Abstract
Purpose
Botulinum toxin has played a remarkable role in management of forehead wrinkles. Most used is intramuscular technique due to its deposition into the muscles, however, with adverse effects like brow ptosis. This study has been designed for the evaluation of efficacy for intradermal v/s intramuscular route of botulinum toxin injections for forehead wrinkles using clinical correlation.
Methods
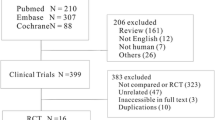
This study included a clinical trial of 32 facial halves divided equally into intradermal and intramuscular injection technique groups, receiving total dose of 8 U. Results were assessed by clinical examination upto 2 weeks and 4 weeks with parameters; objective wrinkle rate, eyebrow height, eyebrow movement, pain, and satisfaction after treatment.
Result
Results showed least mean for objective wrinkle rate in intramuscular group, showing statistically significant improvement. Overall improvement in eyebrow height and eyebrow movement were slightly more for intramuscular group. Pain was lesser for intradermal group, whereas satisfaction of patient of patient post treatment is similar for both the groups.
Conclusion
Among intradermal and intramuscular botulinum toxin injection technique, the effect and potency were better for intramuscular technique, whereas the patient comfort and compliance were better for intradermal technique.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manríquez JJ, Cataldo K, Vera-Kellet C, Harz-Fresno I (2014) Wrinkles. BMJ Clin Evid 22(2014):1711
Satriyasa BK (2019) Botulinum toxin (Botox) A for reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles: a literature review of clinical use and pharmacological aspect. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 10(12):223–228
Jun JY, Park JH, Yoon CS, Lee JH (2018) Intradermal injection of botulinum toxin: a safer treatment modality for forehead wrinkles. Ann Dermatol 30(4):458–461
Kim YJ, Lim OK, Choi WJ (2020) Are there differences between intradermal and intramuscular injections of botulinum toxin on the forehead? Dermatol Surg 46(12):e126–e131
Cula GO, Bargo PR, Nkengne A, Kollias N (2013) Assessing facial wrinkles: automatic detection and quantification. Skin Res Technol 19(1):e243–e251
Cartwright MJ, Kurumety UR, Nelson CC, Frueh BR, Musch DC (1994) Measurements of upper eyelid and eyebrow dimensions in healthy white individuals. Am J Ophthalmol 117(2):231–234
Jabbour S, Kechichian E, Nasr M (2019) Reply: the impact of upper face botulinum toxin injections on eyebrow height and forehead lines: a randomized controlled trial and an algorithmic approach to forehead injection. Plast Recon Surg 144:510e-e511
Carruthers A, Carruthers J (2007) Eyebrow height after botulinum toxin type A to the glabella. Dermatol Surg. 33(1 spec no):S26-31
Cox SE, Finn JC, Stetler L, Mackowiak J, Kowalski JW (2003) Development of the facial lines treatment satisfaction questionnaire and initial results for botulinum toxin type A-treated patients. Dermatol Surg 29(5):444–9
Stotland MA, Kowalski JW, Ray BB (2007) Patient-reported benefit and satisfaction with botulinum toxin type A treatment of moderate to severe glabellar rhytides: results from a prospective open-label study. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(5):1386–1393
Cotofana S, Fratila AA, Schenck TL, Redka-Swoboda W, Zilinsky I, Pavicic T (2016) The anatomy of the aging face: a review. Facial Plast Surg 32(3):253–260
Gart MS, Gutowski KA (2016) Overview of botulinum toxins for aesthetic uses. Clin Plast Surg 43(3):459–471
Majid OW (2010) Clinical use of botulinum toxins in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39(3):197–207
Petchngaovilai C (2009) Midface lifting with botulinum toxin: intradermal technique. J Cosmet Dermatol 8:312–316
Trindade de Almeida AR, Marques E, de Almeida J, Cunha T et al (2007) Pilot study comparing the diffusion of two formulations of botulinum toxin type A in patients with forehead hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg 33:S37–S43
Gordin EA, Luginbuhl AL, Ortlip T, Heffelfinger RN, Krein H (2014) Subcutaneous vs intramuscular botulinum toxin: split-face randomized study. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 16(3):193–8
Kapoor R, Shome D, Jain V, Dikshit R (2010) Facial rejuvenation after intradermal botulinum toxin: is it really the botulinum toxin or is it the pricks? Dermatol Surg 36(Suppl 4):2098–2105
Jung GS, Kim HS (2021) A novel technique to reduce pain from intradermal injection of botulinum toxin type A. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 9(2):e3417
Sapra P, Demay S, Sapra S, Khanna J, Mraud K, Bonadonna J (2017) A single-blind, split-face, randomized, pilot study comparing the effects of intradermal and intramuscular injection of two commercially available botulinum toxin a formulas to reduce signs of facial aging. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 10:34–44
Lee SK (2012) Multiple intradermal small bolus injection of botulinum toxin: the limit and the potentiality. J Cosmet Laser Ther 14:304–306
Chang SP, Tsai HH, Chen WY, Lee WR, Chen PL, Tsai TH (2008) The wrinkles soothing effect on the middle and lower face by intradermal injection of botulinum toxin type A. Int J Dermatol 47:1287–1294
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Tamil Nadu, India for support to carry out this research.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
Ethical approval of this study has been obtained from the Institutional Review Board- SRMDC/IRB/2020/MDS/No.403.
Informed consent
No. of human participants involved in the study: 16 nos. Informed consent obtained from all the participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mitra, R., Raja, V.B.K.K. & Panneerselvam, E. Comparison of Wrinkle Patterns Generated by Intradermal and Intramuscular Botulinum Toxin Injections by Clinical Evaluation. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02141-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02141-4