Abstract
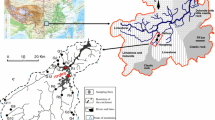
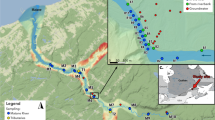
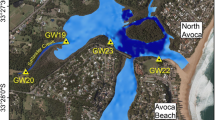
In recent years, it has become apparent that carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from inland water bodies and lakes are an important component of the global carbon cycle. Large-scale lake heterotrophy is thought to be a major driver of CO2 production and may mask other processes such as groundwater input. This study uses radon (222Rn, a natural groundwater tracer) to quantify groundwater discharge, and estimates CO2 outgassing to determine the contribution of groundwater-derived CO2 inputs into Lake Ainsworth (New South Wales, Australia). Lake Ainsworth was a source of CO2 to the atmosphere throughout the study period with outgassing rates ranging from 10.6 to 152.3 mmol m2 day−1. Annual groundwater fluxes were determined using a radon mass balance equated to about 55 ± 50 % of the total volume of water input (via direct precipitation and groundwater) into the lake. In spite of large uncertainties, groundwater seepage was a source of CO2 supersaturation in Lake Ainsworth equivalent to 13 ± 25 % of total CO2 outgassing rates. Hence, groundwater discharge may need to be considered for carbon budgets of other lakes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins M, Santos I, Ruiz-Halpern S, Maher D (2013) Carbon dioxide dynamics driven by groundwater discharge in a coastal floodplain creek. J Hydrol 493:30–42. doi:10.1016/j.hydrol.2013.04.008
Australian Bureau of Meterology (BOM) (2014) Ballina, New South Wales, 2014 Daily weather observation from Ballina Airport. Australian Government, Bureau of Meterology. Retrieved 9 May 2014. http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/dwo/201402/html/IDCJDW2006.201402.shtml
Balmer MB, Downing JA (2011) Carbon dioxide concentrations in eutrophic lakes: undersaturation: undersaturation implies atmospheric uptake. Inland Waters 1(2):125–132. doi:10.5268/IW-1.2.366
Borges AV, Abril G (2011) 5.04-Carbon dioxide and methane dynamics in Estuaries. In: Eric W, Donald M (eds) Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 119–161
Burnett WC, Peterson RN, Santos IR, Hicks RW (2010) Use of automated radon measurements for rapid assessment of groundwater flow into Florida streams. J Hydrol 380(3):298–304. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.11.005
Call M, Maher DT, Santos IR, Ruiz-Halpern S, Mangion P, Sanders CJ, Erler DV, Eyre BD (2015) Spatial and temporal variability of carbon dioxide and methane fluxes over semi-diurnal and spring-neap-spring timescales in a mangrove creek. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 150:211–225. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.11.023
Cole JJ, Caraco NF, Kling GW, Kratz TK (1994) Carbon dioxide supersaturation in the surface waters of lakes. Science 265(5178):1568–1570. doi:10.1126/science.265.5178.1568
Cole JJ, Prairie YT, Caracao NF, McDowell WH, Travnik LJ, Striegl RG, Melack J (2007) Plumbing the global carbon cycle: Integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 10(1):172–185
Corbett DR, Dillon K, Burnett W, Chanton J (2000) Estimating the groundwater contribution into Florida Bay via natural tracers, 222Rn and CH4. Limnol Oceanogr 45(7):1546–1557. doi:10.4319/lo.2000.45
Dimova NT, Burnett WC (2011) Evaluation of groundwater discharge into small lakes based on the temporal distribution of radon-222. Limnol Oceanogr 56(2):486–494. doi:10.4319/lo.2011.56.2.0486
Dimova NT, Burnett WC, Chanton JP, Corbett JE (2013) Application of radon-222 to investigate groundwater discharge into small shallow lakes. J Hydrol 486:112–122. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.01.043
Duarte CM, Prairie Y (2005) Prevalence of heterotrophy and atmospheric CO2 emissions from aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 8(7):862–870. doi:10.1007/s10021-005-0177-4
Dulaiova H, Peterson R, Burnett W, Lane-Smith D (2005) A multi-detector continuous monitor for assessment of 222Rn in the coastal ocean. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263:361–365. doi:10.1007/s10967-005-0063-8
Gatland JR, Santos IR, Maher DT, Duncan TM, Erler DV (2014) Carbon dioxide and methane emissions from an artificially drained coastal wetland during a flood: implications for wetland global warming potential. J Geophys Res-Biogeosci 19(8):1698–1716. doi:10.1002/2013JG002544
