Abstract
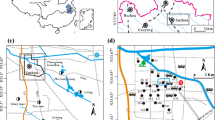
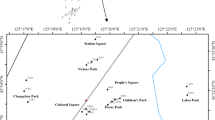
Concentrations of Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, V and Zn in less than 100 μm particles of street dust from Xining, China were measured by wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Correlation analysis, principal component analysis and cluster analysis were used to identify the potential sources of heavy metals in smaller than 100 μm dust. The results showed that the mean concentrations of Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, V and Zn in the studied samples were 50.0, 576.8, 40.8, 408.8, 22.6, 52.9, 57.1 and 108.9 mg kg−1, which were 5.0, 8.2, 1.8, 0.7, 0.8, 2.5, 0.8 and 1.4 times the corresponding background value of Qinghai soil, respectively. Compared with Qinghai soil, Co, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn presented accumulation with different degrees in smaller than 100 μm dust of Xining, especially Cr and Co which were markedly enriched, whereas Mn, Ni and V were deficient. Four main sources were identified based on the results of correlation analysis, principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Ni, V and Cr originated from nature (local soil) and industrial sources (steel plant, metal processing factory, coal power plant). Cu, Pb and Zn mainly derived from traffic source. Mn and Co mainly originated from local soil and construction sources (coating material and paint, etc.), respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aelion CM, Davis HT, McDermott S, Lawson AB (2008) Metal concentrations in rural topsoil in South Carolina: potential for human health impact. Sci Total Environ 402:149–156
Ahmed F, Ishiga H (2006) Trace metal concentrations in street dusts of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Atmos Environ 40:3835–3844
Al-Khashman OA (2007a) Determination of metal accumulation in deposited street dusts in Amman, Jordan. Environ Geochem Health 29:1–10
Al-Khashman OA (2007b) The investigation of metal concentrations in street dust samples in Aqaba city, Jordan. Environ Geochem Health 29:197–207
Al-Khashman OA (2013) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in deposited street dusts in different urbanized areas in the city of Ma’an, Jordan. Environ Earth Sci 70:2603–2612
Al-Rajhi MA, Al-Shayeb SM, Seaward MRD, Edwards HGM (1996) Particle size effect for metal pollution analysis of atmospherically deposited dust. Atmos Environ 30:145–153
Atiemo MS, Ofosu GF, Kuranchie-Mensah H, Tutu AO, Palm NDML, Blankson SA (2011) Contamination assessment of heavy metals in road dust from selected rods in Accra, Ghana. Res J Environ Earth Sci 3:473–480
Banerjee ADK (2003) Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environ Pollut 123:95–105
Benhaddya ML, Hadjel M (2014) Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface soils of Hassi Messaoud, Algeria. Environ Earth Sci 71:1473–1486
Bilos C, Colombo JC, Skorupka CN, Presa MJR (2001) Sources, distribution and variability of airborne trace metals in La Plata City area, Argentina. Environ Pollut 111:149–158
Charlesworth S, Everett M, McCarthy R, Ordóñez A, De Miguel E (2003) A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environ Int 29:563–573
Chen X, Lu X, Yang G (2012) Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. Catena 98:73–78
Chen H, Lu X, Chang Y, Xue W (2014) Heavy metal contamination in dust from kindergartens and elementary schools in Xi’an, China. Environ Earth Sci 71:2701–2709
Christoforidis A, Stamatis N (2009) Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geoderma 151:257–263
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Centre) (1990) The background values of Chinese soils, Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
De Miguel E, Llamas JF, Chacón E, Berg T, Larssen S, Røyset O, Vadset M (1997) Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmos Environ 31:2733–2740
De Miguel E, Iribarren I, Chacón E, Ordoñez A, Charlesworth S (2007) Risk-based evaluation of the exposure of children to trace elements in playgrounds in Madrid (Spain). Chemosphere 66:505–513
Du Y, Gao B, Zhou H, Ju X, Hao H, Yin S (2013) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dusts in urban parks of Beijing, China. Procedia Environ Sci 18:299–309
Duzgoren-Aydin NS, Wong CSC, Aydin A, Song Z, You M, Li XD (2006) Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the urban environment of Guangzhou, SE China. Environ Geochem Health 28:375–391
Faiz Y, Tufail M, Javed MT, Chaudhry MM, Siddique Naila (2009) Road dust pollution of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn along Islamabad Expressway, Pakistan. Microchem J 92:186–192
Fergusson JE, Ryan DE (1984) The elemental composition of street dust from large and small urban areas related to city type, source and particle size. Sci Total Environ 34:101–116
Ferreira-Baptista L, De Miguel E (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 39:4501–4512
Fujiwara F, Rebagliati RJ, Dawidowski L, Gómez D, Polla G, Pereyra V, Smichowski P (2011) Spatial and chemical patterns of size fractionated road dust collected in a megacitiy. Atmos Environ 45:1497–1505
Han YM, Du PX, Cao JJ, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Han YM, Cao JJ, Posmentier ES, Fung K, Tian H, An ZS (2008) Particulate-associated potentially harmful elements in urban road dusts in Xi’an, China. Appl Geochem 23:835–845
