to west, showing a geomorphological shape as narrow ridge and wide valley. (2) Topographic relief is a key factor influencing the spatial distribution of mountain settlements. In the vertical direction, the mountain settlements have significant change characteristics. In the horizontal direction, the mountain settlements have significant spatial aggregation characteristics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin NJ, Muller JP, Gong L, Zhang J (2013) A regional investigation of urban land-use change for potential landslide hazard assessment in the Three Gorges reservoir area, people’s republic of China: Zigui to Wanzhou”. Int J Remote Sens 34:2983–3011
Chen JJ, Zhang SW, Li HX, Yu L (2005) Assessment on Sensitivity of Soil Erosion in Jilin Province. Bull Soil Water Conserv 25:49–53 (in Chinese)
Chen ZJ, Li MC, Liu YX (2008) A GIS based research on spatial distribution of rural settlements in Tonglu County. Res Env Yangtze Basin 17:180–184 (in Chinese)
Cпиpидoнoв AN (1956) Geomorphological cartography. Geological Press, Beijing, p 109
Fielding EJ (1994) How flat is Tibet? Geology 22:163–167
Fielding EJ (1996) Tibet uplift and erosion. Tectonophysics 260:55–84
Fragkias M, Seto KC (2009) Evolving rank-size distributions of intra-metropolitan urban clusters in South China. Comput Environ Urban Syst 33:189–199
Grohmann CH (2004) Morphometric analysis in geographic information systems: applications of free software GRASS and R. Comput Geosci 30:1055–1067
Han GF, Yang YC, Yan SY (2013) Vegetation activity trend and its relationship with climate change in the Three Gorges area. China Adv Meteorol 2013:11
Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS (2005) The mapping specification of 1:1000,000 digital Geomorphological map in People’s Republic of China (in Chinese)
Kan A, Zhu LD, Gong JH, Chen ZL (2006) Development of the swath profile tool based on ArcView GIS and its application in morphometric analysis. J Chengdu Univ Tech Sci Tech 33:64–69 (in Chinese)
Kühni A, Pfiffner OA (2001) The relief of the Swiss Alps and adjacent areas and its relation to lithology and structure: topographic analysis from a 250 m DEM. Geomorphology 41:285–307
Lang LL, Cheng WM, Zhu QJ, Long E (2007) A comparative analysis of the multi-criteria DEM extracted relief—taking Fujian Low mountainous region as an example. Geo-information Sci 9:1–6 (in Chinese)
Li JJ, Xie SY, Kuang MS (2001) Geomorphic evolution of the Yangtze Gorges and the time of their formation. Geomorphology 41:125–135
Li Y, Liu C, Zhang H, Gao X (2011) Evaluation on the human settlements environment suitability in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of Chongqing based on RS and GIS. J Geog Sci 21:346–358
Lin YP, Hong NM, Chiang LC, Liu YL, Chu HJ (2012) Adaptation of land-use demands to the impact of climate change on the hydrological processes of an urbanized watershed. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 9:4083–4102
Liu XH, Yang QK, Tang GA (2001) Extraction and application of relief of China based on DEM and GIS method. Bull Soil Water Conserv 21:57–62 (in Chinese)
Liu J, Zhan J, Deng X (2005) Spatio-temporal patterns and driving forces of urban land expansion in China during the economic reform era. Ambio 34:450–455
Römer W (2010) Multiple planation surfaces in basement regions: implications for the reconstruction of periods of denudation and uplift in southern Zimbabwe. Geomorphology 114:199–212
Summerfield MA (2000) Geomorphology and Global Tectonics. Ltd. Press, John Wiley & Sons, London, p 368
Tu HM, Liu ZD (1990) Demonstrating on optimum statistic unit of topographic relief in China. J Hubei Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 12:266–271 (in Chinese)
Tullos Desiree (2009) Assessing the influence of environmental impact assessments on science and policy: an analysis of the Three Gorges Project. J Environ Manage 90:S208–S223
Wang Y, Liu HB, Wu W, Ning MQ (2006) Quantitative morphologic analysis of the three gorges region based on GIS. Sci Surve Mapp 31:93–95 (in Chinese)
Wang P, Wolf SA, Lassoie JP, Dong SK (2013) Compensation policy for displacement caused by dam construction in China: an institutional analysis. Geoforum 48:1–9
Xie SY, Yuan DX, Wang JL, Kuang MS (2006) Features of the planation surface in the surrounding area of the three gorges of Yangtze. Carsologica Sinica 25:41–45 (in Chinese)
Yu H, Deng W, Liu SQ (2013) The impact of relief amplitude on population and economic development in three Gorges Reservoir. Res Env Yangtze Basin 22:686–690 (in Chinese)
Zhang ZH, Xiao R (2014) Ashton shortridge and Jiaping Wu. spatial point pattern analysis of human settlements and geographical associations in Eastern Coastal China—A case study. Int J Env Res Publ Health 11:2818–2833
Zhang HP, Liu SF, Sun YP, Chen YS (2006) The acquisition of local topographic relief and its application: an SRTM-DEM analysis. Rem Sens Land Res 1:31–35 (in Chinese)
Zhang J, Li XD, Chen CY, Liu JY (2008) Analysis of the topographic relief in Xinjiang. J Lanzhou Univ (Nat Sci) 4:10–19 (in Chinese)
Zhu HC, Chen N, Liu HY, Tang GA (2005) Research on the relief based on 1:10000 DEM—a case study in the loess plateau of north Shaanxi province. J Yangtze Univ 30:86–88 (in Chinese)
Zou BW, Ma WF, Long Y, Hou SS, Zhang L (2011) Extraction method of swath profile based on ArcGIS and its application in landform analysis. Geogr Geo-Information Sci 27:42–44 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
Funding for this research was provided from a National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41101552), Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2015CB452706), Directional Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No.KZCX2-EW-317), West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences (2013 Yuhui), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41401198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, Y., Yong, L., Shaoquan, L. et al. The influences of topographic relief on spatial distribution of mountain settlements in Three Gorges Area. Environ Earth Sci 74, 4335–4344 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4443-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4443-2