Halbedel S, Koschorreck M (2013) Regulation of CO2 emission from temperate streams and reservoirs. Biogeosciences 10:7539–7551. doi:10.5194/bg-10-7539-2013
Kluge T, Ilmberger J, Von Rohden C, Aeschbach-Hertig W (2007) Tracing and quantifying groundwater inflow into lakes using radon-222. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 11(5):1621–1631. doi:10.5194/hess-11-1621-2007
Lazzarino JK, Bachmann RW, Hoyer MV, Canfield DE Jr (2009) Carbon dioxide supersaturation in Florida lakes. Hydrobiologia 627(1):169–180. doi:10.1007/s10750-009-9723-y
Lee JM, Kim G (2006) A simple and rapid method for analysing radon in coastal and groundwater using a radon-air monitor. J Environ Radioact 89:219–228. doi:10.5355/JAST.2011.A115
Lewis E, Wallace DWR (1998) Program developed for CO2 system calculations. Oak Ridge, Tennessee: Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, US Department of Energy
Linnaluoma J (2012). Factors controlling carbon gas fluxes in boreal lakes. Department of Environmental Sciences, (PhD thesis) Lahti, Helsinki: Unigrafia
Macklin PA, Maher DT, Santos IR (2014) Estuarine canal estate waters: hotspots of CO2 outgassing driven by enhanced groundwater discharge? Mar Chem 167:87–92. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2014.08.002
Maher D, Eyre BD (2010) Benthic fluxes of dissolved organic carbon in three temperate Australian estuaries: Implications for global estimates of benthic DOC fluxes. J Geophy Res Biogeosci. doi:10.1029/2010JG001433
Maher DT, Eyre BD (2012) Carbon budgets for three autotrophic Australian estuaries: implication for global estimates of the coastal air-water CO2 flux. Global Biogeochem Cycles. doi:10.1029/2011GB004075
Maher DT, Santos IR, Golsby-Smith L, Gleeson J, Eyre BD (2013a) Groundwater-derived dissolved inorganic and organic carbon exports from a mangrove tidal creek: the missing mangrove carbon sink? Limnol Oceanogr 58(2):475–488. doi:10.4319/lo.2013.58.2.0475
Maher DT, Santos IR, Golsby-Smith L, Gleeson J, Eyre BD (2013b) Groundwater-derived dissolved inorganic and organic carbon exports from a mangrove tidal creek: the missing mangrove carbon sink? Limnol Oceanogr 58(2):475–488
Maher DT, Cowley K, Santos IR, Macklin PA, Eyre BD (2015) Methane and carbon dioxide dynamics in a subtropical estuary over a diel cycle: insights from automated in situ radioactive and stable isotope measurements. Mar Chem 168:69–79. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2014.10.017
Marotta H, Duarte CM, Pinho L, Enrich-Prast A (2010) Rainfall leads to increased pCO 2 in Brazilian coastal lakes. Biogeosciences 7(5):1–9. doi:10.5194/bg-7-1607-2010
Mitra S, Wassman R, Vlek PLG (2005) An appraisal of global wetland area and its organic carbon stock. Curr Sci 88(1):25–35. doi:10.1007/s12237-013-9626-z
Pace ML, Prairie YT (2005) Respiration in aquatic ecosystem: respiration in lakes, Chap 7. Oxford University Press, UK, pp 103–121
Peterson RN, Burnett WC, Dimova NT, Santos IR (2009) Comparison of measurement methods for radium-226 on manganese fiber. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 7(196–205):1043. doi:10.4319/lom.2009.7.196
Peterson RN, Santos IR, Burnett WC (2010) Evaluating groundwater discharge to tidal rivers based on a Rn-222 time-series approach. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 86(2):165–178
Pierrot D, Neill C, Sullivan K, Castle R, Wanninkhof R, Luger H, Cosca CE (2009) Recommendations for autonomous under way pCO2 measuring systems and data-reduction routines. Deep-Sea Res II 56:512–522. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.12.005
Rautio A, Korkka-Niemi K (2011) Characterization of groundwater-lake water interactions at Phyhajarvi, a lake in SW Finland. Boreal Environ Res 16(5):363–380. doi:10.1108/14777831211204958
Regnier P, Friedlingstein P, Ciais P, Mackenzie FT, Gruber N, Janssens IA, Thullner M (2013) Antropogenic perturbation of carbon fluxes from land to ocean. Nat Geosci 6(8):597–607. doi:10.1038/ngeo1830
Sacks LA, Swancar A, Lee TM (1998) Estimating ground-water exchange with lakes using water-budget and chemical mass-balance approaches for ten lakes in ridge areas of polk and highlands counties, Florida. Report 98-4133. Southwest Florida Water Management District, US Geological Survey
Santos IR, Eyre BD (2011) Radon tracing of groundwater discharge into an Australian estuary surrounded by coastal acid sulphate soils. J Hydrol 396(3):246–257. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.11.013