Joshi UM, Vijayaraghavan K, Balasubramanian R (2009) Elemental composition of urban street dusts and their dissolution characteristics in various aqueous media. Chemosphere 77:526–533
Khairy MA, Barakat AO, Mostafa AR, Wade TL (2011) Multielement determination by flame atomic absorption of road dust samples in Delta Region. Egypt. Microchem J 97:234–242
Kong S, Lu B, Ji Y, Zhao X, Chen L, Li Z, Han B, Bai Z (2011) Levels, risk assessment and sources of PM10 fraction heavy metals in four types dust from a coal-based city. Microchem J 98:280–290
Li X, Poon CS, Liu PS (2001) Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Appl Geochem 16:1361–1368
Lu X, Li LY, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y (2009a) Contamination assessment of mercury and arsenic in roadway dust from Baoji, China. Atmos Environ 43:2489–2496
Lu X, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y (2009b) Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 161:1058–1062
Lu X, Wang L, Li LY, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173:744–749
Maas S, Scheifler R, Benslama M, Crini N, Lucot E, Brahmia Z, Benyacoub S, Giraudoux P (2010) Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in urban, suburban and agricultural soils in a Mediterranean city of Algeria. Environ Pollut 158:2294–2301
Manno E, Varrica D, Dongarrà G (2006) Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an urban area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela, Sicily. Atmos Environ 40:5929–5941
Nazzal Y, Rosen MA, Al-Rawabdeh AM (2013) Assessment of metal pollution in urban road dusts from selected highways of the Greater Toronto Area in Canada. Environ Monit Assess 185:1847–1858
Nazzal Y, Ghrefat H, Rosen MA (2014) Application of multivariate geostatistics in the investigation of heavy metal contamination of roadside dusts from selected highways of the Greater Toronto Area, Canada. Environ Earth Sci 71:1409–1419
Nicholson KW (1988) A review of particle resuspension. Atmos Environ 22:2639–2651
Nriagu JO (1988) A silent epidemic of environmental metal poisoning? Environ Pollut 50:139–161
Ordóñez A, Loredo J, De Miguel E, Charlesworth S (2003) Distribution of heavy metals in the street dusts and soils of an industrial city in Northern Spain. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:160–170
Oskarsson A, Hallén IP, Sundberg J (1995) Exposure to toxic elements via breast milk. Analyst 120:765–770
Sabin LD, Lim JH, Stolzenbach KD, Schiff KC (2006) Atmospheric dry deposition of trace metals in the coastal region of Los Angeles, California, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2334–2341
Sezgin N, Ozcan HK, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2003) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ Int 29:979–985
Shi G, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi C, Teng J (2008) Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 156:251–260
Shi X, Chen L, Wang J (2013) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal pollution in street dust of Xianyang city, NW China. Environ Earth Sci 69:1973–1979
Tang R, Ma K, Zhang Y, Mao Q (2013) The Spatial Characteristics and Pollution Levels of Metals in Urban Street Dust of Beijing, China. Appl Geochem 35:88–98
Tanner PA, Ma HL, Yu PKN (2008) Fingerprinting metals in urban street dust of Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong. Environ Sci Technol 42:7111–7117
Tokalıoğlu Ş, Kartal Ş (2006) Multivariate analysis of the data and speciation of heavy metals in street dust samples from the Organized Industrial District in Kayseri (Turkey). Atmos Environ 40:2797–2805
Tong STY (1998) Indoor and outdoor household dust contamination in Cincinnati, Ohio, USA. Environ Geochem Health 20:123–133
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
Xia X, Chen X, Liu R, Liu H (2011) Heavy metals in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 186:2043–2050
Yang Z, Lu W, Long Y, Bao X, Yang Q (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City, China. J Geochem Expl 108:27–38
Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Q, Liang Z (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, northeast of China. Sci Total Environ 408:726–733
Zheng Y, Gao Q, Wen X, Yang M, Chen H, Wu Z, Lin X (2013) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in foliage dust near pedestrian bridges in Guangzhou, South China in 2009. Environ Earth Sci 70:107–113
Zhu Z, Sun G, Bi X, Li Z, Yu G (2013) Identification of trace metal pollution in urban dust from kindergartens using magnetic, geochemical and lead isotopic analyses. Atmos Environ 77:9–15
Žibret G, Tonder DV, Žibret L (2013) Metal content in street dust as a reflection of atmospheric dust emissions from coal power plants, metal smelters, and traffic. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:4455–4468
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China through Grant 41271510 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central University through Grant GK201305008. We thank Mengmeng Zhang, Xiang Ding and Tingting Feng for their helps with the experiments. We also thank Editor-in-Chief Dr. Olaf Kolditz and anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions and critical reviews of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, N., Lu, X., Chao, S. et al. Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in less than 100 μm particles of street dust from Xining, China. Environ Earth Sci 73, 2319–2327 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3578-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3578-x