Abstract
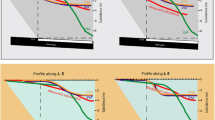
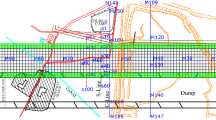
Subsidence as a result of an underground coal mine is a hazard to human life, properties and environment. This incidence usually occurs over a long period of time which directly or indirectly pertinent with various factors that needs to be carefully considered and systematically analyzed when exploring land subsidence. In reality the relationships among factors, their effects and the subsidence are crucial to have the suitable management plan for the mine-induced ground subsidence around the mining area. In this research, primarily the development of subsidence caused by the extraction of 1203 slice has been evaluated under the profile functions and influence functions methods. The results show that the calculated subsidence profile is almost trough-like subsidence where the maximum amount of subsidence is about 0.89 m. Secondly, based on this result, the analysis on different factors such as the deeper coal bed (420 m depth level) and higher angle of draw (42.5o) show less subsidence which are 0.58 and 0.87 m, respectively, whereas the dip of the coal bed up to 20o does not have significant effect on subsidence. In latter cases, the different preceding scientific papers have been consulted and analyzed for recognizing various influencing factors of subsidence which replicate that the geology and stratigraphic configuration, structural setting of the coal basin, hydro-geological characteristics, less competent nature of overlying rock body, applied mining method, presence of multi-coal seams, ultra thicken coal seam and so on are the major factors in affecting the subsidence event in the area. Moreover, intensive site investigations revealed similar pattern of subsidence and its associated factors around the mine.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam M (1972) Tectonic classification of Bengal basin. Geological Society of America, Bull, p 83
Allgaier FK (1982) Surface subsidence over longwall panels in the western US. Proc., state of the art of ground control in longwall mining and mining subsidence, SME-AIME, pp 199–210
Asia Energy Corporation (AEC) (2005) The Phulbari coal mine development—Bangladesh (unpublished report)
Bahuguna PP, Srivastava AMC, Saxena NC (1991) A critical review of mine subsidence prediction methods. J Min Sci Technol 13(3):369–382
Bakr MA, Rahman QMA, Islam MM, Islam MK, Uddin MN, Resan SA, Haider MJ, Islam MS, Ali MW, Choudhury MEA, Mannan KM, Anam ANMH (1996) Geology and coal deposits of Barapukuria basin. Records of Geological Survey of Bangladesh, Bangladesh
Can E, Kuscu S, Kartal ME (2012) Effects of mining subsidence on masonry buildings in Zonguldak hard coal region in Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 66(8):2503–2518. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1473-2
Chang HC, Linlin GE, Chris R (2004) Environmental impact assessment of mining subsidence by using Spaceborne Radar Interferometry 3rd FIG Regional Conference Jakarta, Indonesia, October 3–7, p 13
Chekan G, Listak J (1993) Design practices for multiple-seam longwall mines, Information Circular 9360, US Bureau of Mines, Pittsburgh, PA, p 35
Choi JK, Kim KD, Lee S, Won JS (2010) Application of a fuzzy operator to susceptibility estimations of coal mine subsidence in Taebaek City, Korea. Environ Earth Sci 59(5):1009–1022. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0093-6
CMC (1994) Preliminary geology and exploration report of Barapukuria coal mine, Bangladesh
CMC (2012) Daily geology and hydrology report of Barapukuria coal mine, Bangladesh
CMC (2013) Daily geology and hydrology report of Barapukuria coal mine, Bangladesh
Hartman HL (1992) SME mining engineering handbook, vol 1. Port City, Baltimore
Holla L (1985) Mining subsidence in New South Wales, 1. Surface Subsidence Prediction in the Southern Coalfield, NSW. Department of Mineral Resources, Sydney
Holla L (1988) Effects of underground mining on domestic structures—predictions versus performance, 5th Australia–NewZealand Conference on Geomechanics, Sydney, 22–23 August
Hoshour K (2011) Massive protest against Phulbari and Barapukuria coal mines in Bangladesh International Accountability Project, News Articles published in March 4, p 1
Howladar MF (2012) Coal mining impacts on water environs around the Barapukuria coal mining area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci 70(1):215–226. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2117-x
Howladar MF (2013) A comparative study between the field and empirically predicted subsidence around the Barapukuria coal mine, Dinajpur, Bangladesh, Unpublished research report, pp 1–25
Imam B (2005) Energy resources of Bangladesh. University Grants Commission of Bangladesh, Dhaka, p 277
Islam MR (2009) Geo-environmental hazards associated with multi-slice longwall mining of the Gondwana Barapukuria coal basin, NW Bangladesh: constraints from numerical simulation, Ph.D Thesis, University of the Ryukyus, p 184
Islam MR, Hayashi D (2008) Geology and coal bed methane resource potential of the Gondwana Barapukuria coal basin, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Int J Coal Geol 75:127–143
Islam MR, Islam MS (2005) Water inrush hazard in Barapukuria coal mine, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Geol 24:1–17