Santos IR, Niencheski F, Burnett WC, Peterson RN, Chanton JP, Andrade CF, Knoeller K (2008) Tracing anthropogenically driven groundwater discharge into a coastal lagoon from southern Brazil. J Hydrol 353(3):275–293. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.02.010
Santos IR, Burnett WC, Dittmar T, Suryaputra IGNA, Chanton J (2009) Tidal pumping drives nutrient and dissolved organic matter dynamics in a Gulf of Mexico subterranean estuary. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73(5):1325–1339. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2008.11.029
Santos IR, Maher DT, Eyre BD (2012a) Coupling automated radon and carbon dioxide measurements in coastal waters. Environ Sci Technol 46(14):7685–7691. doi:10.1021/es301961b
Santos IR, Perran LMC, Rogers L, Weys J, Eyre BD (2012b) The “salt wedge pump”: convection-driven pore-water exchange as a source of dissolved organic and inorganic carbon and nitrogen to an estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 57(5):1415–1426. doi:10.4319/lo.2012.57.5.1415
Schmidt A, Schubert M (2007) Using radon-222 for tracing groundwater discharge into an open-pit lignite mining lake—a case study. Isot Environ Health Stud 43(4):387–400. doi:10.1080/10256010701705419
Schmidt A, Stringer CE, Haferkorn U, Schubert M (2008) Quantification of groundwater discharge into lakes using radon-222 as naturally occurring tracer. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-00008-01186-00253
Schmidt A, Gibson JJ, Santos IR, Schubert M, Tattrie K (2010) The contribution of groundwater discharge to the overall water budget of two typical Boreal lakes in Alberta/Canada estimated from a radon mass balance. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 14:79–89. doi:10.5194/hess-14-79-2010
Schubert M, Paschke A, Lieberman E, Burnett WC (2012) Air–water partitioning of 222Rn and its dependence on water temperature and salinity. Environ Sci Technol 46:3905–3911. doi:10.1021/es204680
Senden D, Howels L, Anderson P (1996) Australian water and coastal Studies Pty Ltd. (1996). The ecology lab Pty Ltd and Coastal and Marine Geosciences. Lake Processes Study. Prepared by: Ballina Shire Council
Shaw GD, White ES, Gammons ChH (2013) Characterizing groundwater-lake interactions and its impact on lake water quality. J Hydrol 492:69–78. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.04.018
Stringer CE, Burnett W (2004) Sample bottle design improvements for radon emanation analysis of natural waters. Health Phys 87(6):642–646
Tranvik LJ, Downing JA, Cotner JB, Loiselle SA, Striegl RG, Ballatore TJ, Weyhenmeyer GA (2009) Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnol Oceanogr 54(6, part 2):2298–2314. doi:10.4319/lo.2009.54.6_part_2.2298
Twigg CH (1996) A nutrient budget for a coastal dune lake in north-eastern NSW, Australia. (Unpublished Honours thesis). Southern Cross University, School of Environmental Science and Engineering. Lismore, NSW
Wanninkhof R (1992) Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. J Geophys Res 97(C5):7373–7382. doi:10.1029/92JC00188
Weiss R (1974) Carbon dioxide in water and seawater: the solubility of a non-ideal gas. Mar Chem 2(3):203–215. doi:10.1016/0304-4203(74)90015-2
Willyweather (Weather, Wind, Tides and Rain Radar Services Pty Ltd) (2014). Retrieved May 9, 2014, from http://www.willyweather.com.au/
Xing Y, Xie P, Yang H, Ni L, Wang Y, Rong K (2005) Methane and carbon dioxide fluxes from a shallow hypereutrophic subtropical Lake in China. Atmos Environ 39:5532–5540. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.06.010
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Australian Research Council (DP120101645, DE150100581 and LE120100156). We thank Fiona Cambell, Mitchell Call, Paul Macklin, Ben Stewart, Arquimedes Key Bernat Plewe, Quinn de Rosa Pontello, Arun Looman and Chiara O’Reilly for their assistance during the fieldwork, and we also would like to acknowledge Graham Plumb from the Ballina Shire Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perkins, A.K., Santos, I.R., Sadat-Noori, M. et al. Groundwater seepage as a driver of CO2 evasion in a coastal lake (Lake Ainsworth, NSW, Australia). Environ Earth Sci 74, 779–792 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4082-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4082-7