Jeran PW, Barton TM (1985) Comparison of the subsidence over two different longwall panels, US. US Bureau Mines Info Circ 9042:25–33
Karaman A, Seyhan T, Isik MF (2013) Detecting the footprint of a longwall mine panel claimed to infringe on a permit boundary at the Soma-Darkale coalfield (Manisa, Turkey) using surface fractures and microgravity measurements. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1895–1902. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2277-3
Karmis M, Triplett T, Haycocks C, Goodman G (1983) Mining subsidence and its prediction in the Appalachian coalfield. Proceedings of the 24th US Symposium on Rock Mechanics, pp 665–675
Khan FH (1991) Geology of Bangladesh. Willey Eastern Limited, India, pp 33–40
Khan AA, Chouhan RKS (1996) The crustal dynamics and the tectonic trends in the Bengal basin. J Geodyn 22:267–286
Kratzsch H (1983) Mining subsidence engineering. Fleming R.F.S., Trans. Springer–Verlag, New York, pp 1–40
Lee DK, Mojtabai N, Lee HB, Song WK (2013) Assessment of the influencing factors on subsidence at abandoned coal mines in South Korea. Environ Earth Sci 68(3):647–654. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1768-y
Mamun AAM (2008) Mine induced subsidence assessment of Moupukur area, Barapukuria, Unpublished M.Sc. Thesis, University of Rajshahi, Bangladesh
Mills CE (1934) Ground movement and subsidence at the United Verde mine. Transactions of the AIME 109:153–172
National Coal Board, UK (NCB) (1975) Subsidence engineers handbook. Production Department, London, p 49
Oh HJ, Ahn SC, Choi JK, Lee S (2011) Sensitivity analysis for the GIS-based mapping of the ground subsidence hazard near abandoned underground coal mines. Environ Earth Sci 64(2):347–358. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0855-1
Park DW (1987) Effect of mine subsidence on ground water hydrology, society of mining engineers. AIME 87–98:8
Peng S, Chiang H (1984) Longwall mining. Wiley, New York, p 708
Quamruzzaman C, Howladar MF, Golam AK, Ahmed M (2009) Surface subsidence prediction in Barapukuria coal mine, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Int J Earth Sci Eng 2:55–62
Singh BK, Dhar BB (1997) Sinkhole subsidence due to mining. Geotech Geol Eng 15:327–341
Singh M, Dunn M (1981) Investigation of problems and benefits of underground multiple seam coal mining, Final Technical Report, US Department of Energy, p 292
SME (1986) Mine subsidence. In: Singh, Madan M (eds) Society of mining engineers, AIME, Littleton, pp 73–143
SME (1992) Mining engineering handbook. In: Hartman, Howard L (eds) Society of mining, metallurgy and exploration, Inc, Port City, Baltimore
Soliman MM, LaMoreaux PE, Memon BA, LaMoreaux JW, Assaad FA (2008) Environmental hydrogeology, 2nd edn. IWA Publishers, pp 81–101
Steve BMS, James R, Kuipers PE (2002) Technical report on underground hard-rock mining: subsidence and hydrologic environmental impacts, 50. Center for Science in Public Participation, Bozeman, p 72
TEC (Total Environment Centre) (2007) Impacts of longwall coal mining on the environment in New South Wales, Sydney South, Australia, pp 1–35
Wardell Armstrong (1991) Techno-economic feasibility study, Barapukuria coal project, Dinajpur District, Bangladesh. vol 1 and 2, chapter 1 and 2
Whittaker BN, Reddish DJ (1989) Subsidence: occurrence, prediction and control: developments in geotechnical engineering, vol 56. Elsevier, New York, p 528
Wu QY, Pang JW, Qi SZ, Li YP, Han CC, Liu TX, Huang LM (2009) Impacts of coal mining subsidence on the surface landscape in Longkou city, Shandong Province of China. Environ Earth Sci 59(4):783–791. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0074-9
Xue GQ, Yan YJ, Cheng JL (2011) Researches on detection of 3-D underground cave based on TEM technique. Environ Earth Sci 64(2):425–430. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0862-2
Acknowledgments
Firstly, the authors are very grateful to Professor Dr. Olaf Kolditz and Professor Dr. Gunter Doerhoefer, Editor-in-Chief for their kind co-operation regarding the encouraging review processes, advice and publication of the research. Secondly, they are cordially thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their critical evaluation and final suggestion to publish this research. Authors are also thankful to Mr. Pulok Kanti Deb, Assistant Prof, and Mr. Maksudur Rahman, Final year student, Dept. of Petroleum and Mining Engineering for helping to format this research paper. Authors are also greatly thankful to Barapukuria Coal Mine Authority for providing necessary data and support for this research. Finally, the authors are greatly thankful to the Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh, for necessary funding for the successful completion of the research otherwise it was completely impossible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howladar, M.F., Hasan, K. A study on the development of subsidence due to the extraction of 1203 slice with its associated factors around Barapukuria underground coal mining industrial area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci 72, 3699–3713 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3419-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3419-y